Abstract
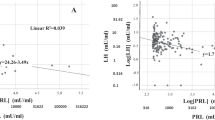
Growth hormone (GH) supplementation may help to preserve erectile function. We assessed whether serum insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels, a surrogate for GH levels, correlate with sexual function scores in 65 men who completed the Sexual Health Inventory for Men (SHIM) and Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC) questionnaires, and had serum IGF-1 and testosterone levels determined. Median±s.d. IGF-1 level, SHIM and EPIC scores were 235.0±86.4, 19.5±8.7 and 56.4±28.3 mg ml−1, respectively. IGF-1 levels and total SHIM score correlate significantly (r=0.31, P=0.02), as do IGF-1 levels and all individual SHIM question scores, and IGF-1 levels and the sexual domain of the EPIC questionnaire (r=0.30, P=0.02). No correlation was observed between IGF-1 levels and Gleason score, IGF-1 and testosterone level or SHIM score and testosterone level. These data support a potential role for the GH axis in erectile function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erfurth EM, Hagmar LE, Saaf M, Hall K . Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 correlate with serum free testosterone and sex hormone binding globulin levels in healthy young and middle-aged men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1996; 44: 659–664.
Muniyappa R, Sorkin JD, Veldhuis JD, Harman SM, Munzer T, Bhasin S et al. Long-term testosterone supplementation augments overnight growth hormone secretion in healthy older men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2007; 293: E769–E775.
Wang C, Nieschlag E, Swerdloff R, Behre HM, Hellstrom WJ, Gooren LJ et al. ISA, ISSAM, EAU, EAA and ASA recommendations: investigation, treatment and monitoring of late-onset hypogonadism in males. Int J Impot Res 2009; 21: 1–8.
Araujo AB, Esche GR, Kupelian V, O'Donnell AB, Travison TG, Williams RE et al. Prevalence of symptomatic androgen deficiency in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 4241–4247.
Bain J . Andropause. Testosterone replacement therapy for aging men. Can Fam Physician 2001; 47: 91–97.
Vermeulen A . The future of hormone replacement therapy in the aging male. Aging Male 2000; 3: 210–213.
Foresta C, Zuccarello D, De Toni L, Garolla A, Caretta N, Ferlin A . Androgens stimulate endothelial progenitor cells through an androgen receptor-mediated pathway. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2008; 68: 284–289.
Malkin CJ, Pugh PJ, Morris PD, Kerry KE, Jones RD, Jones TH et al. Testosterone replacement in hypogonadal men with angina improves ischaemic threshold and quality of life. Heart 2004; 90: 871–876.
Navarro-Dorado J, Orensanz LM, Recio P, Bustamante S, Benedito S, Martinez AC et al. Mechanisms involved in testosterone-induced vasodilatation in pig prostatic small arteries. Life Sci 2008; 83: 569–573.
Seyrek M, Yildiz O, Ulusoy HB, Yildirim V . Testosterone relaxes isolated human radial artery by potassium channel opening action. J Pharmacol Sci 2007; 103: 309–316.
Kouloumenta V, Hatziefthimiou A, Paraskeva E, Gourgoulianis K, Molyvdas PA . Non-genomic effect of testosterone on airway smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 2006; 149: 1083–1091.
Dominguez JM, Gil M, Hull EM . Preoptic glutamate facilitates male sexual behavior. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 1699–1703.
Motofei IG . A dual physiological character for sexual function: libido and sexual pheromones. BJU Int 2009; 104: 1702–1708.
Corpas E, Harman SM, Blackman MR . Human growth hormone and human aging. Endocr Rev 1993; 14: 20–39.
Kaufman JM, Taelman P, Vermeulen A, Vandeweghe M . Bone mineral status in growth hormone-deficient males with isolated and multiple pituitary deficiencies of childhood onset. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1992; 74: 118–123.
Juul A, Scheike T, Davidsen M, Gyllenborg J, Jorgensen T . Low serum insulin-like growth factor I is associated with increased risk of ischemic heart disease: a population-based case-control study. Circulation 2002; 106: 939–944.
Laughlin GA, Barrett-Connor E, Criqui MH, Kritz-Silverstein D . The prospective association of serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-1 levels with all cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in older adults: the Rancho Bernardo Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 114–120.
McCallum RW, Petrie JR, Dominiczak AF, Connell JM . Growth hormone deficiency and vascular risk. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2002; 57: 11–24.
Uckert S, Scheller F, Stief CG, Knapp WH, Sohn M, Becker AJ et al. Potential mechanism of action of human growth hormone on isolated human penile erectile tissue. Urology 2010; 75: 968–973.
Becker AJ, Uckert S, Stief CG, Truss MC, Machtens S, Scheller F et al. Possible role of human growth hormone in penile erection. J Urol 2000; 164: 2138–2142.
Wang C, Nieschlag E, Swerdloff R, Behre HM, Hellstrom WJ, Gooren LJ et al. Investigation, treatment and monitoring of late-onset hypogonadism in males. Int J Androl 2009; 32: 1–10.
