Abstract
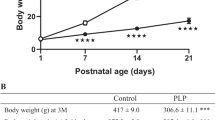
Brain serotonin plays a crucial role in the regulation of food intake and body weight homeostasis. Previous data suggest an interaction with corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). To further examine the interaction between these neurotransmitters, the selective serotonin reuptake-inhibitor (SSRI) fluvoxamine was given intraperitoneally in fa/fa Zucker rats with and without the CRH-receptor-antagonist α-helical CRH administered intracerebroventriculary (i.c.v.). The saline treated animals gained weight. Fluvoxamine led to a significant weight loss while not affecting food intake. Furthermore, insulin levels in this animal model were reduced following fluvoxamine administration. These effects were antagonized by α-helical CRH and are thus most likely mediated via CRH or CRH-like peptides.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leibowitz SF . Behavioral studies of the hypothalamus. In: Morgane PJ, Panksepp J (eds). Handbook of the hypothalamus Vol 1, Part A: Marcel Dekker: New York 1980 299–437.
Leibowitz SF, Brown LL . Brain neurotransmitters and appetite regulation Psychopharmac Bull 1980 21: 412–418.
Jordan S, Kramer GL, Zukas PK, Moeller M, Petty F . In vivo biogenic amine efflux in medial prefrontal cortex with imipramine, fluoxetine, and fluvoxamine Synapse 1994 18: 294–297.
Laflamme N, Bovetto S, Richard D, Rivest S . Effect of dexfenfluramine on the transcriptional activation of CRF and its type 1 receptor within the paraventricular nucleus of the rat hypothalamus Br J Pharmac 1996 117: 1021–1034.
Bovetto S, Rouillard C, Richard D . Role of CRF in the effects of 5-HT-receptor agonists on food intake and metabolic rate Am J Physiol 1996 271: R1231–1238.
Kamradt MC, Van de Kar LD, Gray TS . D-fenfluramine induces serotonin-mediated Fos expression in corticotropin-releasing factor and oxytocin neurons of the hypothalamus, and serotonin-independent fos expression in enkephalin and neurotensin neurons of the amygdala Neurosience 1999 90: 851–858.
Hotta M, Shibasaki T, Yamauchi N, Ohno H, Benoit R, Ling N, Demura H . The effects of chronic central administration of corticotropin-releasing factor on food intake, body weight, and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical hormones Life Sci 1991 48: 1483–1491.
Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Walker CD, Greco-Perotto R, Jeanrenaud B . Central corticotropin-releasing factor administration prevents the excessive body weight gain of genetically obese (fa/fa) rats Endocrinology 1989 124: 733–739.
Egawa M, Yoshimatsu H, Bray GA . Central regulation of stress responses: regulation of the autonomic nervous system and visceral function by corticotropin releasing factor-41 Am J Physiol 1991 260: R328–R334.
Richard D, Rivest R, Naimi N, Timofeeva E, Rivest S . Expression of corticotropin-releasing factor and its receptors in the brain of lean and obese Zucker rats Endocrinology 1996 137: 4786–4795.
Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Hochstrasser AC, Jeanrenaud B . Hyperinsulinemia of preobese and obese fa/fa rats is partly vagus nerve mediated Am J Physiol 1983 244: E317–E322.
Krahn DD, Gosnell BA, Grace M, Levine AS . CRF antagonist partially reverses CRF- and stress-induced effects on feeding Brain Res Bull 1986 17: 285–289.
Paxinos G, Watson C . The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates Academic Press: San Diego, CA 1986
Schulz C, Lehnert H . Activation of noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus by corticotropin-releasing factor—a microdialysis study Neuroendocrinology 1996 63: 454–458.
Brown MR, Gray TS, Fisher LA . Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor antagonist: effects on the autonomic nervous system and cardiovascular function Regul Pept 1986 16: 321–329.
Heinrichs SC, Pich EM, Miczek KA, Britton KT, Koob GF . Corticotropin-releasing factor antagonist reduces emotionality in socially defeated rats via direct neurotropic action Brain Res 1992 581: 190–197.
Lehnert H, Schulz C, Dieterich K . Physiological and neurochemical and aspects of corticotropin-releasing factor actions in the brain: the role of the locus coeruleus Neurochem Res 1998 23: 1039–1052.
Krahn DD, Gosnell BA, Grace M, Levine AS . CRF antagonist partially reverses CRF- and stress-induced effects on feeding Brain Res Bull 1986 17: 285–289.
Rothwell NJ & Lee FR . Thermogenesis, brown adipose tissue and dexfenfluramine in animal studies Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1992 16: (Suppl 3): S67–S71.
Egawa M, Yoshimatsu H, Bray GA . Preoptic area injection of corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulates sympathetic activity Am J Physiol 1990 259: R799–R806.
Acknowledgements
Fluvoxamine was kindly provided by Pharmacia & Upjohn, Sweden. The experimental protocols for animals and their care were in accordance with the German law and were approved by the committee on animal care. All experiments met the highest standards of humane animal care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wieczorek, I., Schulz, C., Jarry, H. et al. The effects of the selective serotonin reuptake-inhibitor fluvoxamine on body weight in Zucker rats are mediated by corticotropin-releasing hormone. Int J Obes 25, 1566–1569 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801729
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801729
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Is increased antidepressant exposure a contributory factor to the obesity pandemic?
Translational Psychiatry (2016)
-
Short-term fluoxetine treatment induces neuroendocrine and behavioral anxiogenic-like responses in adolescent male rats
Experimental Brain Research (2015)
-
BDNF Level in the Rat Prefrontal Cortex Increases Following Chronic but Not Acute Treatment with Duloxetine, a Dual Acting Inhibitor of Noradrenaline and Serotonin Re-uptake
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2008)