Abstract
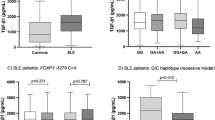
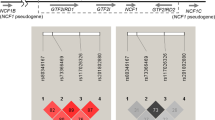
Angiotensin II is a strong candidate for the perpetuation of autoimmunity, nephritis and visceral damage in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Our goal was to determine whether angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) gene polymorphisms are associated with SLE and/or lupus nephritis (LN). We genotyped 644 SLE patients and 1130 family members for three ACE gene polymorphisms: Alu insertion/deletion (I/D), 23949 (CT)2/3 and 10698 (G)3/4. All patients met the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria for SLE, and all LN patients met ACR renal criteria and/or had biopsy evidence of LN. We used the transmission/disequilibrium test (TDT) to examine associations between each polymorphism and SLE, including Caucasian, non-Caucasian, and LN subgroups. We also examined transmission of haplotypes defined by these polymorphisms. The ACE I/D polymorphism was associated with SLE among non-Caucasians (61% transmission, P = 0.026) and the 23949 (CT)2/3 polymorphism was associated with LN among non-Caucasians (69% transmission, P = 0.014). Several haplotypes defined by these 2 markers demonstrated strikingly increased transmission among non-Caucasians (81% - 66% transmission, P = 0.0046 to 0.010). Due to the choice of study design and analytic method these results are unlikely to be due to population admixture. Our findings suggest that DNA sequence variation in the ACE gene influences the risk of developing SLE and LN.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J et al. Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 5-year period. A multicenter prospective study of 1,000 patients. European Working Party on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Medicine (Baltimore) 1999 78: 167–175
Winchester RJ, Lahita RG . Genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus In Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Wiley: New York 1987 pp 81–118
Arnett FC . The genetics of human lupus In: Wallace DJ, Hahn BH (eds) Dubois’ Lupus Erythematosus 5th edn. Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore 1997 pp 77–117
Freedman BI, Wilson CH, Spray BJ, Tuttle AB, Olorenshaw IM, Kammer GM . Familial clustering of end-stage renal disease in blacks with lupus nephritis Am J Kidney Dis 1997 29: 729–732
Schelling JR, Zarif L, Sehgal A, Iyengar S, Sedor JR . Geneticsusceptibility to end-stage renal disease Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 1999 8: 465–472
Klahr S, Morrissey JJ . The role of vasoactive compunds, growth factors and cytokines in the progression of renal disease Kidney Int 2000 57 (Suppl 75): S7–S14
Taal MW, Omer SA, Nadim MK, Mackenzie HS . Cellular and molecular mediators in common pathway mechanisms of chronic renal disease progression Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2000 9: 323–331
Nataraj C, Oliverio MI, Mannon RB et al. Angiotensin II regulates cellular immune responses through a calcineurin-dependent pathway J Clin Invest 1999 104: 1693–1701
Suzuki Y, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J . Angiotensin II: a double-edged sword in inflammation J Nephrol 2000 13 (Suppl 3): S101–S110
Paillard F, Chansel D, Brand E et al. Genotype-phenotype relationships for the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in a normal population Hypertension 1999 34: 423–429
Harjacek M, Anic B, Bosnic D et al. The role of genetic polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme in lupus nephritis Arthritis Rheum 1999 42: S302
Pullmann R Jr, Lukac J, Skerenova M et al. Association between systemic lupus erythematosus and insertion/deletion polymorphism of the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) gene Clin Exp Rheumatol 1999 17: 593–596
Prkacin I, Novak B, Sertic J, Mrzljak A . Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism in patients with systemic lupus Acta Med Croatica 2001 55: 73–76
Tassiulas IO, Aksentijevich I, Salmon JE et al. Angiotensin Iconverting enzyme gene polymorphisms in systemic lupus erythematosus: decreased prevalence of DD genotype in African American patients Clin Nephrol 1998 50: 8–13
Sato H, Akai Y, Iwano M et al. Association of an insertion polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene with the activity of systemic lupus erythematosus Lupus 1998 7: 530–534
Akai Y, Sato H, Iwano M et al. Association of an insertion polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene with the activity of lupus nephritis Clin Nephrol 1999 51: 141–146
