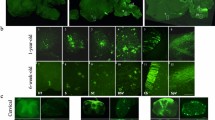
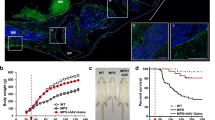
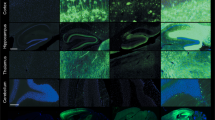
Abstract
Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB (MPS IIIB) or Sanfilippo Syndrome type B is a lysosomal storage disease resulting from the deficiency of N-acetyl glucosaminidase (NAGLU) activity. We previously showed that intracranial adeno-associated virus (AAV)-based gene therapy results in partial improvements of several aspects of the disease. In an attempt to further correct the disease, MPS IIIB mice were treated at 2–4 days of age with intracranial AAV2/5-NAGLU (IC-AAV), intravenous lentiviral-NAGLU (IV-LENTI) or the combination of both (BOTH). The BOTH group had the most complete biochemical and histological improvements of any treatment group. Compared with untreated MPS IIIB animals, all treatments resulted in significant improvements in motor function (rotarod) and hearing (auditory-evoked brainstem response). In addition, each treatment group had a significantly increased median life span compared with the untreated group (322 days). The combination arm had the greatest increase (612 days), followed by IC-AAV (463 days) and IV-LENTI (358 days). Finally, the BOTH group had nearly normal circadian rhythm measures with improvement in time to activity onset. In summary, targeting both the systemic and central nervous system disease of MPS IIIB early in life appears to be the most efficacious approach for this inherited metabolic disorder.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yogalingam G, Hopwood JJ . Molecular genetics of mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA and IIIB: diagnostic, clinical, and biological implications. Hum Mutat 2001; 18: 264–281.
Weber B, Blanch L, Clements PR, Scott HS, Hopwood JJ . Cloning and expression of the gene involved in Sanfilippo B syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis III B). Hum Mol Genet 1996; 5: 771–777.
Zhao HG, Li HH, Bach G, Schmidtchen A, Neufeld EF . The molecular basis of Sanfilippo syndrome type B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 6101–6105.
Li HH, Yu WH, Rozengurt N, Zhao HZ, Lyons KM, Anagnostaras S et al. Mouse model of Sanfilippo syndrome type B produced by targeted disruption of the gene encoding alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 14505–14510.
Heldermon CD, Hennig AK, Ohlemiller KK, Ogilvie JM, Herzog ED, Breidenbach A et al. Development of sensory, motor and behavioral deficits in the murine model of Sanfilippo syndrome type B. PLoS One 2007; 2: e772.
Fu H, Samulski RJ, McCown TJ, Picornell YJ, Fletcher D, Muenzer J . Neurological correction of lysosomal storage in a mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB mouse model by adeno-associated virus-mediated gene delivery. Mol Ther 2002; 5: 42–49.
Cressant A, Desmaris N, Verot L, Brejot T, Froissart R, Vanier MT et al. Improved behavior and neuropathology in the mouse model of Sanfilippo type IIIB disease after adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer in the striatum. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 10229–10239.
Fu H, Kang L, Jennings JS, Moy SS, Perez A, Dirosario J et al. Significantly increased lifespan and improved behavioral performances by rAAV gene delivery in adult mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB mice. Gene Therapy 2007; 14: 1065–1077.
Di Natale P, Di Domenico C, Gargiulo N, Castaldo S, Gonzalez YRE, Mithbaokar P et al. Treatment of the mouse model of mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB with lentiviral-NAGLU vector. Biochem J 2005; 388: 639–646.
Fu H, DiRosario J, Kang L, Muenzer J, McCarty DM . Restoration of central nervous system alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity and therapeutic benefits in mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB mice by a single intracisternal recombinant adeno-associated viral type 2 vector delivery. J Gene Med 2010; 12: 624–633.
McCarty DM, DiRosario J, Gulaid K, Muenzer J, Fu H . Mannitol-facilitated CNS entry of rAAV2 vector significantly delayed the neurological disease progression in MPS IIIB mice. Gene Therapy 2009; 16: 1340–1352.
Heldermon CD, Ohlemiller KK, Herzog ED, Vogler C, Qin E, Wozniak DF et al. Therapeutic efficacy of bone marrow transplant, intracranial AAV-mediated gene therapy, or both in the mouse model of MPS IIIB. Mol Ther 2010; 18: 873–880.
Ellinwood NM, Ausseil J, Desmaris N, Bigou S, Liu S, Jens JK et al. Safe, efficient, and reproducible gene therapy of the brain in the Dog Models of Sanfilippo and Hurler Syndromes. Mol Ther 2010; 19: 251–259.
