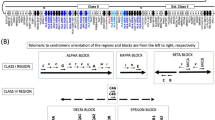
Abstract
Since the complete sequencing of a human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) haplotype, interest in non-human leucocyte antigen (HLA) genes encoded in the MHC has been growing. Non-HLA genes, which outnumber the HLA genes, may contribute to or account for HLA and disease associations. Most information on non-HLA genes has been obtained in separate studies of individual loci. To comprehensively address polymorphisms of relevant non-HLA genes in ‘conserved extended haplotypes’ (CEH), we investigated 101 International Histocompatibility Workshop reference cell lines and nine additional anonymous samples representing all 37 unambiguously characterized CEHs at MICA, NFKBIL1, LTA, NCR3, AIF1, HSPA1A, HSPA1B, BF, NOTCH4 and a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) at HLA-DQA1 as well as MICA, NOTCH4, HSPA1B and all five tumour necrosis factor short tandem repeat (STR) polymorphisms. This work (1) provides an extensive catalogue of MHC polymorphisms in all CEHs, (2) unravels interrelationships between HLA and non-HLA haplotypical lineages, (3) resolves reported typing ambiguities and (4) describes haplospecific markers for a number of CEHs. Analysis also identified a DQA1 SNP and segments containing MHC class III polymorphisms that corresponded with class II (DRB3 and DRB4) lineages. These results portray the MHC where lineages containing non-HLA and HLA variants in linkage disequilibrium may operate in concert and can guide more thorough design and interpretation of HLA–disease relationships.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Horton R, Wilming L, Rand V, Lovering RC, Bruford EA, Khodiyar VK et al. Gene map of the extended human MHC. Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5: 889–899.
Corzo D, Yunis JJ, Yunis EJ, Howard A, Lieberman JA . HSP70-2 9.0 kb variant is in linkage disequilibrium with the HLA-B and DRB1* alleles associated with clozapine-induced agranulocytosis. J Clin Psychiat 1994; 55 (Suppl B): 149–152.
Corzo D, Yunis JJ, Salazar M, Lieberman JA, Howard A, Awdeh Z et al. The major histocompatibility complex region marked by HSP70-1 and HSP70-2 variants is associated with clozapine-induced agranulocytosis in two different ethnic groups. Blood 1995; 86: 3835–3840.
Price P, Witt C, Allcock R, Sayer D, Garlepp M, Kok CC et al. The genetic basis for the association of the 8.1 ancestral haplotype (A1, B8, DR3) with multiple immunopathological diseases. Immunol Rev 1999; 167: 257–274.
Allen MH, Veal C, Faassen A, Powis SH, Vaughan RW, Trembath RC et al. A non-HLA gene within the MHC in psoriasis. Lancet 1999; 353: 1589–1590.
Tazi Ahnini R, Camp NJ, Cork MJ, Mee JB, Keohane SG, Duff GW et al. Novel genetic association between the corneodesmosin (MHC S) gene and susceptibility to psoriasis. Hum Mol Genet 1999; 8: 1135–1140.
Gonzales S, Martinez-Borra J, Del Rio JS et al. The OTF3 gene polymorphism confers susceptibility to psoriasis independent of the association of HLA-Cw*0602. J Invest Dermatol 2000; 115: 824–828.
Milicic A, Lindheimer F, Laval S, Rudwaleit M, Ackerman H, Wordsworth P et al. Interethnic studies of TNF polymorphisms confirm the likely presence of a second MHC susceptibility locus in ankylosing spondylitis. Genes Immun 2000; 1: 418–422.
de la Concha EG, Fernandez-Arquero M, Lopez-Nava G, Martin E, Allcock RJ, Conejero L et al. Susceptibility to severe ulcerative colitis is associated with polymorphism in the central MHC gene IKBL. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: 1491–1495.
de la Concha EG, Fernandez-Arquero M, Gual L, Vigil P, Martinez A, Urcelay E et al. MHC susceptibility genes to IgA deficiency are located in different regions on different HLA haplotypes. J Immunol 2002; 169: 4637–4643.
de Jong MM, Nolte IM, de Vries EG, Schaapveld M, Kleibeuker JH, Oosterom E et al. The HLA class III subregion is responsible for an increased breast cancer risk. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: 2311–2319.
