Abstract
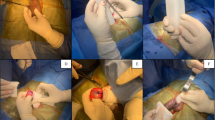
Cross-linked dextran and polymethylmethacrylate mixture (Lipen-10) is newly developed tissue filler. The purpose of this study was to evaluate tolerability and efficacy of Lipen-10 on penile enhancement. Twenty adult males were included in this study. Lipen-10 was injected into the subcutaneous tissue of the penile shaft. The penile girth and length were measured in the flaccid state, before and 1, 3 and 6 months after the injection. The circumference increased by 3.7±1.2 cm (50.8%, P<0.0001) at penile base, 4.2±0.9 cm (59.0%, P<0.001) at mid-shaft, and 3.8±1.0 cm (53.2%, P<0.0001) at distal shaft and the length increased by 2.3±1.4 cm (63.2%, P<0.001). There was, however, no significant difference between 3 and 6 months post-treatment in girth and length (P-values: 0.796, 0.498, 0.600 and 0.084 for penile base, mid- and distal-shaft and length, respectively). The complications were only one mild asymmetry of penile shape and one 5-mm-sized nodule in the injected site. There were no clinically significant adverse events in all subjects. Penile injection of Lipen-10 led to a significant increase in penile size, showed a good durability and was well-tolerated, without serious adverse events. These results suggest that penile injection of Lipen-10 may be a new effective method for penile enhancement.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Francoeur R, Perper T, Scherzer N . A descriptive dictionary and atlas of sexology 1st edn. Greenwood Press: New York, NY, 1991.
Vardi Y, Gruenwald I . The status of penile enhancement procedures. Curr Opin Urol 2009; 19: 601–605.
Lemperle G, Morhenn V, Charrier U . Human histology and persistence of various injectable filler substances for soft tissue augmentation. Aesth Plast Surg 2003; 27: 354–366.
Stenberg A, Lackgren G . A new bioimplant for the endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux: Experimental and short-term clinical results. J Urol 1995; 154: 800–803.
Artefill. Prescribing information San Diego, CA: Artes Medical, Inc, 2007 www.artefill.com.
Goldberg DJ . Breakthroughs in US dermal fillers for facial soft-tissue augmentation. J Cosmet Laser Ther 2009; 11: 240–247.
Eppley BL, Summerlin DJ, Prevel CD, Sadove AM . Effects of positively charged biomaterial for dermal and subcutaneous augmentation. Aesth Plast Surg 1994; 18: 413–416.
Panfilov DE . Augmentative phalloplasty. Aesth Plast Surg 2006; 30: 183–197.
Yacobi Y, Tsivian A, Grinberg R, Kessler O . Short-term results of incremental penile girth enhancement using liquid injectable silicone: words of praise for a change. Asian J Androl 2007; 9: 408–413.
Moon DG, Kwak TI, Kim JJ, Cho YY . Effects of hyaluronic acid gel in penile augmentation. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14 (Suppl 3): S40.
Vardi Y, Harshai Y, Gil T, Gruenwald I . A critical analysis of penile enhancement procedures for patients with normal penile size: surgical techniques, success, and complications. Eur Urol 2008; 54: 1042–1050.
Nguyen A, Pasyk KA, Bouvier TN, Hassett CA, Argenta LA . Comparative study of survival of autologous adipose tissue taken and transplanted by different techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 1990; 85: 378–386.
Wassermann RJ, Greenwald DP . Debilitating silicone granuloma of the penis and scrotum. Ann Plast Surg 1995; 35: 505–510.
Moon DG, Yoo JW, Bae JH, Han CS, Kim YK, Kim JJ . Sexual function and psychological characteristics of penile paraffinoma. Asian J Androl 2003; 5: 191–194.
Narins RS, Beer K . Liquid injectable silicone: a review of its history, immunology, technical considerations, complications, and potential. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006; 118 (Suppl): 77S.
Comper WD, Laurent TC . Physiological function of connective tissue polysaccharides. Physiol Rev 1978; 58: 255–315.
Broder KW, Cohen SR . An overview of permanent and semipermanent fillers. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006; 118: 7S–14S.
Jang MW, Jin BK, Lee SH, Park JH, Ryu JM, Yun SP et al. Effect of PMMA ans cross-linked dextran mixture on bio-safety and volume in rat. Tissue Eng Regen Med 2010; 7: 57–63.
Johl SS, Burgett RA . Dermal filler agents: a practical review. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2006; 17: 471–479.
Lemperle G, Knapp TR, Sadick NS, Lemperle SM . Artefill permanent injectable for soft tissue augmentation: I. Mechanism of action and injection techniques. Aesth Plast Surg 2010; 34: 264–272.
Läckgren G, Wåhlin N, Sköldenberg E, Stenberg A . Long-term follow-up of children treated with dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer for vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol 2001; 166: 1887–1892.
Monheit GD, Coleman KM . Hyaluronic acid fillers. Dermatol Ther 2006; 19: 141–150.
Lim JY, Kim HS, Kim YH, Kim KM, Choi HS . PMMA (polymethylmetacrylate) microsphere and stabilized hyaluronic acid as an injection laryngoplasty material for the treatment of glottal insufficiency: in vivo canine study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2008; 265: 321–326.
Acknowledgements
Authors were investigators on clinical trial sponsored by Chungwha Medipower Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, D., Lee, W. & Kim, S. Tolerability and efficacy of newly developed penile injection of cross-linked dextran and polymethylmethacrylate mixture on penile enhancement: 6 months follow-up. Int J Impot Res 25, 99–103 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2012.41
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2012.41
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Penile length augmentation surgical and non-surgical approaches for aesthetical purposes
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)
-
Multidisciplinary approach and management of patients who seek medical advice for penile size concerns: a narrative review
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)
-
Focusing on sexual rehabilitation besides penile rehabilitation following radical prostatectomy is important
International Journal of Impotence Research (2021)
-
Penile girth augmentation by injectable fillers: a comprehensive review of imaging features and inflammatory complications
Abdominal Radiology (2021)
-
Complications of glans penis augmentation
International Journal of Impotence Research (2019)