Molad Y, Gal E, Magal N et al. Renal outcome and vascular morbidity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): lack of association with the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism Semin Arthritis Rheum 2000 30: 132–137
Kaufman KM, Kelly J, Gray-McGuire C et al. Linkage analysis of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) insertion/deletion polymorphism and systemic lupus erythematosus Mol Cell Endocrinol 2001 177: 81–85
Kruglyak L, Daly MJ, Reeve-Daly MP, Lander ES . Parametric and non-parametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach Am J Hum Genet 1996 58: 1347–1363
Rabinowitz D, Laird N . A unified approach to adjusting association tests for population admixture with arbitrary pedigree structure and arbitrary missing marker information Hum Hered 2000 50: 211–223
Guan T, Lui Z, Chen Z . Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism and the clinical pathological features and progression in lupus nephritis Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 1997 36: 461–464
Kennon B, Petrie JR, Small M, Connell JM . Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene and diabetes mellitus Diabet Med 1999 16: 448–458
McLaughlin KJ, Harden PN, Ueda S, Boulton-Jones JM, Connell JM, Jardine AG . The role of genetic polymorphisms of angiotensin-converting enzyme in the progression of renal diseases Hypertension 1996 28: 912–915
Syrjanen J, Huang XH, Mustonen J, Koivula T, Lehtimaki T, Pasternack A . Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and prognosis of IgA nephropathy Nephron 2000 86: 115–121
Staessen JA, Wang JG, Ginocchio G et al. The deletion/insertion polymorphism of the angiotensin converting enzyme gene and cardiovascular-renal risk J Hypertens 1997 15: 1579–1592
Kunz R, Bork JP, Fritsche L, Ringel J, Sharma AM . Association between the angiotensin-converting enzyme-insertion/deletion polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy: a methodologic appraisal and systematic review J Am Soc Nephrol 1998 9: 1653–1663
Zhu X, Bouzekri N, Southam L et al. Linkage and association analysis of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE)-gene polymorphisms with ACE concentration and blood pressure Am J Hum Genet 2001 68: 1139–1148
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus Arthritis Rheum 1982 25: 1271–1277
Hochberg MC . Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus [letter] Arthritis Rheum 1997 40: 1725
Churg J, Sobin LH . Renal Disease: Classification and atlas ofglomerular disease Igaku-Shoin: Tokyo 1982
Bali D, Gourley IS, Kostyu DD et al. Genetic analysis of multiplex rheumatoid arthritis families Genes Immun 1999 1: 28–36
Abecasis GR, Cookson WO . GOLD – graphical overview of linkage disequilibrium Bioinformatics 2000 16: 182–183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by NIH R01 AR44804, ES09911, T32 DK07219 and a grant from the Arthritis Foundation. This study was carried out in part in the General Clinical Research Center, Moffitt Hospital, University of California, San Francisco, with funds provided by the National Center for Research Resources, 5 M01 RR-00079, U.S. Public Health Service.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parsa, A., Peden, E., Lum, R. et al. Association of angiotensin-converting enzyme polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus and nephritis: analysis of 644 SLE families. Genes Immun 3 (Suppl 1), S42–S46 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363907
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363907
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) I/D variation with biochemical parameters and oxidative stress markers in systemic lupus erythematosus patients in west of Iran
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
Differential manifestations of prepubescent, pubescent and postpubescent pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A retrospective study of 96 Chinese children and adolescents
Pediatric Rheumatology (2012)
-
Association study of ACE polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus in Northern Chinese Han population
Molecular Biology Reports (2012)
-
Association of the genetic polymorphisms of the ACE gene and the eNOSgene with lupus nephropathy in northern Chinese population
BMC Medical Genetics (2010)
-
Specific combinations of HLA-DR2 and DR3 class II haplotypes contribute graded risk for disease susceptibility and autoantibodies in human SLE
European Journal of Human Genetics (2007)