Abstract
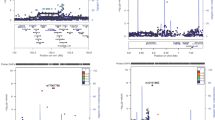
Type 1 diabetes results from autoimmune destruction of pancreatic islet β-cells, possibly initiated or exacerbated by viral infections. Recent studies have demonstrated that antibodies towards enterovirus and autoantibodies towards islet cell components develop in the long preclinical phase of type 1 diabetes. We therefore hypothesised that susceptibility to type 1 diabetes could be influenced by genetic factors controlling production of antiviral antibodies or autoantibodies or both. To search for evidence of linkage or association (linkage disequilibrium) between type 1 diabetes and the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH) region, 351 North American and British families with ⩾2 diabetic children were genotyped for IGH region microsatellites. Using affected sibpair analysis, significant evidence for linkage was obtained for three markers close to the IGH gene cluster (P values 0.004, 0.002, 0.002). No evidence was found for association using family-based methods. To attempt to confirm these findings, a smaller dataset (241 families, 138 with ⩾2 diabetic children) from Denmark, a more genetically-homogeneous population, was genotyped for one marker only. These families showed no linkage, but significant evidence for association (P = 0.019). This study suggests that a locus (assigned the symbol IDDM16) in the IGH region, possibly an IGH gene, influences susceptibility to type 1 diabetes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singal DP, Blajchman MA . Histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens, lymphocytotoxic antibodies and tissue antibodies in patients with diabetes mellitus Diabetes 1973 22: 429–432
Nerup J, Platz P, Andersen OO et al. HL-A antigens and diabetes mellitus Lancet 1974 II: 864–866
Cudworth AG, Woodrow JC . HL-A antigens and diabetes mellitus Lancet 1974 2: 1153 (letter)
Risch N . Assessing the role of HLA-linked and unlinked determinants of disease Am J Hum Genet 1987 40: 1–14
Bell GI, Horita S, Karam JH . A polymorphic locus near the human insulin gene is associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Diabetes 1984 33: 1504–1509
Field LL, Tobias R, Magnus T . A locus on chromosome 15q26 (IDDM3) produces susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Nat Genet 1994 8: 189–194
Luo D-F, Bui MM, Muir A, Maclaren NK, Thomson G, She J-X . Affected sibpair mapping of a novel susceptibility gene to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM8) on chromosome 6 Am J Hum Genet 1995 57: 911–919
Zamani M, Pociot F, Raeymaekers P, Nerup J, Cassiman JJ . Linkage of type I diabetes to 15q26 (IDDM3) in the Danish population Hum Genet 1996 98: 491–496
Davies JL, Kawaguchi Y, Bennett ST et al. A genome-wide search for human type 1 diabetes susceptibility genes Nature 1994 371: 30–136
Hashimoto L, Habita C, Beressl JP et al. Genetic mapping of a susceptibility locus for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus on chromosome 11q Nature 1994 371: 161–164
Luo D-F, Buzzetti R, Rotter JI et al. Confirmation of three susceptibility genes to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: IDDM4, IDDM5, and IDDM8 Hum Mol Genet 1996 5: 693–698
Nakagawa Y, Kawaguchi Y, Twells RC et al. Fine mapping of the diabetes-susceptibility locus, IDDM4, on chromosome 11q13 Am J Hum Genet 1998 63: 547–556
Merriman T, Twells R, Merriman M et al. Evidence by allelic association-dependent methods for a type 1 diabetes polygene (IDDM6) on chromosome 18q21 Hum Mol Genet 1997 6: 1003–1010
Owerbach D, Gabbay KH . The HOXD8 locus (2q31) is linked to type I diabetes: Interaction with chromosome 6 and 11 disease susceptibility genes Diabetes 1995 44: 132–136
Copeman JB, Cucca F, Hearne CM et al. Linkage disequilibrium mapping of a type 1 diabetes susceptibility gene (IDDM7) to chromosome 2q31-q33 Nat Genet 1995 9: 80–85
Reed P, Cucca F, Jenkins S et al. Evidence for a type 1 diabetes susceptibility locus (IDDM10) on human chromosome 10p11-q11 Hum Mol Genet 1997 6: 1011–1016
Mein CA, Esposito L, Dunn MG et al. A search for type 1 diabetes susceptibility genes in families from the United Kingdom Nat Genet 1998 19: 297–300
