Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Obesity is associated with increased morbidity and mortality from atherosclerotic disease. Nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) are elevated in obese subjects and weight loss is associated with an attenuation of these risk factors. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) has been linked to plaque rupture, and is, thus, a candidate marker of future myocardial events. The aim of this study was to determine the influence of weight loss on MMP-9 plasma concentrations.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
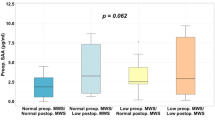
CRP, IL-6 and MMP-9 were analyzed from samples of 45 morbidly obese, middle-aged women before gastric banding and 1 y postsurgical treatment in this prospective study. The body mass index (BMI) of subjects decreased from 42.5±4.9 to 32.3±5.3 kg/m2 1 y after gastric banding. In parallel, both MMP-9 and CRP were reduced by 23 and 41%, respectively. A positive relationship was found between BMI and MMP-9 (r=0.312, P<0.05), and between CRP and IL-6 (r=0.508, P<0.05), whereas no correlation was found between CRP and MMP-9.
CONCLUSIONS:
We conclude that weight loss is associated with a pronounced decrease in the nontraditional cardiovascular risk markers MMP-9 and CRP, which could indicate future beneficial effects of weight loss on the cardiovascular risk in weight loosing subjects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manson JE, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Hankinson SE, Hennekens CH, Speizer FE . Body weight and mortality among women. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 677–685.
Stevens J, Cai J, Pamuk ER, Williamson DF, Thun MJ, Wood JL . The effect of age on the association between body-mass index and mortality. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 1–7.
Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A . Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002; 105: 1135–1143.
Visser M, Bouter LM, McQuillan GM, Wener MH, Harris TB . Elevated C-reactive protein levels in overweight and obese adults. JAMA 1999; 282: 2131–2135.
Ferroni P, Basili S, Martini F, Cardarello CM, Ceci F, Di Franco M, Bertazzoni G, Gazzaniga PP, Alessandri C . Serum metalloproteinase 9 levels in patients with coronary artery disease: a novel marker of inflammation. J Invest Med 2003; 51: 295–300.
Loftus IM, Naylor AR, Goodall S, Crowther M, Jones L, Bell PR, Thompson MM . Increased matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in unstable carotid plaques. A potential role in acute plaque disruption. Stroke 2000; 31: 40–47.
Torgerson JS, Sjostrom L . The Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study—rationale and results. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25 (Suppl 1): S2–S4.
Ebenbichler CF, Laimer M, Kaser S, Ritsch A, Sandhofer A, Weiss H, Aigner F, Patsch JR . Relationship between cholesteryl ester transfer protein and atherogenic lipoprotein profile in morbidly obese women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2002; 22: 1465–1469.
Hanusch-Enserer U, Brabant G, Roden M . Ghrelin concentrations in morbidly obese patients after adjustable gastric banding. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 2159–2160.
Laimer M, Ebenbichler CF, Kaser S, Sandhofer A, Weiss H, Nehoda H, Aigner F, Patsch JR . Weight loss increases soluble leptin receptor levels and the soluble receptor bound fraction of leptin. Obes Res 2002; 10: 597–601.
Kopp HP, Kopp CW, Festa A, Krzyzanowska K, Kriwanek S, Minar E, Roka R, Schernthaner G . Impact of weight loss on inflammatory proteins and their association with the insulin resistance syndrome in morbidly obese patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003; 23: 1042–1047.
Laimer M, Ebenbichler CF, Kaser S, Sandhofer A, Weiss H, Nehoda H, Aigner F, Patsch JR . Markers of chronic inflammation and obesity: a prospective study on the reversibility of this association in middle-aged women undergoing weight loss by surgical intervention. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26: 659–662.
Hanusch-Enserer U, Cauza E, Spak M, Endler G, Dunky A, Tura A, Wagner O, Rosen HR, Pacini G, Prager R . Improvement of insulin resistance and early atherosclerosis in patients after gastric banding. Obes Res 2004; 12: 284–291.
