Abstract
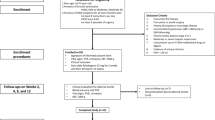
This study was conducted to determine whether mirodenafil 100 mg, when administered on demand to patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) who are receiving α1-blocker therapy, is safe with regard to the cardiovascular system and whether it improves lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and sexual function. The study involved 121 LUTS/BPH patients who had been treated for at least 3 months with α1-blockers before being administered with mirodenafil 100 mg on demand. Before the start of mirodenafil administration, the blood pressure, heart rate, international prostate symptom score (IPSS)/quality of life (QoL), peak urine flow rate (Qmax), post-voiding residual urine volume (PVR), and international index of erectile function-5 (IIEF-5) of each patient were measured. At 4 and 8 weeks after commencing mirodenafil administration, the blood pressure and heart rate were measured again, any adverse effects of mirodenafil were assessed, and sexual function and voiding symptoms were re-evaluated. Of the 121 patients, 73 (60.3%) completed the 8-week clinical trial. Significant changes in blood pressure and heart rate were not observed during the study. Significant improvements in the IIEF-5 and the IPSS/QoL, but not the Qmax or PVR, were observed. The results of this study suggest that the administration of mirodenafil 100 mg on demand may induce few hypotensive interactions and may be acceptably effective with regard to improving LUTS and sexual function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosen R, Altwein J, Boyle P, Kirby RS, Lukacs B, Meuleman E et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and male sexual dysfunction: the multinational survey of the aging male (MSAM-7). Eur Urol 2003; 44: 637–649.
Braun M, Wassmer G, Klotz T, Reifenrath B, Mathers M, Engelmann U . Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: results of the ‘Cologne Male Survey’. Int J Impot Res 2000; 12: 305–311.
Boyle P, Robertson C, Mazzetta C, Keech M, Hobbs R, Fourcade R et al. The association between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction in four centres: the UrEpik study. BJU Int 2003; 92: 719–725.
McVary KT, Foley J, Slawin K . The long-term effects of doxazosin, finasteride, and the combination on sexual function in men participating in the MTOPS trial. J Urol 2004; 171: 1194.
Deedwania PC . Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction in the metabolic syndrome. Curr Diab Rep 2003; 3: 289–292.
Khan MA, Thompson CS, Dashwood MR, Mumtaz FH, Morgan RJ, Mikhailidis DP . Endothelin-1 and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of urinary tract disorders secondary to bladder outlet obstruction. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2003; 1: 27–31.
Gradini R, Realacci M, Ginepri A, Naso G, Santangelo C, Cela O et al. Nitric oxide synthases in normal and benign hyperplastic human prostate: immunohistochemistry and molecular biology. J Pathol 1999; 189: 224–229.
Yassin A, Saad F, Hoesl CE, Traish AM, Hammadeh M, Shabsigh R . Alpha-adrenoceptors are a common denominator in the pathophysiology of erectile function and BPH/LUTS--implications for clinical practice. Andrologia 2006; 38: 1–12.
Carson CC . Combination of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and alpha-blockers in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: treatments of lower urinary tract symptoms, erectile dysfunction, or both? BJU Int 2006; 97 (Suppl 2): 39–43; discussion 44-35.
Naderi N, Mochtar CA, de la Rosette JJ . Real life practice in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Curr Opin Urol 2004; 14: 41–44.
Giannitsas K, Mitropoulos D, Konstantinopoulos A, Athanasopoulos A, Perimenis P . Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2008; 9: 1687–1693.
Roehrborn CG, McConnell JD, Barry MJ . AUA guidelines on the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). J Urol 2003; 170: 530–547.
Hatzimouratidis K, Amar E, Eardley I, Giuliano F, Hatzichristou D, Montorsi F et al. Guidelines on male sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. Eur Urol 2010; 57: 804–814.
Wang C . Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Curr Opin Urol 2010; 20: 49–54.
Oger S, Behr-Roussel D, Gorny D, Lecoz O, Lebret T, Denoux Y et al. Combination of doxazosin and sildenafil exerts an additive relaxing effect compared with each compound alone on human cavernosal and prostatic tissue. J Sex Med 2009; 6: 836–847.
Shin HI, Lee J, Kim DK . Synthesis of 5-ethyl-2-{5-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl) piperazin-1-ylsulfonyl]-2-n-propoxyphenyl}-7-n-propyl-3, 5-dihydro-4H-pyrrolo [3, 2-d]-[2-14C] pyrimid. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 2006; 49: 1141–1149.
