Abstract
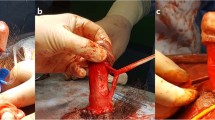
Several biodegradable materials have been experimented for penile enhancement, but none show the potential for clinical use. This study was designed to use porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS) augmenting the normal tunica albuginea to increase the functional girth of the rat penis. In all, 20 adult male Sprague–Dawley rats constituted the study population. The animals were divided into two groups: group 1 consisted of the control (n=10) and group 2 (n=10) consisted of rats that underwent penile enhancement by a longitudinal I-shaped incision of the tunica albuginea on both sides, and the dissection of the plane between tunica albuginea and cavernosal tissue was carried out (n=10). The incision was then patched with a 3 × 10 mm2 piece of SIS, using a 6/0 nylon suture material. The penile length and mid-circumference were then measured using a Vernier Caliper before and 2 months after surgery. All rat penises underwent histological examination using Masson's trichome and Verhoff's van Giesen's stain for collagen and elastic fibers. The penile length, mid-circumference and degree of fibrosis score were expressed as mean±s.e. (standard error) and analyzed using a Wilcoxon rank-sum test. A statistical significance was accepted at P-value ⩽0.05. Our results showed similar preoperative penile length and circumference in both groups. However, 2 months after the surgery, the mean penile circumference of the SIS group has grown significantly larger than the control group, while the mean penile length remained unchanged. The histological study of the rat penises revealed minimal amounts of fibrosis under the graft, and the elastic fibers of the graft showed orientation in a circular manner. In conclusion, SIS appears promising for material use in a penile enhancement.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alter GJ . Penile enhancement. AUA Update Ser 1996; 15: 94–100.
El-Sakka AI, Hassan MU, Nunes L, Bhatnagar RS, Yen TS, Lue TF . Histological and ultrastructural alterations in an animal model of Peyronie's disease. Br J Urol 1998; 181: 445–452.
Hunter GC, Henderson AM, Westerband A, Kobayashi H, Suzuki F, Yan ZQ et al. The contribution of inducible nitric oxide and cytomegalovirus to the stability of complex carotid plaque. J Vasc Surg 1999; 30: 36–49.
Ashkar L, Heller E . The silastic bladder patch. J Urol 1967; 98: 679–683.
Bohne AW, Osborn RW, Hettle PJ . Regeneration of the urinary bladder in the dog following total cystectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1955; 100: 259.
Bohne AW, Urwiller KL . Experience with urinary bladder regeneration. J Urol 1957; 77: 725.
Kudish HG . The use of polyvinyl sponge for experimental cystoplasty. J Urol 1957; 78: 232.
Swinney J, Tomlinson BE, Walder DN . Urinary tract substitution. Br J Urol 1961; 33: 414.
Fisham IJ, Flores FN, Scott B, Spjut HJ, Morrow B . Use of fresh placental membranes for bladder reconstruction. J Urol 1987; 138: 1291.
Gorham S, McCafferty I, Baraza R, Scott R . Preliminary development of a collagen membrane for use in urological surgery. Urol Res 1984; 12: 295–299.
Kambic H, Kay R, Chen JF, Matsushita M, Harasaki H, Zilber S . Biodegradable pericardial implants for bladder augmentation: a 2.5-year study in dogs. J Urol 1992; 148: 539–543.
Scott R, Mohammed R, Gorham SD, French DA, Monsour MJ, Shivas A et al. The evolution of a biodegradable membrane for use in urological surgery: a summary of 109 in vivo experiments. Br J Urol 1988; 62: 26–31.
Hodde JP, Record RD, Liang HA, Badylak SF . Vascular endothelial growth factor in porcine-derived extracellular matrix. Endothelium 2001; 8: 11–24.
McPherson TB, Badylak SF . Characterization of fibronectin derived from porcine small intestinal submucosa. Tissue Eng 1998; 4: 75–83.
Voytik-Harbin SL, Brightman AO, Kraine MR, Waisner B, Badylak SF . Identification of extractable growth factors from small intestinal submucosa. J Cell Biochem 1997; 67: 478–491.
Dejardin LM, Arnoczky SP, Clarke RB . Use of small intestinal submucosal implants for regeneration of large fascial defects: an experimental study in dogs. J Biomed Mater Res 1999; 46: 203–211.
Kropp BP, Eppley BL, Prevel CD, Rippy MK, Harruff RC, Badylak SF et al. Experimental assessment of small intestinal submucosa as a bladder wall substitute. Urology 1995; 46: 396–400.
Kropp BP, Rippy MK, Badylak SF, Adams MC, Keating MA, Rink RC et al. Regenerative urinary bladder augmentation using small intestinal submucosa: urodynamic and histopathologic assessment in long-term canine bladder augmentations. J Urol 1996; 155: 2908–3104.
Pope JC, Davis MM, Smith Jr ER, Walsh MJ, Ellison PK, Rink RC et al. The ontogeny of canine small intestinal submucosa regenerated bladder. J Urol 1997; 158: 1105–1110.
Leungwattanakij S . Penile reconstruction using porcine small intestinal submucosa in a rat model. Thai J Urol 2002; 23: 10–18.
Knoll LD . Use of porcine small intestinal submucosal graft in the surgical management of Peyronie's disease. Urology 2001; 57: 753–757.
Monga M, Cosgrove D, Zupkas P, Jain A, Kasyan A, Wilkes N et al. Small intestinal submucosa as a tunica albuginea graft material. J Urol 2002; 168: 1215–1221.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by an educational grant from the Faculty of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital. We express our thanks to Dr Narong Kulvatunyou for his help in preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leungwattanakij, S., Pummangura, N. & Ratana-Olarn, K. Penile enhancement using a porcine small intestinal submucosa graft in a rat model. Int J Impot Res 18, 39–43 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901358
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901358
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Penile enhancement with rectus muscle fascia and testicular tunica vaginalis grafts: an experimental animal study
International Urology and Nephrology (2015)