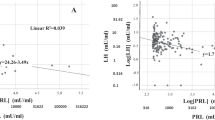
Abstract
The interplay between peripheral and central mechanisms of erectile function are not fully elucidated although basic science is moving ahead in this area. It is important from a clinical point of view to understand these mechanisms so that we may begin to make further therapeutic advances in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). It is now widely understood that central disinhibition plays a crucial role in the induction of erectile responses and this has led to the development of the central initiator, apomorphine SL (Ixense™) [apo SL]. Apo SL acts in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus as a dopamine receptor agonist. It works as a proerectile conditioner at this level to increase the responses of the erectile pathway following appropriate sexual stimulation. This unique central mode of action of apo SL has thus proved efficacious in approximately 70% of ED patients although persistence may be required to produce a robust effect for the maximum number of patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKenna KE . Central control of penile erection. Int J Impot Res 1998; 10(Suppl 1): S25–S34.
Numan M . Neural basis of maternal behavior in the rat. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1988; 13: 47–62.
Kanosue K, Zhang YH, Yanase-Fujiwara M, Hosono T . Hypothalamic network for thermoregulatory shivering. Am J Physiol 1994; 267: R275–R282.
Bourque CW, Oliet SH, Richard D . Osmoreceptors, osmoreception, and osmoregulation. Front Neuroendocrinol 1994; 15: 231–274.
Eaton RC et al. D2 receptors in the paraventricular nucleus regulate genital responses and copulation in male rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1991; 39: 177–181.
Chen KK, Chan SH, Chang LS, Chan JY . Participation of paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus in central regulation of penile erection in the rat. J Urol 1997; 158: 238–244.
Buijs RM, Geffard M, Pool CW, Hoorneman EM . The dopaminergic innervation of the supraoptic and paraventricular nucleus. A light and electron microscopical study. Brain Res 1984; 323: 65–72.
Marson L, McKenna KE . The identification of a brainstem site controlling spinal sexual reflexes in male rats. Brain Res 1990; 515: 303–308.
Marson L, McKenna KE . A role for 5-hydroxytryptamine in descending inhibition of spinal sexual reflexes. Exp Brain Res 1992; 88: 313–320.
Giuliano FA, Rampin O, Benoit G, Jardin A . Neural control of penile erection. Urol Clin North Am 1995; 22: 747–766.
Andersson KE, Hedlund P, Alm P . Sympathetic pathways and adrenergic innervation of the penis. Int J Impot Res 2000; 12: S5–S12.
Wagner G, Mulhall J . Pathophysiology and diagnosis of male erectile dysfunction. BJU Int 2001; 88(Suppl 3): 3–10.
Argiolas A, Hedlund H . The pharmacology and clinical pharmacokinetics of apomorphine SL. BJU Int 2001; 88(Suppl 3): 18–21.
Chen KK, Chan JY, Chang LS . Dopaminergic neurotransmission at the paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus in central regulation of penile erection in the rat. J Urol 1999; 162: 237–242.
Rampin O . Mode of action of a new oral treatment for erectile dysfunction: apomorphine SL. BJU Int 2001; 88(Suppl 3): 22–24.
Mirone VG, Stief CG . Efficacy of apomorphine SL in erectile dysfunction. BJU Int 2001; 88(Suppl 3); 25–29.
Altwein JE, Keuler FU . Oral treatment of erectile dysfunction with apomorphine SL. Urol Int 2001; 67: 257–263.
Heaton JP, Dean J, Sleep DJ . Sequential administration enhances the effect of apomorphine SL in men with erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14: 61–64.
Gerstenberg T, Hedlund H In: Graugaard C, Hertoft P, Møhl B (eds.). Hjerne & Seksualitet: Aspekter af Teori & klinik. Munksgaard, 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stief, C. Central mechanisms of erectile dysfunction: what a clinician may want to know. Int J Impot Res 15 (Suppl 2), S3–S6 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900989
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900989
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Microvascular dysfunction and efficacy of PDE5 inhibitors in BPH–LUTS
Nature Reviews Urology (2014)