Vogler C, Levy B, Grubb JH, Galvin N, Tan Y, Kakkis E et al. Overcoming the blood-brain barrier with high-dose enzyme replacement therapy in murine mucopolysaccharidosis VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 14777–14782.
Sferra TJ, Backstrom K, Wang C, Rennard R, Miller M, Hu Y . Widespread correction of lysosomal storage following intrahepatic injection of a recombinant adeno-associated virus in the adult MPS VII mouse. Mol Ther 2004; 10: 478–491.
Lin D, Donsante A, Macauley S, Levy B, Vogler C, Sands MS . Central nervous system-directed AAV2/5-mediated gene therapy synergizes with bone marrow transplantation in the murine model of globoid-cell leukodystrophy. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 44–52.
Donsante A, Levy B, Vogler C, Sands MS . Clinical response to persistent, low-level beta-glucuronidase expression in the murine model of mucopolysaccharidosis type VII. J Inherit Metab Dis 2007; 30: 227–238.
Sands MS, Barker JE . Percutaneous intravenous injection in neonatal mice. Lab Anim Sci 1999; 49: 328–330.
Deakin JA, Lyon M . A simplified and sensitive fluorescent method for disaccharide analysis of both heparan sulfate and chondroitin/dermatan sulfates from biological samples. Glycobiology 2008; 18: 483–491.
Lawrence R, Brown JR, Al-Mafraji K, Lamanna WC, Beitel JR, Boons GJ et al. Disease-specific non-reducing end carbohydrate biomarkers for mucopolysaccharidoses. Nat Chem Biol 2012; 8: 197–204.
Lawrence R, Olson SK, Steele RE, Wang L, Warrior R, Cummings RD et al. Evolutionary differences in glycosaminoglycan fine structure detected by quantitative glycan reductive isotope labeling. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 33674–33684.
Yogalingam G, Weber B, Meehan J, Rogers J, Hopwood JJ . Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB: characterisation and expression of wild-type and mutant recombinant alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase and relationship with sanfilippo phenotype in an attenuated patient. Biochim Biophys Acta 2000; 1502: 415–425.
Colville GA, Watters JP, Yule W, Bax M . Sleep problems in children with Sanfilippo syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol 1996; 38: 538–544.
Gorlin R . Genetic hearing loss associated with endocrine and metabolic disorders. In: Gorlin RJ, Toriello HV, Cohen MM, (eds). Hereditary Hearing Loss and its Syndromes. Oxford Monographs on Medical Genetics vol. 28. Oxford University Press: New York, 1995, pp 318–354.
Bredenkamp JK, Smith ME, Dudley JP, Williams JC, Crumley RL, Crockett DM . Otolaryngologic manifestations of the mucopolysaccharidoses. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1992; 101: 472–478.
Leung LS, Weinstein GW, Hobson RR . Further electroretinographic studies of patients with mucopolysaccharidoses. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser 1971; 7: 32–40.
Yoshimitsu M, Sato T, Tao K, Walia JS, Rasaiah VI, Sleep GT et al. Bioluminescent imaging of a marking transgene and correction of Fabry mice by neonatal injection of recombinant lentiviral vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 16909–16914.
Biffi A, Bartolomae CC, Cesana D, Cartier N, Aubourg P, Ranzani M et al. Lentiviral vector common integration sites in preclinical models and a clinical trial reflect a benign integration bias and not oncogenic selection. Blood 2011; 117: 5332–5339.
Wang GP, Levine BL, Binder GK, Berry CC, Malani N, McGarrity G et al. Analysis of lentiviral vector integration in HIV+ study subjects receiving autologous infusions of gene modified CD4+ T cells. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 844–850.
Cartier N, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Bartholomae CC, Veres G, Schmidt M, Kutschera I et al. Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy with a lentiviral vector in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Science 2009; 326: 818–823.
Zheng Y, Ryazantsev S, Ohmi K, Zhao HZ, Rozengurt N, Kohn DB et al. Retrovirally transduced bone marrow has a therapeutic effect on brain in the mouse model of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB. Mol Genet Metab 2004; 82: 286–295.
Fu H, Dirosario J, Killedar S, Zaraspe K, McCarty DM . Correction of neurological disease of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB in adult mice by rAAV9 trans-blood-brain barrier gene delivery. Mol Ther 2011; 19: 1025–1033.
Moss RB, Milla C, Colombo J, Accurso F, Zeitlin PL, Clancy JP et al. Repeated aerosolized AAV-CFTR for treatment of cystic fibrosis: a randomized placebo-controlled phase 2B trial. Hum Gene Ther 2007; 18: 726–732.
Hasbrouck NC, High KA . AAV-mediated gene transfer for the treatment of hemophilia B: problems and prospects. Gene Therapy 2008; 15: 870–875.
