Abstract
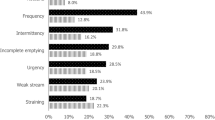
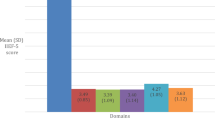
An analysis of prevalence and associated common risk factors of ED and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) was performed in Russian Federation by cross-sectional multicenter survey. International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) score and International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) were used for data collection in 1225 men between 20 and 77 years interviewed in six regions of Russian Federation. In addition, each participant's social, demographic, lifestyle, sexual and medical history was taken with special emphasis on risk factors for ED. Upon the basis of IIEF erectile domain score interpretation, ED was found in 530 (48.9%) men, consisting of mild and mild to moderate, moderate and severe ED in 375 (34.6%), 78 (7.2%) and 77 (7.1%) respondents, respectively. According to IPSS assessment, LUTSs were present in 649 (59.9%) responders; inclusive 370 (34.2%), 216 (19.9%) and 63 (5.8%) men with mild, moderate and severe LUTS, respectively. Men with both ED and LUTS shared common co-morbidities and lifestyle risk factors with age-adjusted odds ratio between 1.2 and 5.2. In logistic regression model (R2=0.361), the strongest associated with ED factor found was IPSS symptom score, followed by hypertension, IPSS-related quality of life, age, diabetes mellitus, obesity and unmotivated fatigue.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun M, Wassmer G, Klotz T, Reifenrath B, Mathers M, Engelmann U . Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: results of the ‘Cologne Male Survey’. Int J Impot Res 2000; 12: 305–311.
Boyle P, Robertson C, Mazzetta C, Keech M, Hobbs R, Fourcade R et al. The association between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction in four centres: the UrEpik study. BJU Int 2003; 92: 719–725.
Prins J, Blanker MH, Bohnen AM, Thomas S, Bosch JLHR . Prevalence of erectile dysfunction: a systematic review of population-based studies. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14: 422–432.8.
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB . Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 1994; 151: 54–61.
Laumann EO, Paik A, Rosen RC . The epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: results from the National Health and Social Life Survey. Int J Impot Res 1999; 11 (Suppl 1): S60–S64.
Rosen R, Altwein J, Boyle P, Kirby RS, Lukacs B, Meuleman E et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and male sexual dysfunction: the multinational survey of the aging male (MSAM-7). Eur Urol 2003; 44: 637–649.
Kupelian V, Araujo AB, Chiu GR, Rosen RC, McKinlay JB . Relative contributions of modifiable risk factors to erectile dysfunction. Results from the Boston Area Community Health (BACH) Survey. Prev Med 2010; 50: 19–25.
Jackson G, Boon N, Eardley I, Kirby M, Dean J, Hackett G et al. Erectile dysfunction and coronary artery disease prediction: evidence-based guidance and consensus. Int J Clin Pract 2010; 64: 848–857.
Miner M, Seftel AD, Nehra A, Ganz P, Kloner RA, Montorsi P et al. Prognostic utility of erectile dysfunction for cardiovascular disease in younger men and those with diabetes. Am Heart J 2012; 164: 21–28.
Roosen A, Chapple CR, Dmochowski RR, Fowler CJ, Gratzke C, Roehrborn CG et al. A refocus on the bladder as the originator of storage lower urinary tract symptoms: a systematic review of the latest literature. Eur Urol 2009; 56: 810–819.
Kupelian V, Wei JT, O’Leary MP, Kusek JW, Litman HJ, Link CL et al. Prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms and effect on quality of life in a racially and ethnically diverse random sample: the Boston Area Community Health (BACH) survey. Arch Intern Med 2006; 166: 2381–2387.
Taylor BC, Wilt TJ, Fink HA, Lambert LC, Marshall LM, Hoffman AR et al. Prevalence, severity and health correlates of lower urinary tract symptoms among older men: the MrOS study. Urology 2006; 68: 804–809.
Favilla V, Cimino S, Castelli T, Madonia M, Barbagallo I, Morgia G . Relationship between lower urinary tract symptoms and serum levels of sex hormones in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int 2010; 106: 1700–1703.
Lee RK, Chung D, Chughtai B, Te AE, Kaplan SA . Central obesity as measured by waist circumference is predictive of severity of lower urinary tract symptoms. BJU Int 2012; 110: 540–545.
Gacci M, Eardley I, Giuliano F, Hatzichristou D, Kaplan SA, Maggi M et al. Critical analysis of the relationship between sexual dysfunctions and lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol 2011; 60: 809–825.1.
Seftel AD, de la Rosette J, Birt J, Porter V, Zarotsky V, Viktrup L . Coexisting lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: a systematic review of epidemiological data. Int J Clin Pract 2013; 67: 32–45.2.
Ozayar A, Zumrutbas AE, Yaman O . The relationship between lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), diagnostic indicators of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and erectile dysfunction in patients with moderate to severely symptomatic BPH. Int Urol Nephrol 2008; 40: 933–939.
Shiri R, Hakkinen J, Koskimaki J, Hakama M, Tammela TL, Auvinen A . Erectile dysfunction influences the subsequent incidence of lower urinary tract symptoms and bother. Int J Impot Res 2007; 19: 317–320.
