Abstract
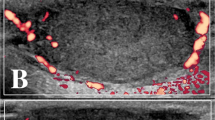
Tumor growth is dependent both on endothelial and tumor cells. The aim of this study was to investigate dynamically whether changes in tumor vasculature implicate tumor tissue degeneration during antiangiogenic therapies. In order to quantify intra-tumor vascularization and necrosis, we have used ultrasound technology. This study has identified essential parameters needed to quantify specifically and sensitively the number of microvessels and the extent of necrosis in xenografted human carcinomas during natural tumor evolution, using contrast-enhanced high-frequency ultrasonography with (HFCDUS) or without (HFUS) color Doppler. We showed that quantification of intra-tumor microvessels between HFCDUS and immunohistochemistry is correlated using an anti-CD31 antibody. Furthermore, quantification of tumor necrosis with HFUS was confirmed by histological examination of hematoxylin–eosin–saffranin-stained sections over the observation period. Subsequently, for the assessment of novel angiogenic inhibitors, HFCDUS and HFUS were used to elucidate the underlying dynamics linking vessel inhibition and tumor eradication. We describe a novel application for HFCDUS/HFUS that constitutes an effective, convenient, and non-invasive method for clinical assessment of angiogenic inhibitors. In conclusion, we showed that tumor cells abruptly became necrotic following an antivascular therapy, whereas untreated tumors were protected from degeneration by a significant blood supply.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HFUS:
-
high-frequency ultrasonography
- HFCDUS:
-
high-frequency color Doppler ultrasonography
- IHC:
-
immunohistochemistry
References
Folkman J . Anti-angiogenesis: new concept for therapy of solid tumor. Ann Surg 1972; 175: 409–416.
Weidner N, Simple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J . Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 1–8.
Hlatky L, Hahnfeldt P, Folkman J . Clinical application of antiangiogenic therapy: microvessel density, what it does and doesn't tell us. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 94: 883–893.
Sharieff W . Bevacizumab in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2335–2342.
Brower V . Evidence of efficacy: researchers investigating markers for angiogenesis inhibitors. J Natl Cancer Inst 2003; 95: 1425–1427.
O'Reilly MS, Holmgren L, Shing Y, Rosenthal RA, Moses M, Lane WS et al. Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell 1994; 79: 315–328.
Cheng WF, Lee CN, Chen CA, Chu JS, Kung CCS, Hsieh CY et al. Comparaison between in vivo and in vitro methods for evaluating tumor angiogenesis using cervical carcinoma as a model. Angiogenesis 1999; 3: 295–304.
McDonald DM, Choyke PL . Imaging of angiogenesis: from microscope to clinic. Nat Med 2003; 9: 713–725.
Taylor KJW, Ramos I, Carter D, Morse SS, Snower D, Forhine K . Correlation of Doppler US tumor signals with neovascular morphologic features. Radiology 1988; 166: 57–62.
Fleischer AC, Wojcicki WE, Donnelly EF, Pickens DR, Thirsk G, Thurman GB et al. Quantified color Doppler sonography of tumor vascularity in an animal model. J Ultrasound Med 1999; 18: 547–551.
Forsberg F, Merton DA, Liu JB, Needleman L, Goldberg BB . Clinical applications of ultrasound contrasts agents. Ultrasonics 1998; 3: 695–701.
Calliada F, Campani R, Bottinelli O, Bozzini A, Sommaruga MG . Ultrasound contrast agents: basic principles. Eur J Radiol 1998; 27: S157–S160.
Lassau N, Kolscielny S, Opolon P, de Baere T, Perronneau P, Leclere J et al. Evaluation of contrast-enhanced color Doppler ultrasound for the quantification of angiogenesis in vivo. Invest Rad 2001; 36: 50–55.
Magnon C, Galaup A, Mullan B, Rouffiac V, Bidart JM, Griscelli F et al. Canstatin acts on endothelial and tumor cells via mitochondrial damage initiated through interaction with αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 4353–4361.
Chen D, Chang R, Huang Y . Computer-aided diagnosis applied to US of solid breast nodules by using neural networks. Radiology 1999; 213: 407–412.