Tazi-Ahnini R, Cork MJ, Wengraf D, Wilson AG, Gawkrodger DJ, Birch MP et al. Notch4, a non-HLA gene in the MHC is strongly associated with the most severe form of alopecia areata. Hum Genet 2003; 112: 400–403.
Newton J, Brown MA, Milicic A, Ackerman H, Darke C, Wilson JN et al. The effect of HLA-DR on susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis is influenced by the associated lymphotoxin alpha-tumor necrosis factor haplotype. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 90–96.
Yamashita T, Hamaguchi K, Kusuda Y, Kimura A, Sakata T, Yoshimatsu H . IKBL promoter polymorphism is strongly associated with resistance to type 1 diabetes in Japanese. Tissue Antigens 2004; 63: 223–230.
Price P, Wong AM, Williamson D, Voon D, Baltic S, Allcock RJ et al. Polymorphisms at positions −22 and −348 in the promoter of the BAT1 gene affect transcription and the binding of nuclear factors. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 967–974.
Price P, Santoso L, Mastaglia F, Garlepp M, Kok CC, Allcock R et al. Two major histocompatibility complex haplotypes influence susceptibility to sporadic inclusion body myositis: critical evaluation of an association with HLA-DR3. Tissue Antigens 2004; 64: 575–580.
Windsor L, Puschendorf M, Allcock R, Scott A, Sayer D, Kucharzak R et al. Does a central MHC gene in linkage disequilibrium with HLA-DRB1*0401 affect susceptibility to type 1 diabetes? Genes Immun 2005; 6: 298–304.
Traherne JA, Barcellos LF, Sawcer SJ, Compston A, Ramsay PP, Hauser SL et al. Association of the truncating splice site mutation in BTNL2 with multiple sclerosis is secondary to HLA-DRB1*15. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 155–161.
Autieri MV, Carbone CM . Overexpression of allograft inflammatory factor-1 promotes proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by cell cycle deregulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001; 21: 1421–1426.
Leong KG, Hu X, Li L, Noseda M, Larrivee B, Hull C et al. Activated Notch4 inhibits angiogenesis: role of beta 1-integrin activation. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 2830–2841.
Milner CM, Campbell RD . Polymorphic analysis of the three MHC-linked HSP70 genes. Immunogenetics 1992; 36: 357–362.
Partanen J, Milner C, Campbell RD, Maki M, Lipsanen V, Koskimies S . HLA-linked heat-shock protein 70 (HSP70-2) gene polymorphism and celiac disease. Tissue Antigens 1993; 41: 15–19.
Cascino I, D'Alfonso S, Cappello N, Giordano M, Pugliese A, Awdeh Z et al. Gametic association of HSP70-1 promoter region alleles and their inclusion in extended HLA haplotypes. Tissue Antigens 1993; 42: 62–66.
Gunther E, Walter L . Genetic aspects of the hsp70 multigene family in vertebrates [Review]. Experientia 1994; 50: 987–1001.
Levo A, Partanen J . Mutation-haplotype analysis of steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21) deficiency in Finland. Implications for the population history of defective alleles. Hum Genet 1997; 99: 488–497.
Naruse TK, Nose Y, Ando R, Araki N, Shigenari A, Ando A et al. Extended HLA haplotypes in Japanese homozygous typing cells. Tissue Antigens 1998; 51: 305–308.
Allcock RJ, Baluchova K, Cheong KY, Price P . Haplotypic single nucleotide polymorphisms in the central MHC gene IKBL, a potential regulator of NF-kappaB function. Immunogenetics 2001; 52: 289–293.
Turner DM, Pravica V, Sinnott PJ, Hutchinson IV . Polymorphism in the promoter region of the gene encoding human allograft inflammatory factor-1. Eur J Immunogenet 2001; 28: 449–450.