Demir O, Akgul K, Akar Z, Cakmak O, Ozdemir I, Bolukbasi A et al. Association between severity of lower urinary tract symptoms, erectile dysfunction and metabolic syndrome. Aging Male 2009; 12: 29–34.
Hammarsten J, Peeker R . Urological aspects of the metabolic syndrome. Nat Rev Urol 2011; 8: 483–494.
Kirby M, Chapple C, Jackson G, Eardley I, Edwards D, Hackett G et al. Erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms: a consensus on the importance of co-diagnosis. Int J Clin Pract 2013; 67: 606–618.
Pushkar DI, Kamalov AA, Al-Shukri SK, Erkovich AA, Kogan MI, Pavlov VN et al. [Analysis of the results of epidemiological study on prevalence of erectile dysfunction in the Russian Federation]. Urologiia 2012; 6: 5–9.
Barry MJ, Fowler FJ Jr, O'Leary MP, Bruskewitz RC, Holtgrewe HL, Mebust WK et al. The American Urological Association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association. J Urol 1992; 148: 1549–1557.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A . The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 1997; 49: 822–830.
Rosen RC, Allen KR, Ni X, Araujo AB . Minimal clinically important differences in the erectile function domain of the International Index of Erectile Function scale. Eur Urol 2011; 60: 1010–1016.
Amidu N, Owiredu WK, Woode E, Addai-Mensah O, Gyasi-Sarpong KC, Alhassan A . Prevalence of male sexual dysfunction among Ghanaian populace: myth or reality? Int J Impot Res 2010; 22: 337–342.
Ponholzer A, Temml C, Mock K, Marszalek M, Obermayr R, Madersbacher S . Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in 2869 men using a validated questionnaire. Eur Urol 2005; 47: 80–85.
Martin-Morales A, Sanchez-Cruz JJ, Saenz de Tejada I, Rodriguez- Vela L, Jiminez-Cruz JF, Burgos-Rodriguez R . Prevalence and independent risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Spain: results of the Epidemiologia de la Disfunction Erectil Masculina Study. J Urol 2001; 166: 569–574.
Solomon H, Man J, Jackson G . Erectile dysfunction and the cardiovascular patient: endothelial dysfunction is the common denominator. Heart 2003; 89: 251–253.
Lee JC, Bénard F, Carrier S, Talwar V, Defoy I . Do men with mild erectile dysfunction have the same risk factors as the general erectile dysfunction clinical trial population? BJU Int 2011; 107: 956–960.
Rupp HA, Wallen K . Relationship between testosterone and interest in sexual stimuli: the effect of experience. Horm Behav 2007; 52: 581–589.
Mulligan T, Frick MF, Zuraw QC, Stemhagen A, McWhirter C . Prevalence of hypogonadism in males aged at least 45 years: the HIM study. Int J Clin Pract 2006; 60: 762–769.
Sanda MG, Dunn RL, Michalski J, Sandler HM, Northouse L, Hembroff L et al. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostatecancer survivors. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1250–1261.
Zippe C, Nandipati K, Agarwal A, Raina R . Sexual dysfunction after pelvic surgery. Int J Impot Res 2006; 18: 1–18.
Lizza EF, Rosen RC . Definition and classification of erectile dysfunction: report of the Nomenclature Committee of the International Society of Impotence Research. Int J Impot Res 1999; 11: 141–143.
Lee WH, Kim YC, Choi HK . Psychogenic versus primary organic impotence. Int J Impotence Res 1994; 6: 93–97.
Rynja S, Bosch R, Kok E, Wouters G, de Kort L . IIEF-15: unsuitable for assessing erectile function of young men? J Sex Med 2010; 7: 2825–2830.
Cao S, Yin X, Wang Y, Zhou H, Song F, Lu Z . Smoking and risk of erectile dysfunction: systematic review of observational studies with meta-analysis. PLoS One 2013; 8: e60443.
Pauker-Sharon Y, Arbel Y, Finkelstein A, Halkin A, Herz I, Banai S et al. Cardiovascular risk factors in men with ischemic heart disease and erectile dysfunction. Urology 2013; 82: 377–380.
Al Naimi A, Majzoub AA, Talib RA, Canguven O, Al Ansari A . Erectile dysfunction in qatar: prevalence and risk factors in 1,052 participants-a pilot study. Sex Med 2014; 2: 91–95.
Fahrner EM . Sexual dysfunction in male alcohol addicts: prevalence and treatment. Arch Sex Behav 1987; 16: 247–257.
Cheng JY, Ng EM, Chen RY, Ko JS . Alcohol consumption and erectile dysfunction: meta-analysis of population-based studies. Int J Impot Res 2007; 19: 343–352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korneyev, I., Alexeeva, T., Al-Shukri, S. et al. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms in Russian Federation men: analysis from a national population-based multicenter study. Int J Impot Res 28, 74–79 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2016.8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2016.8
This article is cited by
-
Prevalence and associated factors of moderate to severe erectile dysfunction among adult men in Malaysia
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Population-level prevalence, effect on quality of life, and treatment behavior for erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation in Poland
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Stem-cell therapy for erectile dysfunction: a review of clinical outcomes
International Journal of Impotence Research (2021)
-
Two Birds with One Stone: Regular Use of PDE5 Inhibitors for Treating Male Patients with Erectile Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy (2019)