Field LL, Tobias R, Thomson G, Plon S . Susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus maps to a locus (IDDM11) on chromosome 14q24.3-q31 Genomics 1996 33: 1–8
Nistico L, Buzzetti R, Pritchard LE et al. The CTLA-4 gene region of chromosome 2q33 is linked to, and associated with, type 1 diabetes Hum Mol Genet 1996 5: 1075–1080
Marron MP, Raffel LJ, Garchon HJ et al. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) is associated with CTLA4 polymorphisms in multiple ethnic groups Hum Mol Genet 1997 6: 1275–1282
Larsen ZM, Kristiansen OP, Mato E et al. IDDM12 (CTLA4) on 2q33 and IDDM13 on 2q34 in genetic susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Autoimmunity 1999 31: 34–35
Morahan G, Huang D, Tait BD, Colman PG, Harrison LC . Markers on distal chromosome 2q linked to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Science 1996 272: 1811–1813
Delepine M, Pociot F, Habita C et al. Evidence of a non-MHC susceptibility locus in type I diabetes linked to HLA on chromosome 6 Am J Hum Genet 1997 60: 174–187
Verge CF, Vardi P, Babu S et al. Evidence for oligogenic inheritance of type 1 diabetes in a large Bedouin Arab family J Clin Invest 1998 102: 1569–1575
Morahan G, Huang D, Ymer S et al. Linkage disequilibrium of a type 1 diabetes susceptibility locus with a regulatory IL12B allele Nat Genet 2001 27: 218–221
Rowe RE, Wapelhorst B, Bell GI, Risch N, Spielman RS, Concannon P . Linkage and association between insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) susceptibility and markers near the glucokinase gene on chromosome 7 Nat Genet 1995 10: 240–242
Concannon P, Gogolin-Ewens KJ, Hinds DA et al. A second-generation screen of the human genome for susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Nat Genet 1998 19: 292–296
Cucca F, Goy JV, Kawaguchi Y et al. A male-female bias in type 1 diabetes and linkage to chromosome Xp in MHC HLA-DR3-positive patients Nat Genet 1998 19: 301–302
Kristiansen OP, Zamani M, Johannesen J et al. Linkage and association between a CD4 gene polymorphism and IDDM in a Danish IDDM multiplex family material Diabetes 1998 47: 281–283
Verge CF, Gianani R, Kawasaki E et al. Prediction on type I diabetes in first-degree relatives using a combination of insulin, GAD, and ICA512bdc/IA-2 autoantibodies Diabetes 1996 45: 926–933
Roll U, Christie MR, Fuchtenbusch M, Payton MA, Hawkes CJ, Ziegler AG . Perinatal autoimmunity in offspring of diabetic parents. The German Multicenter BABY-DIAB study: detection of humoral immune responses to islet antigens in early childhood Diabetes 1996 45: 967–973
Lindberg B, Ivarsson SA, Landin-Olsson M, Sundkvist G, Svanberg L, Lernmark A . Islet autoantibodies in cord blood from children who developed type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus before 15 years of age Diabetologia 1999 42: 181–187
Ziegler AG, Hummel M, Schenker M, Bonifacio E . Autoantibody appearance and risk for development of childhood diabetes in offspring of parents with type 1 diabetes: the 2-year analysis of the German BABYDIAB Study Diabetes 1999 48: 460–468
Bingley PJ, Bonifacio E, Williams AJK, Genovese S, Bottazzo GF, Gale EAM . Prediction of IDDM in the general population: strategies based on combinations of autoantibody markers Diabetes 1997 46: 1701–1710
Leslie RDG, Atkinson MA, Notkins AL . Autoantigens IA-2 and GAD in Type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes Diabetologia 1999 42: 3–14
Hawa M, Rowe R, Lan MS et al. Value of antibodies to islet protein tryosine phosphatase-like molecule in predicting type I diabetes Diabetes 1997 46: 1270–1275
Redondo MJ, Rewers M, Yu L et al. Genetic determination of islet cell autoimmunity in monozygotic twin, dizygotic twin, and non-twin siblings of patients with type 1 diabetes: prospective twin study BMJ 1999 318: 698–702
Roivainen M, Knip M, Hyoty H et al. Several different enterovirus serotypes can be associated with prediabetic autoimmune episodes and onset of overt IDDM. Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group Med Virol 1998 56: 74–78