Paick JS, Choi HK, Kim SC, Ahn TY, Kim JJ, Park JK et al. Efficacy and safety of oral SK3530 for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in Korean men: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed dose, parallel group clinical trial. Asian J Androl 2008; 10: 791–798.
Lee J, Yoo HH, Rhim KJ, Sohn DR, Kim DH . Metabolism and excretion of 5-ethyl-2-{5-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl) piperazine-1-sulfonyl]-2-propoxyphenyl}-7-propyl-3, 5-dihydropyrrolo [3, 2-d]-pyrimidin-4-one (SK3530) in rats. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2007; 21: 1139–1149.
Paick JS, Kim JJ, Kim SC, Moon KH, Min KS, Park K et al. Efficacy and safety of mirodenafil in men taking antihypertensive medications. J Sex Med 2010; 7: 3143–3152.
Auerbach SM, Gittelman M, Mazzu A, Cihon F, Sundaresan P, White WB . Simultaneous administration of vardenafil and tamsulosin does not induce clinically significant hypotension in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 2004; 64: 998–1003; discussion 1003-1004.
Giuliano F, Kaplan SA, Cabanis MJ, Astruc B . Hemodynamic interaction study between the alpha1-blocker alfuzosin and the phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor tadalafil in middle-aged healthy male subjects. Urology 2006; 67: 1199–1204.
Nieminen T, Tammela TL, Koobi T, Kahonen M . The effects of tamsulosin and sildenafil in separate and combined regimens on detailed hemodynamics in patients with benign prostatic enlargement. J Urol 2006; 176 (Part 1): 2551–2556.
Kaplan SA, Gonzalez RR, Te AE . Combination of alfuzosin and sildenafil is superior to monotherapy in treating lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol 2007; 51: 1717–1723.
Bechara A, Romano S, Casabe A, Haime S, Dedola P, Hernandez C et al. Comparative efficacy assessment of tamsulosin vs tamsulosin plus tadalafil in the treatment of LUTS/BPH. Pilot study. J Sex Med 2008; 5: 2170–2178.
Liguori G, Trombetta C, De Giorgi G, Pomara G, Maio G, Vecchio D et al. Efficacy and safety of combined oral therapy with tadalafil and alfuzosin: an integrated approach to the management of patients with lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction. Preliminary report. J Sex Med 2009; 6: 544–552.
Chung BH, Lee JY, Lee SH, Yoo SJ, Lee SW, Oh CY . Safety and efficacy of the simultaneous administration of udenafil and an alpha-blocker in men with erectile dysfunction concomitant with BPH/LUTS. Int J Impot Res 2009; 21: 122–128.
Tuncel A, Nalcacioglu V, Ener K, Aslan Y, Aydin O, Atan A . Sildenafil citrate and tamsulosin combination is not superior to monotherapy in treating lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction. World J Urol 2010; 28: 17–22.
Roumeguere T, Zouaoui Boudjeltia K, Hauzeur C, Schulman C, Vanhaeverbeek M, Wespes E . Is there a rationale for the chronic use of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia? BJU Int 2009; 104: 511–517.
Kang DH, Lee JY, Park SY, Moon HS, Jeong TY, Yoo TK et al. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil 5 mg Administered once daily in Korean men with erectile dysfunction: a prospective, multicenter study. Korean J Urol 2010; 51: 647–652.
Shindel AW . 2009 update on phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor therapy part 1: recent studies on routine dosing for penile rehabilitation, lower urinary tract symptoms, and other indications (CME). J Sex Med 2009; 6: 1794–1808; quiz 1793, 1809-1710.
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by SK Chemical, Seoul, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Cho, S., Oh, C. et al. Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with mirodenafil and α1-blocker for benign prostatic hyperplasia-induced lower urinary tract symptoms accompanied by erectile dysfunction: a multicenter, open-label, prospective study. Int J Impot Res 23, 249–256 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2011.34
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2011.34
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Role of Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors
Drugs & Aging (2014)
-
Efficacy and safety of the simultaneous administration of mirodenafil and an α-blocker in men with BPH-LUTS: a multicenter open-label prospective study
International Journal of Impotence Research (2013)
-
The Link Between Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Sexual Dysfunction
Current Bladder Dysfunction Reports (2013)