Nathwani AC, Rosales C, McIntosh J, Rastegarlari G, Nathwani D, Raj D et al. Long-term safety and efficacy following systemic administration of a self-complementary AAV vector encoding human FIX pseudotyped with serotype 5 and 8 capsid proteins. Mol Ther 2011; 19: 876–885.
Li H, Malani N, Hamilton SR, Schlachterman A, Bussadori G, Edmonson SE et al. Assessing the potential for AAV vector genotoxicity in a murine model. Blood 2010; 117: 3311–3319.
Reiss J, Hahnewald R . Molybdenum cofactor deficiency: mutations in GPHN, MOCS1, and MOCS2. Hum Mutat 2010; 32: 10–18.
Bell P, Moscioni AD, McCarter RJ, Wu D, Gao G, Hoang A et al. Analysis of tumors arising in male B6C3F1 mice with and without AAV vector delivery to liver. Mol Ther 2006; 14: 34–44.
Embury JE, Frost S, Charron CE, Madrigal E, Perera O, Poirier AE et al. Hepatitis virus protein X-phenylalanine hydroxylase fusion proteins identified in PKU mice treated with AAV-WPRE vectors. Gene Therapy Mol Biol 2008; 12: 69–76.
Donsante A, Miller DG, Li Y, Vogler C, Brunt EM, Russell DW et al. AAV vector integration sites in mouse hepatocellular carcinoma. Science 2007; 317: 477.
Donsante A, Vogler C, Muzyczka N, Crawford JM, Barker J, Flotte T et al. Observed incidence of tumorigenesis in long-term rodent studies of rAAV vectors. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 1343–1346.
Rosas LE, Grieves JL, Zaraspe K, La Perle KM, Fu H, McCarty DM . Patterns of scAAV vector insertion associated with oncogenic events in a mouse model for genotoxicity. Mol Ther 2012; 20: 2098–2110.
Hawkins-Salsbury JA, Reddy AS, Sands MS . Combination therapies for lysosomal storage disease: is the whole greater than the sum of its parts? Hum Mol Genet 2011; 20: R54–R60.
Biswas S, LeVine SM . Substrate-reduction therapy enhances the benefits of bone marrow transplantation in young mice with globoid cell leukodystrophy. Pediatr Res 2002; 51: 40–47.
Biffi A, Capotondo A, Fasano S, del Carro U, Marchesini S, Azuma H et al. Gene therapy of metachromatic leukodystrophy reverses neurological damage and deficits in mice. J Clin Inv 2006; 116: 3070–3082.
Jeyakumar M, Norflus F, Tifft CJ, Cortina-Borja M, Butters TD, Proia RL et al. Enhanced survival in Sandhoff disease mice receiving a combination of substrate deprivation therapy and bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2001; 97: 327–329.
Lee JP, Jeyakumar M, Gonzalez R, Takahashi H, Lee PJ, Baek RC et al. Stem cells act through multiple mechanisms to benefit mice with neurodegenerative metabolic disease. Nat Med 2007; 13: 439–447.
Marsh J, Fensom AH . 4-Methylumbelliferyl alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity for diagnosis of Sanfilippo B disease. Clin Genet 1985; 27: 258–262.
Sands MS, Barker JE, Vogler C, Levy B, Gwynn B, Galvin N et al. Treatment of murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII by syngeneic bone marrow transplantation in neonates. Lab Invest 1993; 68: 676–686.
Herzog ED, Aton SJ, Numano R, Sakaki Y, Tei H . Temporal precision in the mammalian circadian system: a reliable clock from less reliable neurons. J Biol Rhythms 2004; 19: 35–46.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by NIH grants NS043205 (MSS), HD055461 (MSS), K08 DK085141-01 (CDH) and by the Sanfilippo Children’s Research Foundation (CDH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Jillian R Brown and Brett E Crawford are full-time employees and shareholders of Zacharon Pharmaceuticals. All other authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heldermon, C., Qin, E., Ohlemiller, K. et al. Disease correction by combined neonatal intracranial AAV and systemic lentiviral gene therapy in Sanfilippo Syndrome type B mice. Gene Ther 20, 913–921 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.14
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.14
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
How close are we to therapies for Sanfilippo disease?
Metabolic Brain Disease (2018)
-
Recommendations on clinical trial design for treatment of Mucopolysaccharidosis Type III
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2017)
-
miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional silencing of transgenes leads to increased adeno-associated viral vector yield and targeting specificity
Gene Therapy (2017)
-
Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB confers enhanced neonatal intracranial transduction by AAV8 but not by 5, 9 or rh10
Gene Therapy (2016)
-
Neonatal cellular and gene therapies for mucopolysaccharidoses: the earlier the better?
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2016)