Tazi-Ahnini R, Timms JM, Cox A, Wilson AG . Identification of novel single nucleotide polymorphisms within the NOTCH4 gene and determination of association with MHC alleles. Eur J Immunogenet 2003; 30: 101–105.
Sanchez-Mazas A, Djoulah S, Busson M, Le Monnier de Gouville I, Poirier JC, Dehay C et al. A linkage disequilibrium map of the MHC region based on the analysis of 14 loci haplotypes in 50 French families. Eur J Hum Genet 2000; 8: 33–41.
Vorechovsky I, Kralovicova J, Laycock MD, Webster AD, Marsh SG, Madrigal A et al. Short tandem repeat (STR) haplotypes in HLA: an integrated 50-kb STR/linkage disequilibrium/gene map between the RING3 and HLA-B genes and identification of STR haplotype diversification in the class III region. Eur J Hum Genet 2001; 9: 590–598.
Ahmad T, Neville M, Marshall SE, Armuzzi A, Mulcahy-Hawes K, Crawshaw J et al. Haplotype-specific linkage disequilibrium patterns define the genetic topography of the human MHC. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: 647–656.
Walsh EC, Mather KA, Schaffner SF, Farwell L, Daly MJ, Patterson N et al. An integrated haplotype map of the human major histocompatibility complex. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 580–590.
Allcock RJ, Windsor L, Gut IG, Kucharzak R, Sobre L, Lechner D et al. High-density SNP genotyping defines 17 distinct haplotypes of the TNF block in the Caucasian population: implications for haplotype tagging. Hum Mutat 2004; 24: 517–525.
Miretti MM, Walsh EC, Ke X, Delgado M, Griffiths M, Hunt S et al. A high-resolution linkage-disequilibrium map of the human major histocompatibility complex and first generation of tag single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 634–646.
Dawkins R, Leelayuwat C, Gaudieri S, Tay G, Hui J, Cattley S et al. Genomics of the major histocompatibility complex: haplotypes, duplication, retroviruses and disease. Immunol Rev 1999; 167: 275–304.
Cattley SK, Williamson JF, Tay GK, Martinez OP, Gaudieri S, Dawkins RL . Further characterization of MHC haplotypes demonstrates conservation telomeric of HLA-A: update of the 4AOH and 10IHW cell panels. Eur J Immunogenet 2000; 27: 397–426.
Yunis EJ, Larsen CE, Fernandez-Vina M, Awdeh ZL, Romero T, Hansen JA et al. Inheritable variable sizes of DNA stretches in the human MHC: conserved extended haplotypes and their fragments or blocks. Tissue Antigens 2003; 62: 1–20.
Degli-Esposti MA, Leaver AL, Christiansen FT, Witt CS, Abraham LJ, Dawkins RL . Ancestral haplotypes: conserved population MHC haplotypes. Hum Immunol 1992; 34: 242–252.
Dorak MT, Mills KI, Gaffney D, Wilson DW, Galbraith I, Henderson N et al. Homozygous MHC genotypes and longevity. Hum Hered 1994; 44: 271–278.
Dorak MT, Lawson T, Machulla HKG, Darke C, Mills KI, Burnett AK . Unravelling an HLA-DR association in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 694–700.
Dorak MT, Lawson T, Machulla HK, Mills KI, Burnett AK . Increased heterozygosity for MHC class II lineages in newborn males. Genes Immun 2002; 3: 263–269.
Dorak MT, Yee LJ, Tang J, Shao W, Lobashevsky ES, Jacobson LP et al. HLA-B, -DRB1/3/4/5, and -DQB1 gene polymorphisms in human immunodeficiency virus-related Kaposi's sarcoma. J Med Virol 2005; 76: 302–310.
Andersson G, Andersson L, Larhammar D, Rask L, Sigurdardottir S . Simplifying genetic locus assignment of HLA-DRB genes. Immunol Today 1994; 15: 58–61.
Dorak MT, Machulla HK, Darke C, Burnett AK . The biallelic polymorphism of HSP70-2 correlates with the genealogy of the HLA-DRB1 genes [abstract]. Hum Immunol 2000; 61 (Suppl 2): S54.