Forsell P, Hallberg D, Hellers G . Gastric banding for morbid obesity: initial experience with a new adjustable band. Obes Surg 1993; 3: 369–374.
Nehoda H, Weiss H, Labeck B, Hourmont K, Lanthaler M, Oberwalder M, Aigner F . Results and complications after adjustable gastric banding in a series of 250 patients. Am J Surg 2001; 181: 12–15.
Hermans MP, Levy JC, Morris RJ, Turner RC . Comparison of insulin sensitivity tests across a range of glucose tolerance from normal to diabetes. Diabetologia 1999; 42: 678–687.
Haffner SM, Kennedy E, Gonzalez C, Stern MP, Miettinen H . A prospective analysis of the HOMA model. The Mexico City Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 1996; 19: 1138–1141.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Ridker PM, Haughie P . Prospective studies of C-reactive protein as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. J Invest Med 1998; 46: 391–395.
Heilbronn LK, Noakes M, Clifton PM . Energy restriction and weight loss on very-low-fat diets reduce C-reactive protein concentrations in obese, healthy women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001; 21: 968–970.
Galis ZS, Sukhova GK, Lark MW, Libby P . Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases and matrix degrading activity in vulnerable regions of human atherosclerotic plaques. J Clin Invest 1994; 94: 2493–2503.
Brown DL, Hibbs MS, Kearney M, Loushin C, Isner JM . Identification of 92-kD gelatinase in human coronary atherosclerotic lesions. Association of active enzyme synthesis with unstable angina. Circulation 1995; 91: 2125–2131.
Blankenberg S, Rupprecht HJ, Poirier O, Bickel C, Smieja M, Hafner G, Meyer J, Cambien F, Tiret L . Plasma concentrations and genetic variation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and prognosis of patients with cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2003; 107: 1579–1585.
Noji Y, Kajinami K, Kawashiri MA, Todo Y, Horita T, Nohara A, Higashikata T, Inazu A, Koizumi J, Takegoshi T, Mabuchi H . Circulating matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in premature coronary atherosclerosis. Clin Chem Lab Med 2001; 39: 380–384.
Moreau M, Brocheriou I, Petit L, Ninio E, Chapman MJ, Rouis M . Interleukin-8 mediates downregulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 expression in cholesterol-loaded human macrophages: relevance to stability of atherosclerotic plaque. Circulation 1999; 99: 420–426.
Marx N, Froehlich J, Siam L, Ittner J, Wierse G, Schmidt A, Scharnagl H, Hombach V, Koenig W . Antidiabetic PPAR gamma-activator rosiglitazone reduces MMP-9 serum levels in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003; 23: 283–288.
Haffner SM, Greenberg AS, Weston WM, Chen H, Williams K, Freed MI . Effect of rosiglitazone treatment on nontraditional markers of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2002; 106: 679–684.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant No. 9442 of the Österreichische Nationalbank.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laimer, M., Kaser, S., Kranebitter, M. et al. Effect of pronounced weight loss on the nontraditional cardiovascular risk marker matrix metalloproteinase-9 in middle-aged morbidly obese women. Int J Obes 29, 498–501 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802897
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802897
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Change in Adipokines and Gastrointestinal Hormones After Bariatric Surgery: a Meta-analysis
Obesity Surgery (2023)
-
M1 Polarized Macrophages Persist in Skin of Post-Bariatric Patients after 2 Years
Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (2022)
-
Effects of exercise training on markers of adipose tissue remodeling in patients with coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: sub study of the randomized controlled EXCADI trial
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2019)
-
Emerging Markers of Atherosclerosis Before and After Bariatric Surgery
Obesity Surgery (2015)
-
Serum SPARC and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and Metalloproteinase-9 Concentrations after Bariatric Surgery in Obese Adults
Obesity Surgery (2014)