Bader W, Böhmer S, Van Leeuwen P, Hackman J, Westhof G, Hatzmann W . Does texture analysis improve breast ultrasound precision? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000; 15: 311–316.
Rioux M, Mailloux C . Crescent-shaped necrosis: a new imaging sign suggestive of stromal tumor of the small bowel. Abdom Imaging 1997; 22: 376–380.
Papakonstantinou O, Bakantaki P, Paspalaki P, Charoulakis N, Gourtsoyiannis N . High-resolution and color Doppler ultrasonography of cervical lymphadenopathy in children. Acta Radiol 2001; 42: 470–476.
Toriyabe Y, Nishimura T, Kita S, Saito Y, Miyokawa N . Differentiation between benign and metastatic cervical lymph nodes with ultrasound. Clin Radiol 1997; 52: 927–932.
Yahata T, Kodama S, Kase H, Sekizuka N, Kurabayashi T, Aoki Y et al. Primary choriocarcinoma of the uterine cervix: clinical, MRI, and color Doppler ultrasonographic study. Gynecol Oncol 1997; 64: 274–278.
Jinno K, Moriwaki S, Tanada M, Wada T, Mandai K, Okada Y . Clinicopathological study on combination therapy consisting of arterial infusion of lipiodo-dissolved SMANCS and transcatheter arterial embolization for hepatocelluar carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1992; 31: S7–S12.
Rouffiac V, Bouquet C, Lassau N, Opolon P, Koscielsy S, Peronneau P et al. Validation of a new method for quantifying in vivo murine tumor necrosis by sonography. Invest Radiol 2004; 39 (6): 350–356.
Galaup A, Magnon C, Rouffiac V, Opolon P, Opolon D, Lassau N et al. Full kringles of plasminogen (AA 1–566) mediates complete regression of breast tumors in mice. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 831–842.
Elias H, Hyde DM . Karger continuing education Ser Vol 1. A Guide to Practical Stereology. New York, 1983.
Rooks V, Beecken WD, Iordanescu I, Taylor G . Sonographic evaluation of orthotopic bladder tumors in mice treated with TNP 470, an angiogenic inhibitor. Acad Radiol 2001; 8: 121–127.
Iordanescu I, Becker C, Zetter B, Dunning P, Taylor GA . Tumor vascularity: evaluation in a murine model with contrast-enhanced color Doppler US-effect of angiogenesis inhibitors. Radiology 2002; 222: 460–467.
Beecken WD, Fernandez A, Panigraphy D, Achilles EG, Kisker O, Flynn E et al. Efficacy of antiangiogenic therapy with TNP-470 in superficial and invasive bladder cancer models in mice. Urology 2000; 56: 521–526.
Roubidoux MA, Sabel MS, Balley JE, Kleer CG, Klein KA, Helvie MA . Small breast cancers: mammographic and US findings at US-guided cryoablation-initial experience. Radiology 2004; 233: 857–867.
Tozaki M, Toi M, Miyamoto Y, Fukuda K . Power Doppler sonography of breast masses: correlation of Doppler spectral parameters with tumor angiogenesis and histologic growth pattern. J Ultrasound Med 2000; 19: 593–600.
Schroeder RJ, Hauff P, Bartels T, Vogel K, Jeschke J, Hidajat N et al. Tumor vascularization in experimental melanoma: correlation between unenhanced and contrast enhanced power Doppler imaging and histological grading. Ultrasound Med Biol 2001; 27: 761–771.
Strohmeyer D, Frauscher F, Klauser A, Recheis W, Eibl G, Horninger W et al. Contrast-enhanced transrectal color Doppler ultrasonography (TRCDUS) for assessment of angiogenesis in prostate cancer. Anticancer Res 2001; 21: 2907–2913.
Yang WT, Tse GM, Lam PK, Metreweli C, Chang J . Correlation between color power Doppler sonographic measurement tumor vasculature and immunohistochemical analysis of microvessels for the quantification of angiogenesis. J Ultrasound med 2002; 21: 1227–1235.