Amar A, Radka SF, Holbeck SL, Kim SJ, Nepom BS, Nelson K et al. Characterization of specific HLA-DQ alpha allospecificities by genomic, biochemical, and serologic analysis. J Immunol 1987; 138: 3986–3990.
Dorak MT, Chalmers EA, Gaffney D, Wilson DW, Galbraith I, Henderson N et al. Human major histocompatibility complex contains several leukemia susceptibility genes. Leuk Lymphoma 1994; 12: 211–222.
Dorak MT, Wilson DW, Galbraith I, Henderson N, Burnett AK, Worwood M . A molecular analysis of the telomeric end of the major histocompatibility complex. DNA typing of HLA-A3 subtypes and -B7. Hum Immunol 1995; 42: 1–8.
Chu X, Braun-Heimer L, Rittner C, Schneider PM . Identification of the recombination site within the steroid 21-hydroxylase gene (CYP21) of the HLA-B47,DR7 haplotype. Exp Clin Immunogenet 1992; 9: 80–85.
Karell K, Klinger N, Holopainen P, Levo A, Partanen J . Major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-linked microsatellite markers in a founder population. Tissue Antigens 2000; 56: 45–51.
Abbal M, Thomsen M, Cambon Thomsen A, Archambeau J, Calot M, Fathallah D . Two subtypes of BfF by isoelectrofocusing: differential linkage to other HLA markers. Hum Genet 1985; 69: 181–183.
Degli-Esposti MA, Leelayuwat C, Daly LN, Carcassi C, Contu L, Versluis LF et al. Updated characterization of ancestral haplotypes using the Fourth Asia-Oceania Histocompatibility Workshop panel. Hum Immunol 1995; 44: 12–18.
Udalova IA, Nedospasov SA, Webb GC, Chaplin DD, Turetskaya RL . Highly informative typing of the human TNF locus using six adjacent polymorphic markers. Genomics 1993; 16: 180–186.
Garcia-Merino A, Alper CA, Usuku K, Marcus-Bagley D, Lincoln R, Awdeh Z et al. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) microsatellite haplotypes in relation to extended haplotypes, susceptibility to diseases associated with the major histocompatibility complex and TNF secretion. Hum Immunol 1996; 50: 11–21.
Dorak MT, Tang J, Tang S, Penman-Aguilar A, Coutinho RA, Goedert JJ et al. Influence of human leukocyte antigen-B22 alleles on the course of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in 3 cohorts of white men. J Infect Dis 2003; 188: 856–863.
Weissensteiner T, Lanchbury JS . TNFB polymorphisms characterize three lineages of TNF region microsatellite haplotypes. Immunogenetics 1998; 47: 6–16.
Kok CC, Croager EJ, Witt CS, Kiers L, Mastaglia FL, Abraham LJ et al. Mapping of a candidate region for susceptibility to inclusion body myositis in the human major histocompatibility complex. Immunogenetics 1999; 49: 508–516.
Wong AM, Allcock RJ, Cheong KY, Christiansen FT, Price P . Alleles of the proximal promoter of BAT1, a putative anti-inflammatory gene adjacent to the TNF cluster, reduce transcription on a disease-associated MHC haplotype. Genes Cells 2003; 8: 403–412.
Marsh SG, Packer R, Heyes JM, Bolton B, Fauchet R, Charron D et al. The International Histocompatibility Workshop cell line panel. In: Charron D (ed). Genetic Diversity of HLA: Functional and Medical Implications. EDK: Paris, 1997, pp 633–647.
Khani-Hanjani A, Hoar D, Horsman D, Keown P . Identification of four novel dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms in the TNF-alpha and TNF-beta genes. Hum Immunol 2000; 61: 511–512.
van der Slik AR, Shing DC, Eerligh P, Giphart MJ . Subtyping for TNFa microsatellite sequence variation. Immunogenetics 2000; 52: 29–34.