Dahlquist GG, Ivarsson S, Lindberg B, Forsgren M . Maternal enteroviral infection during pregnancy as a risk factor for childhood IDDM. A population-based case-control study Diabetes 1995 44: 408–413
Hiltunen M, Hyoty H, Knip M et al. Islet cell antibody seroconversion in children is temporally associated with enterovirus infections. Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group J Infect Dis 1997 175: 554–560
Lönnrot M, Korpela K, Knip M et al. Enterovisus infection as a risk factor for β-cell autoimmunity in a prospectively observed birth cohort Diabetes 2000 49: 1314–1318
Karounos DG, Wolinsky JS, Thomas JW . Monoclonal antibody to rubella virus capsid protein recognizes a beta-cell antigen J Immunol 1993 150: 3080–3085
Maclaren NK, Alkinson MA . Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the hypothesis of molecular mimicry between islet cell antigens and microorganisms Mol Med Today 1997 3: 76–83
Vreugdenhil GR, Geluk A, Ottenhoff TH, Melchers WJ, Roep BO, Galama JM . Molecular mimicry in diabetes mellitus: the homologous domain in coxsackie B virus protein 2C and islet autoantigen GAD65 is highly conserved in the coxsackie B-like enteroviruses and binds to the diabetes associated HLA-DR3 molecule Diabetologia 1998 41: 40–46
Field LL . Non-HLA region genes in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus Bailliere’s Clin Endocrinol Met 1991 5: 413–438
Dugoujon JM, Cambon-Thonsen A . Immunoglobulin allotypes (Gm and Km) and their interactions with HLA antigens in autoimmune diseases: a review Autoimmunity 1995 22: 245–260
Propert D . Innunoglobulin allotypes and RFLPs in disease association Exp Clin Immunogenet 1995 12: 198–205
Field LL, Anderson CE, Neiswanger K, Hodge SE, Spence MA, Rotter RI . Interaction of HLA and immunoglobulin antigens in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes Diabetologia 1984 27: 504–508
Schernthaner G, Mayr WR . Immunoglobulin allotype markers and HLA DR genes in Type 1 diabetes mellitus Metabolism 1984 33: 833–836
Bertrams J, Baur MP . No interaction between HLA and immunoglobulin IgG heavy chain allotypes in Type 1 diabetes J Immunogenet 1985 12: 81–86
Field LL, McArthur RG . The genetics of susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus—possible new markers Clin Invest Med 1987 10: 437–443
Tait BD, Propert DN, Harrison L, Mandel T, Martin FIR . Interaction between HLA antigens and immunoglobulin (Gm) allotypes in susceptibility to type 1 diabetes Tissue Antigens 1986 27: 249–255
Dizier MH, Deschamps I, Hors J, Blanc M, Rivat L, Clerget-Darpoux F . Interactive effect of HLA and Gm tested in a study of 135 juvenile insulin-dependent diabetic families Tissue Antigens 1986 27: 269–278
Rich SS, Weitkamp LR, Guttormsem S, Barbosa J . Gm, Km, and HLA in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a loglinear analysis of association Diabetes 1986 35: 927–932
Field LL, Fothergill-Payne C, Bertrams J, Baur MP . HLA-DR effects in a large German IDDM dataset Genet Epidemiol 1986 Suppl 1: 323–328
Field LL . Genes predisposing to IDDM in multiplex families Genet Epidemiol 1989 6: 101–106
Deschamps I, Blanc M, Dizier MH, Lestradet H, Hors J . A. Gm haplotype study in relation with HLA-DR in 155 insulin-dependent diabetic patients and their affected and non-affected siblings Clin Experimental Endocrinol 1987 89: 325–332
Veijola R, Knip M, Puukka R, Reijonen H, Cox DW, Ilonen J . The immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: affected-sib-pair analysis and association studies Am J Hum Genet 1996 59: 462–470
Risch N, Merikangas K . The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases Science 1996 273: 1516–1517
Sawcer S, Jones HB, Feakes R et al. A genome screen in multiple sclerosis reveals susceptibility loci on chromosome 6p21 and 17q22 Nat Genet 1996 13: 464–468
Nahm MH, Macke K, Kwon OH, Madassery JV, Sherman LA, Scott MG . Immunologic and clinical status of blood donors with subnormal levels of IgG2 J Allergy Clin Immunol 1990 85: 769–777
Oxelius VA . Serum IgG and IgG subclass contents in different Gm phenotypes Scand J Immunol 1993 37: 149–153