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J NCI 2000; 92: 205–216.
Stavros AT, Thickman D, Rapp CL, Dennis MA, Parker SH, Sisney GA . Solid breast nodules: use of sonography to distinguish between benign and malignant. Radiology 1995; 196: 123–134.
Okayama N, Murakuni H, Ogata H . The use of Doppler ultrasound in evaluation of breast cancer metastatic axillary lymph nodes. Oncol Rep 2004; 11: 389–393.
Kedar RP, Cosgrove D, Mcready VR, Bamber JC, Carter ER . Microbubble contrast agent for color Doppler US: effect on breast masses: work in progress. Radiology 1996; 198: 679–686.
Burns P . Harmonic imaging adds to ultrasound capabilities. Diagn Imaging 1995; 7: 10.
Goertz DE, Christopher DA, Yu JL, Kerbel RS, Burns PN, Foster FS . High-frequency color flow imaging of the microcirculation. Ultrasound Med Biol 2000; 26: 63–71.
Gee MS, Saunders HM, Lee JC, Sanzo JF, Jenkins WT, Evans SM et al. Doppler ultrasound imaging detects changes in tumor perfusion during antivascular therapy associated with vascular anatomic alterations. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 2974–2982.
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua P, Alfred EN, Moore DH et al. Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 1992; 84: 1875–1887.
Bosari S, Lee AKC, DeLellis RA, Wiley BD, Heatley GJ, Silverman ML . Microvessel quantification and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma. Hum pathol 1992; 23: 755–761.
Toi M, Kashitani J, Tominaga T . Tumor angiogenesis is an independent prognostic indicator in primary breast carcinoma. Int J cancer 1993; 55: 371–374.
Uzzan B, Nicolas P, Cucherat M, Perret GY . Microvessel density as a prognostic factor in women with breast cancer: a systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 2941–2955.
De Luca M, Luigi B, Formisano C, Formato A, De Werra C, Cappucio M et al. Solitary necrotic nodule of the liver misinterpreted as malignant lesion: considerations on two cases. J Surg Oncol 2000; 74: 219–222.
Asselin-Paturel C, Lassau N, Guinebretière JM, Zhang J, Gay F, Bex F et al. Transfer of the murine interleukin-12 gene in vivo by a semliki forest virus vector induces B16 tumor regression through inhibition of tumor vessel formation monitored by Doppler ultrasonography. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 606–615.
Krix M, Kiessling F, Vosseler S, Farhan N, Mueller MM, Bohlen P et al. Sensitive non-invasive monitoring of tumor perfusion during antiangiogenic therapy by intermittent bolus-contrast power Doppler sonography. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 8264–8270.
Klement G, Huang P, Mayer B, Green SK, Man S, Bohlen P et al. Differences in therapeutic indexes of combination metronomic chemotherapy and an anti-VEGFR-2 antibody in multidrug-resistant human breast cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 221–232.
Galaup A, Opolon P, Bouquet C, Li H, Opolon D, Bissery MC et al. Combined effects of docetaxel and angiostatin gene therapy in prostate tumor model. Mol Ther 2003; 7: 731–740.
Horak ER, Leek R, Klenk N, LeJeune S, Smith K, Stuart N et al. Angiogenesis, assessed by platelet/endothelila cell adhesion molecule antibodies, as indicator of node metastases and survival in breast cancer. Lancet 1992; 340: 1120–1124.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the SCEA and specially Patrice Ardouin, Annie Rouches, Monique Stanciu, Jennifer Huard, and Désiré Challuau for animal care. We warmly acknowledge Dr Brian Mullan for critical reading. We thank Lorna Saint-Ange for editing. C Magnon and A Galaup were financially supported by the AP HP – INSERM – CEA and CNRS – Fondation Lefoulon Delalande Institut de France, respectively. This work was supported by the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, the Institut Gustave Roussy, the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer, and the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magnon, C., Galaup, A., Rouffiac, V. et al. Dynamic assessment of antiangiogenic therapy by monitoring both tumoral vascularization and tissue degeneration. Gene Ther 14, 108–117 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302849
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302849