Abstract
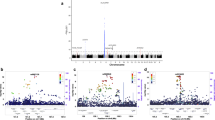
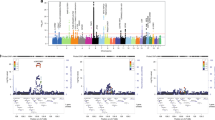
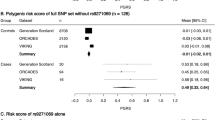
Multiple sclerosis (MS) shares some risk genes with other disorders hallmarked by an autoimmune pathogenesis, most notably IL2RA and CLEC16A. We analyzed 10 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in nine risk genes, which recently emerged from a series of non-MS genome-wide association studies (GWAS), in a Spanish cohort comprising 2895 MS patients and 2942 controls. We identified two SNPs associated with MS. The first SNP, rs6859219, located in ANKRD55 (Chr5), was recently discovered in a meta-analysis of GWAS on rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and emerged from this study with genome-wide significance (odds ratio (OR)=1.35; P=2.3 × 10−9). The second SNP, rs12785878, is located near DHCR7 (Chr11), a genetic determinant of vitamin D insufficiency, and showed a size effect in MS similar to that recently observed in Type 1 diabetes (T1D; OR=1.10; P=0.009). ANKRD55 is a gene of unknown function, and is flanked proximally by the IL6ST–IL31RA gene cluster. However, rs6859219 did not show correlation with a series of haplotype-tagging SNPs covering IL6ST–IL31RA, analyzed in a subset of our dataset (D′< 0.31; r2< 0.011). Our results expand the number of risk genes shared between MS, RA and T1D.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oksenberg JR, Baranzini SE . Multiple sclerosis genetics – is the glass half full, or half empty? Nat Rev Neurol 2010; 6: 429–437.
McElroy JP, Oksenberg JR . Multiple sclerosis genetics 2010. NeurolClin 2011; 29: 219–231.
Alcina A, Vandenbroeck K, Otaegui D, Saiz A, Gonzalez JR, Fernandez O et al. The autoimmune disease-associated KIF5A, CD226 and SH2B3 gene variants confer susceptibility for multiple sclerosis. Genes Immun 2010; 11: 439–445.
Todd JA, Walker NM, Cooper JD, Smyth DJ, Downes K, Plagnol V et al. Robust associations of four new chromosome regions from genome-wide analyses of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 857–864.
Barton A, Eyre S, Ke X, Hinks A, Bowes J, Flynn E et al. Identification of AF4/FMR2 family, member 3 (AFF3) as a novel rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility locus and confirmation of two further pan-autoimmune susceptibility genes. Hum Mol Genet 2009; 18: 2518–2522.
Stahl EA, Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, Xie G, Eyre S, Thomson BP et al. Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis loci. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 508–514.
Hinks A, Eyre S, Ke X, Barton A, Martin P, Flynn E et al. Association of the AFF3 gene and IL2/IL21 gene region with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Genes Immun 2010; 11: 194–198.
Barrett JC, Hansoul S, Nicolae DL, Cho JH, Duerr RH, Rioux JD et al. Genome-wide association defines more than 30 distinct susceptibility loci for Crohn's disease. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 955–962.
Kochi Y, Okada Y, Suzuki A, Ikari K, Terao C, Takahashi A et al. A regulatory variant in CCR6 is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 515–519.
Quan C, Ren YQ, Xiang LH, Sun LD, Xu AE, Gao XH et al. Genome-wide association study for vitiligo identifies susceptibility loci at 6q27 and the MHC. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 614–618.
Jin Y, Birlea SA, Fain PR, Mailloux CM, Riccardi SL, Gowan K et al. Common variants in FOXP1 are associated with generalized vitiligo. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 576–578.
Wang TJ, Zhang F, Richards JB, Kestenbaum B, van Meurs JB, Berry D et al. Common genetic determinants of vitamin D insufficiency: a genome-wide association study. Lancet 2010; 376: 180–188.
Ahn J, Yu K, Stolzenberg-Solomon R, Simon KC, McCullough ML, Gallicchio L et al. Genome-wide association study of circulating vitamin D levels. Hum Mol Genet 2010; 19: 2739–2745.
Cooper JD, Smyth DJ, Walker NM, Stevens H, Burren OS, Wallace C et al. Inherited variation in vitamin D genes is associated with predisposition to autoimmune disease type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2011; 60: 1624–1631.
Ramos-Lopez E, Brück P, Jansen T, Herwig J, Badenhoop K . CYP2R1 (vitamin D 25-hydroxylase) gene is associated with susceptibility to type 1 diabetes and vitamin D levels in Germans. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2007; 23: 631–636.
Handunnetthi L, Ramagopalan SV, Ebers GC . Multiple sclerosis, vitamin D, and HLA-DRB1*15. Neurology 2010; 74: 1905–1910.
Hafler DA, Compston A, Sawcer S, Lander ES, Daly MJ, De Jager PL et al. Risk alleles for multiple sclerosis identified by a genome wide study. N Eng J Med 2007; 357: 851–862.
International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium. Refining genetic associations in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 2008; 7: 567–569.
Franke A, Balschun T, Karlsen TH, Sventoraityte J, Nikolaus S, Mayr G et al. Sequence variants in IL10, ARPC2 and multiple other loci contribute to ulcerative colitis susceptibility. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1319–1323.
Wang K, Baldassano R, Zhang H, Qu HQ, Imielinski M, Kugathasan S et al. Comparative genetic analysis of inflammatory bowel disease and type 1 diabetes implicates multiple loci with opposite effects. Hum Mol Genet 2010; 19: 2059–2067.