Fodil N, Laloux L, Wanner V, Pellet P, Hauptmann G, Mizuki N et al. Allelic repertoire of the human MHC class I MICA gene. Immunogenetics 1996; 44: 351–357.
Fodil N, Pellet P, Laloux L, Hauptmann G, Theodorou I, Bahram S . MICA haplotypic diversity. Immunogenetics 1999; 49: 557–560.
Katsuyama Y, Ota M, Ando H, Saito S, Mizuki N, Kera J et al. Sequencing based typing for genetic polymorphisms in exons, 2, 3 and 4 of the MICA gene. Tissue Antigens 1999; 54: 178–184.
Mendoza-Rincon J, Arguello JR, Perez-Rodriguez M, McWhinnie A, Marsh SG, Fischer G et al. Characterization of the MICA polymorphism by sequence-specific oligonucleotide probing. Immunogenetics 1999; 49: 471–478.
Fischer G, Arguello JR, Perez-Rodriguez M, McWhinnie A, Marsh SG, Travers PJ et al. Sequence-specific oligonucleotide probing for MICB alleles reveals associations with MICA and HLA-B. Immunogenetics 2000; 51: 591–599.
Bolognesi E, Dalfonso S, Rolando V, Fasano ME, Pratico L, Momigliano-Richiardi P . MICA and MICB microsatellite alleles in HLA extended haplotypes. Eur J Immunogenet 2001; 28: 523–530.
Obuchi N, Takahashi M, Nouchi T, Satoh M, Arimura T, Ueda K et al. Identification of MICA alleles with a long Leu-repeat in the transmembrane region and no cytoplasmic tail due to a frameshift-deletion in exon 4. Tissue Antigens 2001; 57: 520–535.
Ahmad T, Marshall SE, Mulcahy-Hawes K, Orchard T, Crawshaw J, Armuzzi A et al. High resolution MIC genotyping: design and application to the investigation of inflammatory bowel disease susceptibility. Tissue Antigens 2002; 60: 164–179.
Perez-Rodriguez M, Arguello JR, Fischer G, Corell A, Cox ST, Robinson J et al. Further polymorphism of the MICA gene. Eur J Immunogenet 2002; 29: 35–46.
Rees MT, Downing J, Darke C . A typing system for the major histocompatibility complex class I chain related genes A and B using polymerase chain reaction with sequence-specific primers. Genet Test 2005; 9: 93–110.
Vitiani LR, Potolicchio I, D'Amato M, Baricordi OR, Sorrentino R . MICA exon 5 microsatellite typing by DNA heteroduplex analysis: a new polymorphism in the transmembrane region. Tissue Antigens 1998; 51: 309–311.
Steinle A, Li P, Morris DL, Groh V, Lanier LL, Strong SK et al. Interactions of human NKG2D with its ligands MICA, MICB, and homologs of the mouse RAE-1 protein family. Immunogenetics 2001; 53: 279–287.
Prasad VK, Yang SY . Allele assignment for HLA-A, -B, and -C genes to the Tenth International Histocompatibility Workshop cell lines. Tissue Antigens 1996; 47: 538–546.
Allcock RJ, Atrazhev AM, Beck S, De Jong PJ, Elliott JF, Forbes S et al. The MHC haplotype project: a resource for HLA-linked association studies. Tissue Antigens 2002; 59: 520–521.
Stewart CA, Horton R, Allcock RJ, Ashurst JL, Atrazhev AM, Coggill P et al. Complete MHC haplotype sequencing for common disease gene mapping. Genome Res 2004; 14: 1176–1187.
Nepom GT, Erlich HA . Immunology and immunogenetics. In: King RA, Rotter JI, Motulsky AG (eds). The Genetic Basis of Common Diseases 2nd edn. Oxford University Press: Oxford, 2002, pp 573–586.
Ribas G, Neville MJ, Campbell RD . Single-nucleotide polymorphism detection by denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography and direct sequencing in genes in the MHC class III region encoding novel cell surface molecules. Immunogenetics 2001; 53: 369–381.
