Abstract
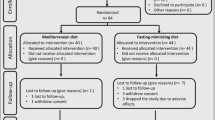
Men with the metabolic syndrome demonstrate an increased prevalence of erectile dysfunction (ED). In the present study, we tested the effect of a Mediterranean-style diet on ED in men with the metabolic syndrome. Men were identified in our database of subjects participating in controlled trials evaluating the effect of lifestyle changes and were included if they had a diagnosis of ED associated with a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome, complete follow-up in the study trial, and intervention focused mainly on dietary changes. Sixty-five men with the metabolic syndrome met the inclusion/exclusion criteria; 35 out of them were assigned to the Mediterranean-style diet and 30 to the control diet. After 2 years, men on the Mediterranean diet consumed more fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grain, and olive oil as compared with men on the control diet. Endothelial function score and inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein) improved in the intervention group, but remained stable in the control group. There were 13 men in the intervention group and two in the control group (P=0.015) that reported an IIEF score of 22 or higher. Mediterranean-style diet rich in whole grain, fruits, vegetables, legumes, walnut, and olive oil might be effective per se in reducing the prevalence of ED in men with the metabolic syndrome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH . Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA 2002; 287: 356–359.
Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP). Expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). JAMA 2001; 285: 2486–2497.
Groop L . Genetics of the metabolic syndrome. Br J Nutr 2000; 83 (Suppl 1): S39–S48.
Lidfeldt J, Nyberg P, Nerbrand C, Samsioe G, Schersten B, Agardh CD . Socio-demographic and psychological factors are associated with features of the metabolic syndrome: the Women's Health in the Lund Area (WHILA) study. Diabetes Obes Metab 2003; 5: 106–112.
Han TS, Sattar N, Williams K, Gonzalez-Villalpando C, Lean ME, Haffner SM . Prospective study of C-reactive protein in relation to the development of diabetes and metabolic syndrome in the Mexico City Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 2016–2021.
Esposito K, Pontillo A, Giugliano F, Giugliano G, Marfella R, Nicoletti G et al. Association of low interleukin-10 levels with the metabolic sindrome in obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 1055–1058.
Tamakoshi K, Kondo T, Hori Y, Ishikawa M, Zhang H, Murata C et al. The metabolic syndrome is associated with elevated circulating C-reactive protein in healthy reference range, a systemic low-grade inflammatory state. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27: 443–449.
Ridker PM, Buring JE, Cook NR, Rifai N . C-reactive protein, the metabolic syndrome, and risk of incident cardiovascular events: an 8-year follow-up of 14 719 initially healthy American women. Circulation 2003; 107: 391–397.
Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CD, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW . C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction: a potential role for cytokines originating from adipose tissue? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999; 19: 972–978.
Ziccardi P, Nappo F, Giugliano G, Esposito K, Marfella R, Cioffi M et al. Reduction of inflammatory cytokine concentrations and improvement of endothelial functions in obese women after weight loss over one year. Circulation 2002; 105: 804–809.
Esposito K, Giugliano F, Martedì E, Feola G, Marfella R, D'Armiento M et al. High proportions of erectile dysfunction in men with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 1201–1203.
Esposito K, Marfella R, Ciotola M, Di Palo C, Giugliano F, Giugliano G et al. Effect of a Mediterranean-style diet on endothelial dysfunction and markers of vascular inflammation in the metabolic syndrome: a randomized trial. JAMA 2004; 292: 1440–1446.
Esposito K, Giugliano F, Di Palo C, Giugliano G, Marfella R, D'Andrea F et al. Effect of lifestyle changes on erectile dysfunction in obese men: a randomized trial. JAMA 2004; 291: 2978–2984.
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD, Lipsky J, Pena BM . Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 1999; 11: 319–326.
Giugliano D, Marfella R, Verrazzo G, Acampora R, Nappo F, Ziccardi P et al. L-arginine for testing endothelium-dependent vascular functions in humans. Am J Physiol 1997; 273: E606–E612.
Esposito K, Nappo F, Giugliano F, Giugliano G, Marfella R, Giugliano D . Effect of dietary antioxidants on post-prandial endothelial dysfunction induced by a high-fat meal in healthy subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 77: 139–143.