Franke A, McGovern DP, Barrett JC, Wang K, Radford-Smith GL, Ahmad T et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis increase to 71 the number of confirmed Crohn's disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 1118–1125.
Gateva V, Sandling JK, Hom G, Taylor KE, Chung SA, Sun X et al. A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1228–1233.
Barrett JC, Clayton DG, Concannon P, Akolkar B, Cooper JD, Erlich HA et al. Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 703–707.
Raychaudhuri S, Thomson BP, Remmers EF, Eyre S, Hinks A, Guiducci C et al. Genetic variants at CD28, PRDM1 and CD2/CD58 are associated with rheumatoid arthritis risk. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1313–1318.
Anderson CA, Boucher G, Lees CW, Franke A, D'Amato M, Taylor KD et al. Meta-analysis identifies 29 additional ulcerative colitis risk loci, increasing the number of confirmed associations to 47. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 246–252.
International Consortium for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Genetics (SLEGEN) Harley JB, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, Jacob CO, Kimberly RP, Moser KL et al. Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 204–210.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007; 447: 661–678.
Vandenbroeck K, Alvarez J, Swaminathan B, Alloza I, Matesanz F, Urcelay E et al. A cytokine gene screen uncovers SOCS1 as genetic risk factor for multiple sclerosis. Genes Immun (e-pub ahead of print 30 June 2011; doi:10.1038/gene.2011.44).
Sedgwick SG, Smerdon SJ . The ankyrin repeat: a diversity of interactions on a common structural framework. Trends BiochemSci 1999; 24: 311–316.
Yang R, Gombart AF, Serrano M, Koeffler HP . Mutational effects on the p16INK4a tumor suppressor protein. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 2503–2506.
Joutel A, Tournier-Lasserve E . Notch signaling pathway and human disease. Semin Cell DevBiol 1998; 9: 619–625.
Jurynczyk M, Selmaj K . Notch: a new player in MS mechanisms. J Neuroimmunol 2010; 218: 3–11.
Smolders J, Damoiseaux J, Menheere P, Terbaert JW, Hupperts R . Association study on two vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and vitamin D metabolites in multiple sclerosis. Ann N Y AcadSci 2009; 1173: 515–520.
Strange RC, Ramachandran S, Zeegers MP, Emes RD, Abraham R, Raveendran V et al. The multiple sclerosis severity score: associations with MC1R single nucleotide polymorphisms and host response to ultraviolet radiation. MultScler 2010; 16: 1109–1116.
Simon KC, Munger KL, Xing Y, Ascherio A . Polymorphisms in vitamin D metabolism related genes and risk of multiple sclerosis. MultScler 2010; 16: 133–138.
Orton SM, Ramagopalan SV, Para AE, Lincoln MR, Chao MJ, Morahan J et al. Vitamin D metabolic pathway genes and risk of multiple sclerosis in Canadians. J NeurolSci 2011; 305: 116–120.
Ramagopalan SV, Maugeri NJ, Handunnetthi L, Lincoln MR, Orton SM, Dyment DA et al. Expression of the multiple sclerosis-associated MHC class I allele HLA-DRB1*1501 is regulated by vitamin D. PloSGenet 2009; 5: e10000369.
Maier LM, Lowe CE, Cooper J, Downes K, Anderson DE, Severson C et al. IL2RA genetic heterogeneity in multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes susceptibility and soluble interleukin-2 receptor production. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000322.
Cavanillas ML, Fernandez O, Comabella M, Alcina A, Fedetz M, Izquierdo G et al. Replication of top markers of a genome-wide association study in multiple sclerosis in Spain. Genes Immun 2011; 12: 110–115.
Poser CM, Paty DW, Scheinberg L, McDonald WI, Davis FA, Ebers GC et al. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol 1983; 13: 227–231.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Skol AD, Scott LJ, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M . Joint analysis is more efficient than replication-based analysis for two-stage genome-wide association studies. NatGenet 2006; 38: 209–213.
Johnson AD, Handsaker RE, Pulit SL, Nizzari MM, O'Donnell CJ, de Bakker PI . SNAP: a web-based tool for identification and annotation of proxy SNPs using HapMap. Bioinformatics 2008; 24: 2938–2939.
Acknowledgements
We thank patients with multiple sclerosis and control subjects for making this study feasible. Financial support for the study was provided by: the Gobierno Vasco (reference IT512-10; Convocatoria ‘Grupos de Investigación 2010–2015’), the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación-FondosFeder (SAF2009-11491), the Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria FIS (RETICS-REEM RD07/0060, PI081636, PI10/1985, PS09/02105), the Junta de Andalucía (P07-CVI-02551), Ikerbasque, the Basque Foundation for Science (Bilbao) and FundaciónIlundain. SNP genotyping services were provided by the Spanish ‘Centro Nacional de Genotipado CEGEN-USC, http://www.cegen.org’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alloza, I., Otaegui, D., de Lapuente, A. et al. ANKRD55 and DHCR7 are novel multiple sclerosis risk loci. Genes Immun 13, 253–257 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2011.81
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2011.81
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vitamin D and Genetic Susceptibility to Multiple Sclerosis
Biochemical Genetics (2021)
-
Systems genetics analysis of pharmacogenomics variation during antidepressant treatment
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2018)
-
The Microbiota, Immunoregulation, and Mental Health: Implications for Public Health
Current Environmental Health Reports (2016)
-
Does environmental confounding mask pleiotropic effects of a multiple sclerosis susceptibility variant on vitamin D in psychosis?
npj Schizophrenia (2015)