Jeffery KJ, Siddiqui AA, Bunce M, Lloyd AL, Vine AM, Witkover AD et al. The influence of HLA class I alleles and heterozygosity on the outcome of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I infection. J Immunol 2000; 165: 7278–7284.
Kikuchi I, Ueda A, Mihara K, Miyanaga O, Machidori H, Ishikawa E et al. The effect of HLA alleles on response to interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1998; 10: 859–863.
Allcock RJ, Christiansen FT, Price P . The central MHC gene IKBL carries a structural polymorphism that is associated with HLA-A3,B7,DR15. Immunogenetics 1999; 49: 660–665.
Mallal S, Nolan D, Witt C, Masel G, Martin AM, Moore C et al. Association between presence of HLA-B*5701, HLA-DR7, and HLA-DQ3 and hypersensitivity to HIV-1 reverse-transcriptase inhibitor abacavir. Lancet 2002; 359: 727–732.
Gorski J, Rollini P, Mach B . Structural comparison of the genes of two HLA-DR supertypic groups: the loci encoding DRw52 and DRw53 are not truly allelic. Immunogenetics 1987; 25: 397–402.
Klein J, Gutknecht J, Fischer N . The major histocompatibility complex and human evolution. Trends Genet 1990; 6: 7–11.
Kasahara M, Klein D, Vincek V, Sarapata DE, Klein J . Comparative anatomy of the primate major histocompatibility complex DR subregion: evidence for combinations of DRB genes conserved across species. Genomics 1992; 14: 340–349.
Ayala FJ, Escalante A, O'hUigin C, Klein J . Molecular genetics of speciation and human origins [Review]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 6787–6794.
Svensson AC, Setterblad N, Sigurdardottir S, Rask L, Andersson G . Primate DRB genes from the DR3 and DR8 haplotypes contain ERV9 LTR elements at identical positions. Immunogenetics 1995; 41: 74–82.
Satta Y, Mayer WE, Klein J . HLA-DRB intron 1 sequences: implications for the evolution of HLA-DRB genes and haplotypes. Hum Immunol 1996; 51: 1–12.
Bergstrom TF, Mack SJ, Gyllensten U, Erlich HA . Evolution of HLA-DRB loci, DRB1 lineages, and alleles: analyses of intron-1 and intron-2 sequences. In: Kasahara M (ed). Major Histocompatibility Complex: Evolution, Structure, and Function. Springer: Tokyo, 2000, pp 329–346.
Hughes AL . Evolution of introns and exons of class II major histocompatibility complex genes of vertebrates. Immunogenetics 2000; 51: 473–486.
Dorak MT, Machulla HK, Hentschel M, Mills KI, Langner J, Burnett AK . Influence of the major histocompatibility complex on age at onset of chronic lymphoid leukaemia. Int J Cancer 1996; 65: 134–139.
Ditchkoff SS, Lochmiller RL, Masters RE, Hoofer SR, van den Bussche RA . Major-histocompatibility-complex-associated variation in secondary sexual traits of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus): evidence for good-genes advertisement. Evolution 2001; 55: 616–625.
Pociot F, Ronningen KS, Nerup J . Polymorphic analysis of the human MHC-linked heat shock protein 70 (HSP70-2) and HSP70-Hom genes in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Scand J Immunol 1993; 38: 491–495.
Pugliese A, Awdeh ZL, Galluzzo A, Yunis EJ, Alper CA, Eisenbarth GS . No independent association between HSP70 gene polymorphism and IDDM. Diabetes 1992; 41: 788–791.
Caplen NJ, Patel A, Millward A, Campbell RD, Ratanachaiyavong S, Wong FS et al. Complement C4 and heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) genotypes and type I diabetes mellitus. Immunogenetics 1990; 32: 427–430.
Snoek M, van Dinten L, van Vugt H . A novel gene, G7e, resembling a viral envelope gene, is located at the recombinational hot spot in the class III region of the mouse MHC. Genomics 1996; 38: 5–12.
Levo A, Westman P, Partanen J . An approach to mapping haplotype-specific recombination sites in human MHC class III. Immunogenetics 1996; 43: 136–140.
