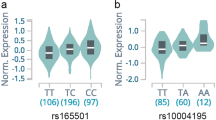
Abstract
Graves’ disease (GD) and Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) represent the commonest forms of autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) each presenting with distinct clinical features. Progress has been made in determining association of HLA class II DRB1, DQB1 and DQA1 loci with GD demonstrating a predisposing effect for DR3 (DRB1*03-DQB1*02-DQA1*05) and a protective effect for DR7 (DRB1*07-DQB1*02-DQA1*02). Small data sets have hindered progress in determining HLA class II associations with HT. The aim of this study was to investigate DRB1-DQB1-DQA1 in the largest UK Caucasian HT case control cohort to date comprising 640 HT patients and 621 controls. A strong association between HT and DR4 (DRB1*04-DQB1*03-DQA1*03) was detected (P=6.79 × 10−7, OR=1.98 (95% CI=1.51–2.59)); however, only borderline association of DR3 was found (P=0.050). Protective effects were also detected for DR13 (DRB1*13-DQB1*06-DQA1*01) (P=0.001, OR=0.61 (95% CI=0.45–0.83)) and DR7 (P=0.013, OR=0.70 (95% CI=0.53–0.93)). Analysis of our unique cohort of subjects with well characterized AITD has demonstrated clear differences in association within the HLA class II region between HT and GD. Although HT and GD share a number of common genetic markers this study supports the suggestion that differences in HLA class II genotype may, in part, contribute to the different immunopathological processes and clinical presentation of these related diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tunbridge WM, Evered DC, Hall R, Appleton D, Brewis M, Clark F et al. The spectrum of thyroid disease in a community: the Whickham survey. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1977; 7: 481–493.
Jacobson EM, Tomer Y . The CD40, CTLA-4, thyroglobulin, TSH receptor, and PTPN22 gene quintet and its contribution to thyroid autoimmunity: back to the future. J Autoimmun 2007; 28: 85–98.
Heward JM, Brand OJ, Barrett JC, Carr-Smith JD, Franklyn JA, Gough SC . Association of PTPN22 haplotypes with Graves’ disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 685–690.
Ueda H, Howson JM, Esposito L, Heward J, Snook H, Chamberlain G et al. Association of the T-cell regulatory gene CTLA4 with susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Nature 2003; 423: 506–511.
Simmonds MJ, Gough SC . Genetic insights into disease mechanisms of autoimmunity. Br Med Bull 2004; 71: 93–113.
Heward JM, Allahabadia A, Daykin J, Carr-Smith J, Daly A, Armitage M et al. Linkage disequilibrium between the human leukocyte antigen class II region of the major histocompatibility complex and Graves’ disease: replication using a population case control and family-based study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 3394–3397.
Simmonds MJ, Howson JM, Heward JM, Cordell HJ, Foxall H, Carr-Smith J et al. Regression mapping of association between the human leukocyte antigen region and Graves disease. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 157–163.
Moens H, Farid NR, Sampson L, Noel EP, Barnard JM . Hashimoto's thyroiditis is associated with HLA-DRw3. N Engl J Med 1978; 299: 133–134.
Weissel M, Hofer R, Zasmeta H, Mayr WR . HLA-DR and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Tissue Antigens 1980; 16: 256–257.
Farid NR, Thompson C . HLA and autoimmune endocrine disease 1985. Mol Biol Med 1986; 3: 85–97.
Stenszky V, Balazs C, Kraszits E, Juhasz F, Kozma L, Balazs G et al. Association of goitrous autoimmune thyroiditis with HLA-DR3 in eastern Hungary. J Immunogenet 1987; 14: 143–148.
Badenhoop K, Schwarz G, Walfish PG, Drummond V, Usadel KH, Bottazzo GF . Susceptibility to thyroid autoimmune disease: molecular analysis of HLA-D region genes identifies new markers for goitrous Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1990; 71: 1131–1137.
Tandon N, Zhang L, Weetman AP . HLA associations with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1991; 34: 383–386.
Shi Y, Zou M, Robb D, Farid NR . Typing for major histocompatibility complex class II antigens in thyroid tissue blocks: association of Hashimoto's thyroiditis with HLA-DQA0301 and DQB0201 alleles. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1992; 75: 943–946.
Tamai H, Kimura A, Dong RP, Matsubayashi S, Kuma K, Nagataki S et al. Resistance to autoimmune thyroid disease is associated with HLA-DQ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994; 78: 94–97.
Santamaria P, Barbosa JJ, Lindstrom AL, Lemke TA, Goetz FC, Rich SS . HLA-DQB1-associated susceptibility that distinguishes Hashimoto's thyroiditis from Graves’ disease in type I diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994; 78: 878–883.
Wan XL, Kimura A, Dong RP, Honda K, Tamai H, Sasazuki T . HLA-A and -DRB4 genes in controlling the susceptibility to Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Hum Immunol 1995; 42: 131–136.