Grubb R . Advances in human immunoglobulin allotypes Exp Clin Immunogenet 1995 12: 191–197
Pandey JP, French MA . GM phenotypes influence the concentrations of the four subclasses of immunoglobulin G in normal human serum Hum Immunol 1996 51: 99–102
Granoff DM, Holmes SJ . G2m(23) immunoglobulin allotype and immunity to Haemophilus influenzae type b J Infect Dis 1992 165 (Suppl 1): S66–S69
Nakao Y, Matsumoto H, Miyazaki T et al. IgG heavy-chain (Gm) allotypes and immune response to insulin in insulin-requiring diabetes mellitus N Engl J Med 1981 304: 407–409
Couper JJ, Harrison LC, Aldis JJ, Colman PG, Honeyman MC, Ferrante A . IgG subclass antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase and risk for progression to clinical insulin-dependent diabetes Hum Immunol 1998 59: 493–499
Petersen JS, Kulmala P, Clausen JT, Knip M, Dyrberg T the Childhood Diabetes in Finland Study Group. Progression to type 1 diabetes is associated with a change in the immunoglobulin isotype profile of autoantibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65) Clin Immunol 1999 90: 276–281
Bain SC, Todd JA, Barnett AH . The British Diabetic Association – Warren Repository Autoimmunity 1990 7: 83–85
Lernmark A, Ducat L, Eisenbarth G et al. Family cell lines available for research Am J Hum Genet 1990 47: 1028–1030
Terasaki PI, Bernoco D, Park MS, Ozturk G, Iwaki Y . Microdroplet testing for HLA-A,-B,-C, and -D antigens Am J Clin Pathol 1978 69: 103–120
Rosenshine S, Cascino I, Zeevi A, Duquesnoy RJ, Trucco M . DQ α and β RFLP reveals the composition of the DQ molecule recognized by T-cell clones Immunogenetics 1986 23: 187–196
Cox NJ, Mela AP, Zmijewski CM, Spielman RS . HLA-DR typing “at the DNA level”: RFLPs and subtypes detected with a DRβ cDNA probe Am J Hum Genet 1988 43: 954–963
Macaubas C, Hallmayer J, Kalil J et al. Extensive polymorphism of a (CA)n microsatellite located in the HLA-DQA1/DQB1 Class II region Hum Immunol 1995 42: 209–220
Weber JL, May PE . Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction Am J Hum Genet 1989 44: 388–396
S.A.G.E. Statistical Analysis for Genetic Epidemiology, release 3.1 1997 Computer program package obtained from Dr. RC Elston, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Metro-Health Campus, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, USA.
Thomson G . Mapping disease genes: family based association studies Am J Hum Genet 1995 57: 487–498
Elston RC . Algorithms and inferences: the challenges of multifactorial diseases Am J Hum Genet 1997 60: 255–262
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs E Colle, H Deane, M Gonthier, J Mahon, R McArthur, R Rodgers, E Ryan, D Stephure, L Stewart, R Trussell and D Wherrett for generously assisting in the collection of Canadian families, E Swiergala and M Engel for laboratory expertise, Tam Lu for computing contributions, R Hodorek for secretarial assistance, and all the families who participated in this research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was funded by grants to LLF from the Medical Research Council of Canada (No. MT-7910), the Juvenile Diabetes Foundation International (MRC/JDFI Network), and the Network of Centres of Excellence Programme of the Canadian federal government, and grants to FP and JN from the Medical Research Council of Denmark (No. 9802011) and the Juvenile Diabetes Foundation International (No. 998005). The SAGE program package was supported by U.S. Public Health Service Resource Grant 1-P41-RR03655. LLF was an Alberta Heritage Medical Scientist while at the University of Calgary, where some of this research was conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Field, L., Larsen, Z., Pociot, F. et al. Evidence for a locus (IDDM16) in the immunoglobulin heavy chain region on chromosome 14q32.3 producing susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. Genes Immun 3, 338–344 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363857
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363857
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Looking back and looking forward
Genes & Immunity (2003)
-
Genetics of type 1 diabetes mellitus
Genes & Immunity (2002)