Yunis EJ, Awdeh Z, Johnson A, Suciu-Foca N, Robinson MA, Hartzman R et al. Complotype genetic loci segregate more frequently with HLA-DR than with HLA-B. Immunogenetics 1985; 21: 25–31.
Moriuchi J, Moriuchi T, Silver J . Nucleotide sequence of an HLA-DQ alpha chain derived from a DRw9 cell line: genetic and evolutionary implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1985; 82: 3420–3424.
Gyllensten UB, Erlich HA . Ancient roots for polymorphism at the HLA-DQ alpha locus in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989; 86: 9986–9990.
Loiseau P, Lehn P, Dautry F, Lepage V, Colombani J, Cohen D et al. Correlation between an HLA-DQ alpha length polymorphism of messenger RNA and serologically defined specificities (DQw1, DRw53, DR3+5). Immunogenetics 1986; 23: 111–114.
Hunt C, Morimoto RI . Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1985; 82: 6455–6459.
Muller WE, Krasko A, Skorokhod A, Bunz C, Grebenjuk VA, Steffen R et al. Histocompatibility reaction in tissue and cells of the marine sponge Suberites domuncula in vitro and in vivo: central role of the allograft inflammatory factor 1. Immunogenetics 2002; 54: 48–58.
Schork NJ, Cardon LR, Xu X . The future of genetic epidemiology. Trends Genet 1998; 14: 266–272.
Templeton AR . A cladistic analysis of phenotypic associations with haplotypes inferred from restriction endonuclease mapping or DNA sequencing. V. Analysis of case/control sampling designs: Alzheimer's disease and the apoprotein E locus. Genetics 1995; 140: 403–409.
Templeton AR, Weiss KM, Nickerson DA, Boerwinkle E, Sing CF . Cladistic structure within the human Lipoprotein lipase gene and its implications for phenotypic association studies. Genetics 2000; 156: 1259–1275.
Fejerman L, Bouzekri N, Wu X, Adeyemo A, Luke A, Zhu X et al. Association between evolutionary history of angiotensinogen haplotypes and plasma levels. Hum Genet 2004; 115: 310–318.
Seltman H, Roeder K, Devlin B . Evolutionary-based association analysis using haplotype data. Genet Epidemiol 2003; 25: 48–58.
Vorechovsky I, Cullen M, Carrington M, Hammarstrom L, Webster AD . Fine mapping of IGAD1 in IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency: identification and characterization of haplotypes shared by affected members of 101 multiple-case families. J Immunol 2000; 164: 4408–4416.
Matthews VB, Witt CS, French MA, Machulla HK, De la Concha EG, Cheong KY et al. Central MHC genes affect IgA levels in the human: reciprocal effects in IgA deficiency and IgA nephropathy. Hum Immunol 2002; 63: 424–433.
Diepstra A, Niens M, Vellenga E, van Imhoff GW, Nolte IM, Schaapveld M et al. Association with HLA class I in Epstein–Barr-virus-positive and with HLA class III in Epstein–Barr-virus-negative Hodgkin's lymphoma. Lancet 2005; 365: 2216–2224.
Oh HB, Kim SI, Park MH, Akaza T, Juji T . Probability of finding HLA-matched unrelated marrow donors for Koreans and Japanese from the Korean and Japan Marrow Donor Programs. Tissue Antigens 1999; 53 (4 Part 1): 347–349.
Machulla HK, Batnasan D, Steinborn F, Uyar FA, Saruhan-Direskeneli G, Oguz FS et al. Genetic affinities among Mongol ethnic groups and their relationship to Turks. Tissue Antigens 2003; 61: 292–299.
Dorak MT, Tang J, Penman-Aguilar A, Westfall AO, Zulu I, Lobashevsky ES et al. Association of transmission of HIV-1 with HLA-B allele sharing between serodiscordant heterosexual Zambian couples. Lancet 2004; 363: 2137–2139.
den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE . Nomenclature for the description of human sequence variations. Hum Genet 2001; 109: 121–124.