Hunt PJ, Marshall SE, Weetman AP, Bunce M, Bell JI, Wass JA et al. Histocompatibility leucocyte antigens and closely linked immunomodulatory genes in autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2001; 55: 491–499.
Petrone A, Giorgi G, Mesturino CA, Capizzi M, Cascino I, Nistico L et al. Association of DRB1*04-DQB1*0301 haplotype and lack of association of two polymorphic sites at CTLA-4 gene with Hashimoto's thyroiditis in an Italian population. Thyroid 2001; 11: 171–175.
Farid NR, Sampson L, Moens H, Barnard JM . The association of goitrous autoimmune thyroiditis with HLA-DR5. Tissue Antigens 1981; 17: 265–268.
Manji N, Carr-Smith JD, Boelaert K, Allahabadia A, Armitage M, Chatterjee VK et al. Influences of age, gender, smoking, and family history on autoimmune thyroid disease phenotype. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 4873–4880.
Brand O, Gough S, Heward J . HLA, CTLA-4 and PTPN22: the shared genetic master-key to autoimmunity? Expert Rev Mol Med 2005; 7: 1–15.
Simmonds MJ, Gough SC . Unravelling the genetic complexity of autoimmune thyroid disease: HLA, CTLA-4 and beyond. Clin Exp Immunol 2004; 136: 1–10.
Chistiakov DA . Immunogenetics of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Autoimmune Dis 2005; 2: 1.
Gourraud PA, Boyer JF, Barnetche T, Abbal M, Cambon-Thomsen A, Cantagrel A et al. A new classification of HLA-DRB1 alleles differentiates predisposing and protective alleles for rheumatoid arthritis structural severity. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 593–599.
Cucca F, Lampis R, Congia M, Angius E, Nutland S, Bain SC et al. A correlation between the relative predisposition of MHC class II alleles to type 1 diabetes and the structure of their proteins. Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 2025–2037.
Schonland SO, Lopez C, Widmann T, Zimmer J, Bryl E, Goronzy JJ et al. Premature telomeric loss in rheumatoid arthritis is genetically determined and involves both myeloid and lymphoid cell lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 13471–13476.
Sakaguchi S . Regulatory T cells: key controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell 2000; 101: 455–458.
Hiratani H, Bowden DW, Ikegami S, Shirasawa S, Shimizu A, Iwatani Y et al. Multiple SNPs in intron 7 of thyrotropin receptor are associated with Graves’ disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 2898–2903.
Dechairo BM, Zabaneh D, Collins J, Brand O, Dawson GJ, Green AP et al. Association of the TSHR gene with Graves’ disease: the first disease specific locus. Eur J Hum Genet 2005; 13: 1223–1230.
Simmonds MJ, Howson JM, Heward JM, Carr-Smith J, Franklyn JA, Todd JA et al. A novel and major association of HLA-C in Graves’ disease that eclipses the classical HLA-DRB1 effect. Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16: 2149–2153.
Yeo TW, De Jager PL, Gregory SG, Barcellos LF, Walton A, Goris A et al. A second major histocompatibility complex susceptibility locus for multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2007; 61: 228–236.
Nejentsev S, Howson JM, Walker NM, Szeszko J, Field SF, Stevens HE et al. Localization of type 1 diabetes susceptibility to the MHC class I genes HLA-B and HLA-A. Nature 2007; 450: 887–892.
Bunce M, O’Neill CM, Barnardo MC, Krausa P, Browning MJ, Morris PJ et al. Phototyping: comprehensive DNA typing for HLA-A, B, C, DRB1, DRB3, DRB4, DRB5 & DQB1 by PCR with 144 primer mixes utilizing sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP). Tissue Antigens 1995; 46: 355–367.
Woolf B . On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet 1955; 19: 251–253.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Wellcome Trust for funding the project and all the doctors and nurses from Birmingham, Bournemouth, Cardiff, Exeter, Leeds, Newcastle and Sheffield for recruiting into the AITD UK National Collection of index cases and families.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website (http://www.nature.com/gene)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeitlin, A., Heward, J., Newby, P. et al. Analysis of HLA class II genes in Hashimoto's thyroiditis reveals differences compared to Graves’ disease. Genes Immun 9, 358–363 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.26
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.26
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Durvalumab-induced thyroiditis in a patient with non-small cell lung carcinoma: a case report and review of pathogenic mechanisms
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2022)
-
The detection of up-regulated anti-thyroid antibodies and autoimmune thyroid diseases in patients with autoimmune encephalitis: a retrospective study of 221 patients
Neurological Sciences (2022)
-
Sjögren’s Syndrome and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: Two Sides of the Same Coin
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2019)
-
Certain HLA alleles are associated with stress-triggered Graves’ disease and influence its course
Endocrine (2017)
-
The haplotype of UBE2L3 gene is associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in a Chinese Han population
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2016)