Abstract
Objective: To investigate hypothalamic beacon gene expression at various developmental stages in genetically selected diabetes-resistant and diabetes-prone Psammomys obesus. In addition, effects of dietary energy composition on beacon gene expression were investigated in diabetes-prone P. obesus.
Methods: Hypothalamic beacon gene expression was measured using Taqman™ fluorogenic PCR in 4-, 8- and 16-week-old animals from each genetically selected line.
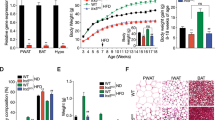
Results: Expression of beacon was elevated in the diabetes-prone compared with diabetes-resistant P. obesus at 4 weeks of age despite no difference in body weight between the groups. At 8 weeks of age, hypothalamic beacon gene expression was elevated in diabetes-prone animals fed a high-energy diet, and was correlated with serum insulin concentration.
Conclusion: P. obesus with a genetic predisposition for the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes have elevated hypothalamic beacon gene expression at an early age. Overexpression of beacon may contribute to the development of obesity and insulin resistance in these animals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shafrir E, Gutman A . Psammomys obesus of the Jerusalem colony: a model for nutritionally induced, non-insulin-dependent diabetes J Basic Clin Phys Pharm 1993 4: 83–99.
Walder KR, Fahey RP, Morton GJ, Zimmet PZ, Collier GR . Characterization of obesity phenotypes in Psammomys obesus (Israeli Sand Rats) Int J Exp Diabetes Res 2000 1: 177–184.
Barnett M, Collier GR, Collier FM, Zimmet P, O'Dea K . A cross-sectional and short-term longitudinal characterization of NIDDM in Psammomys obesus Diabetologia 1994 37: 671–676.
Ziv E, Kalman R, Hershkop K, Barash V, Shafrir E, Bar-On H . Insulin resistance in the NIDDM model Psammomys obesus in the normoglycemic-normoinsulinemic state Diabetologia 1996 39: 1265–1275.
Ziv E, Kalman R . Psammomys obesus: primary insulin resistance leading to nutritionally induced type 2 diabetes In: Sima AAF, Shafrir E (eds) Animal models of diabetes: a primer Harwood Academic: New York 2000 pp 327–342.
Kanety H, Moshe S, Shafrir E, Lunenfeld B, Karasik A . Hyperinsulinemia induces a reversible impairment in insulin receptor function leading to diabetes in the sand rat model of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 1853–1857.
Shafrir E, Ziv E, Mosthaf L . Nutritionally induced insulin resistance and receptor defect leading to beta cell failure in animal models-human implications Ann NY Acad Sci 1999 892: 223–246.
Collier GR, McMillan JS, Windmill K, Walder K, Tenne-Brown J, de Silva A, Trevaskis J, Jones S, Morton GJ, Lee S, Augert G, Civitarese A, Zimmet PZ . Beacon: a novel gene involved in the regulation of energy balance Diabetes 2000 49: 1766–1771.
Walder K, McMillan JS, Lee S, Civitarese A, Zimmet P, Collier GR . Effects of beacon administration on energy expenditure and substrate utilisation in Psammomys obesus (Israeli sand rats) Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001 25: 1281–1285.
Kalman R, Adler JH, Lazarovici G, Bar-On H, Ziv E . The efficiency of sand rat metabolism is responsible for development of obesity and diabetes J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmac 1993 4: 57–68.
Kalman R, Lazarovici G, Bar-On H, Ziv E . Psammomys obesus (sand rat)—morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics of a model for type II diabetes Contemp Top Anim Sci 1996 35: 67–70.
Acknowledgements
Funding for this work was provided by Autogen Ltd, Australia and Merck-Lipha, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walder, K., Ziv, E., Kalman, R. et al. Elevated hypothalamic beacon gene expression in Psammomys obesus prone to develop obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Obes 26, 605–609 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801965
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801965
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Circadian disruption by short light exposure and a high energy diet impairs glucose tolerance and increases cardiac fibrosis in Psammomys obesus
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Psammomys obesus: a Natural Diet-Controlled Model for Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases
Current Atherosclerosis Reports (2018)
-
Porcine ubiquitin-like 5 (UBL5) gene: genomic organization, polymorphisms, mRNA cloning, splicing variants and association study
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)