Burnett AL, Lowenstein CJ, Bredt DS, Chang TS, Snyder SH . Nitric oxide: a physiologic mediator of penile erection. Science 1992; 257: 401–403.
Jung GW, Kwak JY, Yoon S, Yoon JH, Lue TF . IGF-I and TGF-beta2 have a key role on regeneration of nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-containing nerves after cavernous neurotomy in rats. Int J Impot Res 1999; 11: 247–259.
Pu XY, Wang XH, Gao WC, Yang ZH, Li SL, Wang HP et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 restores erectile function in aged rats: modulation the integrity of smooth muscle and nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate signaling activity. J Sex Med 2008; 5: 1345–1354.
Guler HP, Zapf J, Schmid C, Froesch ER . Insulin-like growth factors I and II in healthy man. Estimations of half-lives and production rates. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989; 121: 753–758.
Keenan BS, Richards GE, Ponder SW, Dallas JS, Nagamani M, Smith ER . Androgen-stimulated pubertal growth: the effects of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone on growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I in the treatment of short stature and delayed puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993; 76: 996–1001.
Thum T, Hoeber S, Froese S, Klink I, Stichtenoth DO, Galuppo P et al. Age-dependent impairment of endothelial progenitor cells is corrected by growth-hormone-mediated increase of insulin-like growth-factor-1. Circ Res 2007; 100: 434–443.
Mulhall JP . Exploring the potential role of neuromodulatory drugs in radical prostatectomy patients. J Androl 2009; 30: 377–383.
Becker AJ, Uckert S, Stief CG, Scheller F, Knapp WH, Hartmann U et al. Serum levels of human growth hormone during different penile conditions in the cavernous and systemic blood of healthy men and patients with erectile dysfunction. Urology 2002; 59: 609–614.
Cappelleri JC, Althof SE, Siegel RL, Stecher VJ, Tseng LJ, Duttagupta S . Association between the Erectile Dysfunction Inventory of Treatment Satisfaction and the Self-Esteem and Relationship Questionnaire following treatment with sildenafil citrate for men with erectile dysfunction. Value Health 2005; 8 (Suppl 1): S54–S60.
Wei JT, Dunn RL, Litwin MS, Sandler HM, Sanda MG . Development and validation of the expanded prostate cancer index composite (EPIC) for comprehensive assessment of health-related quality of life in men with prostate cancer. Urology 2000; 56: 899–905.
Rhoden EL, Teloken C, Sogari PR, Souto CA . The relationship of serum testosterone to erectile function in normal aging men. J Urol 2002; 167: 1745–1748.
Yassin AA, Saad F . Improvement of sexual function in men with late-onset hypogonadism treated with testosterone only. J Sex Med 2007; 4: 497–501.
Rhoden EL, Morgentaler A . Symptomatic response rates to testosterone therapy and the likelihood of completing 12 months of therapy in clinical practice. J Sex Med 2010; 7 (1 Part 1): 277–283.
Chiang HS, Cho SL, Lin YC, Hwang TI . Testosterone gel monotherapy improves sexual function of hypogonadal men mainly through restoring erection: evaluation by IIEF score. Urology 2009; 73: 762–766.
Higashi Y, Sukhanov S, Anwar A, Shai SY, Delafontaine P . IGF-1, oxidative stress and atheroprotection. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2010; 21: 245–254.
D'Ercole AJ, Stiles AD, Underwood LE . Tissue concentrations of somatomedin C: further evidence for multiple sites of synthesis and paracrine or autocrine mechanisms of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1984; 81: 935–939.
Chopin LK, Veveris-Lowe TL, Philipps AF, Herington AC . Co-expression of GH and GHR isoforms in prostate cancer cell lines. Growth Horm IGF Res 2002; 12: 126–136.
Rowlands MA, Gunnell D, Harris R, Vatten LJ, Holly JM, Martin RM . Circulating insulin-like growth factor peptides and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cancer 2009; 124: 2416–2429.
Mucci LA, Stark JR, Pollak MN, Li H, Kurth T, Stampfer MJ et al. Plasma levels of acid-labile subunit, free insulin-like growth factor-I, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2010; 19: 484–491.
Gill JK, Wilkens LR, Pollak MN, Stanczyk FZ, Kolonel LN . Androgens, growth factors, and risk of prostate cancer: the Multiethnic Cohort. Prostate 2010; 70: 906–915.
Pierorazio PM, Ferrucci L, Kettermann A, Longo DL, Metter EJ, Carter HB . Serum testosterone is associated with aggressive prostate cancer in older men: results from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. BJU Int 2010; 105: 824–829.
Morote J, Ramirez C, Gomez E, Planas J, Raventos CX, de Torres IM et al. The relationship between total and free serum testosterone and the risk of prostate cancer and tumour aggressiveness. BJU Int 2009; 104: 486–489.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pastuszak, A., Liu, J., Vij, A. et al. IGF-1 levels are significantly correlated with patient-reported measures of sexual function. Int J Impot Res 23, 220–226 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2011.31
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2011.31