Milner CM, Campbell RD . Structure and expression of the three MHC-linked HSP70 genes. Immunogenetics 1990; 32: 242–251.
Dressel R, Gunther E . A pentanucleotide tandem duplication polymorphism in the 3′ untranslated region of the HLA-linked heat-shock protein 70-2 (HSP70-2) gene. Hum Genet 1994; 94: 585–586.
Favatier F, Bornman L, Hightower LE, Gunther E, Polla BS . Variation in hsp gene expression and Hsp polymorphism: do they contribute to differential disease susceptibility and stress tolerance? [Review]. Cell Stress Chaperones 1997; 2: 141–155.
Cascino I, Sorrentino R, Tosi R . Strong genetic association between HLA-DR3 and a polymorphic variation in the regulatory region of the HSP70-1 gene. Immunogenetics 1993; 37: 177–182.
Sugaya K, Sasanuma S, Nohata J, Kimura T, Fukagawa T, Nakamura Y et al. Gene organization of human NOTCH4 and (CTG)n polymorphism in this human counterpart gene of mouse proto-oncogene Int3. Gene 1997; 189: 235–244.
Ando A, Sugaya K, Shigenari A, Naruse TK, Horiuchi M, Shiina T et al. Triplet repeat polymorphism in the NOTCH4 gene within the human major histocompatibility complex in a healthy population and patients with a salivary gland tumor in Japan. Tissue Antigens 1997; 50: 66–70.
Ando A, Shigenari A, Naruse TK, Sugaya K, Juji T, Honda Y et al. Triplet repeat polymorphism within the NOTCH4 gene located near the junction of the HLA class II and class III regions in narcolepsy. Tissue Antigens 1997; 50: 646–649.
Ujike H, Takehisa Y, Takaki M, Tanaka Y, Nakata K, Takeda T et al. NOTCH4 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Neurosci Lett 2001; 301: 41–44.
Davrinche C, Abbal M, Clerc A . Molecular characterization of human complement factor B subtypes. Immunogenetics 1990; 32: 309–312.
Jahn I, Mejia JE, Thomas M, Darke C, Schroder H, Geserick G et al. Genomic analysis of the F subtypes of human complement factor B. Eur J Immunogenet 1994; 21: 415–423.
Warzocha K, Ribeiro P, Bienvenu J, Roy P, Charlot C, Rigal D et al. Genetic polymorphisms in the tumor necrosis factor locus influence non-Hodgkin's lymphoma outcome. Blood 1998; 91: 3574–3581.
Shao W, Lobashevsky ES, Kaslow RA, Dorak MT . MICA intron 1 sequences of conserved extended HLA haplotypes: implications for sequencing-based typing. Genes Immun 2004; 5: 371–374.
Mizuki N, Ota M, Kimura M, Ohno S, Ando H, Katsuyama Y et al. Triplet repeat polymorphism in the transmembrane region of the MICA gene: a strong association of six GCT repetitions with Behcet disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 1298–1303.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially funded by intramural funds from the University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Public Health. We thank the staff at the Tissue Typing Laboratory in Glasgow Royal Infirmary (Scotland, UK), the Regional Tissue Typing Laboratory in the Welsh Blood Service (UK) and the HLA Laboratory in Martin Luther University School of Medicine at Halle (Germany) for various contributions to this study. M Tevfik Dorak is currently supported by the North of England Children's Cancer Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website (http://www.nature.com/gene)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorak, M., Shao, W., Machulla, H. et al. Conserved extended haplotypes of the major histocompatibility complex: further characterization. Genes Immun 7, 450–467 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364315
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364315
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Characterizing the diversity of MHC conserved extended haplotypes using families from the United Arab Emirates
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Immunogenetic determinants of heterosexual HIV-1 transmission: key findings and lessons from two distinct African cohorts
Genes & Immunity (2021)
-
Diversity of HLA Class I and Class II blocks and conserved extended haplotypes in Lacandon Mayans
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
HLA-class II haplotypes and Autism Spectrum Disorders
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Haplotyping the human leukocyte antigen system from single chromosomes
Scientific Reports (2016)