Derby CA, Mohr BA, Goldstein I, Feldman HA, Johannes CB, McKinlay JB . Modifiable risk factors and erectile dysfunction: can lifestyle changes modify risk? Urology 2000; 56: 302–306.
Esposito K, Giugliano D . The metabolic syndrome and inflammation: association or causation? Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2004; 14: 228–232.
Esposito K, Giugliano F, De Sio M, Di Palo C, Carleo D, D'Armiento M et al. Dietary factors in erectile dysfunction. Intern J Impot Res 2006; 18: 370–374.
Litwin MS, Nied RJ, Dhanani N . Health-related quality of life in men with erectile dysfunction. J Gen Intern Med 1998; 13: 159–166.
Ventegodt S . Sex and quality of life in Denmark. Arch Sex Behav 1998; 27: 295–307.
Laumann EO, Paik A, Rosen RC . Sexual dysfunction in the United States: prevalence and predictors. JAMA 1999; 281: 537–544.
Bacon CG, Mittleman MA, Kawachi I, Giovannucci E, Glasser DB, Rimm EB . Sexual function in men older than 50 years of age: results from the Health Professionals follow-up Study. Ann Intern Med 2003; 139: 161–168.
Esposito K, Giugliano D . Diet and inflammation: a link to metabolic and cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J 2005. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehj605.
Sullivan ME, Thompson CS, Dashwood MR, Khan MA, Jeremy JY, Morgan RJ et al. Nitric oxide and penile erections: is erectile dysfunction another manifestation of vascular disease? Cardiovasc Res 1999; 43: 658–665.
Plotnick GD, Corretti MC, Vogel RA . Effect of antioxidant vitamins on the transient impairment of endothelium-dependent brachial artery vasoactivity following a single high-fat meal. JAMA 1997; 278: 1682–1686.
Nappo F, Esposito K, Cioffi M, Giugliano G, Molinari AM, Paolisso G et al. Postprandial endothelial activation in healthy subjects and type 2 diabetic patients: role of fat and carbohydrate meals. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002; 39: 1145–1150.
Esposito K, Nappo F, Giugliano F, Giugliano G, Marfella R, Giugliano D . Effect of dietary antioxidants on post-prandial endothelial dysfunction induced by a high-fat meal in healthy subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 77: 139–143.
Esposito K, Nappo F, Giugliano F, Di Palo C, Ciotola M, Barbieri M et al. Meal modulation of circulating interleukin 18 and adiponectin concentrations in healthy subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 78: 1135–1140.
King ED . Dietary fiber, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Mol Nutr Food Res 2005; 49: 594–600.
Hu FB, Willett WC . Optimal diets for prevention of cardiovascular disease. JAMA 2002; 288: 2569–2578.
Willett WC, Sacks F, Trichopoulou A, Drescher G, Ferro-Luzzi A, Helsing E et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid: a cultural model for healthy eating. Am J Clin Nutr 1995; 61 (Suppl 6): S1402–S1406.
Parikh P, McDaniel MC, Ashen MD, Miller JI, Sorrentino M, Chan V et al. Diets and cardiovascular disease. An evidence-based assessment. Am J Coll Cardiol 2005; 45: 1379–1387.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esposito, K., Ciotola, M., Giugliano, F. et al. Mediterranean diet improves erectile function in subjects with the metabolic syndrome. Int J Impot Res 18, 405–410 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901447
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901447
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prescribing PDE5 Inhibitors: Best Practices, Common Practices, and Controversies
Current Sexual Health Reports (2023)
-
The Italian Society of Andrology and Sexual Medicine (SIAMS), along with ten other Italian Scientific Societies, guidelines on the diagnosis and management of erectile dysfunction
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2023)
-
Erectile dysfunction and metabolic syndrome components in obese men with psoriasis: response to a 12-week randomized controlled lifestyle modification program (exercise with diet restriction)
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -) (2023)
-
The association of popular diets and erectile function among men in the United States
International Journal of Impotence Research (2021)
-
Ausgewogene Ernährung könnte die erektile Funktion erhalten
Info Diabetologie (2021)