Abstract
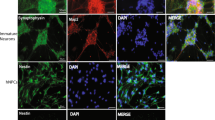
Alternative splicing of pre-mRNA increases proteomic diversity, a crucial mechanism in defining tissue identity. We demonstrate differentially spliced interleukin (IL)-7 in distinct anatomic areas in the adult, in developing human brains and in normal human neuronal progenitor (NHNP) cells. IL-7c (c, the canonical form spanning all six exons) or its variants IL-7δ5, δ4 or δ4/5 were cloned and expressed as recombinant proteins. IL-7 and splice variants were able to shift the differentiation of NHNP cells as compared with the diluent control (P<0.01) defined by anti-β (III)-tubulin and glial fibrillary acidic protein expression, with different degrees (IL-7c>δ4/5>IL-7δ5); IL-7δ4 exhibited a significantly weaker potency. Differentiation was confirmed by transcriptome analysis of IL-7c-stimulated neural NHNP cells, resulting in 58 differentially expressed genes; some of these are involved in neural differentiation, for example, the developmentally regulated transcription factor krüppel-like factor 12, musashi 2, a translational regulator of cell fate or the sonic hedgehog receptor patch 1. This suggests that IL-7 influences neural development at a molecular level by participating in human brain architecture through glia cell formation: a paradigm that alternative splicing in cytokines, for example, for IL-7, has a physiological role in human organ development and progenitor cell differentiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Labrousse VF, Costes L, Aubert A, Darnaudery M, Ferreira G, Amedee T et al. Impaired interleukin-1beta and c-Fos expression in the hippocampus is associated with a spatial memory deficit in P2X(7) receptor-deficient mice. PLoS One 2009; 4: e6006.
Benedict C, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Born J, Marshall L . Enhancing influence of intranasal interleukin-6 on slow-wave activity and memory consolidation during sleep. FASEB J 2009; 23: 3629–3636.
Zhou Z, Peng X, Insolera R, Fink DJ, Mata M . Interleukin-10 provides direct trophic support to neurons. J Neurochem 2009; 110: 1617–1627.
Greco SJ, Rameshwar P . Enhancing effect of IL-1alpha on neurogenesis from adult human mesenchymal stem cells: implication for inflammatory mediators in regenerative medicine. J Immunol 2007; 179: 3342–3350.
Hafler DA, Compston A, Sawcer S, Lander ES, Daly MJ, De Jager PL et al. Risk alleles for multiple sclerosis identified by a genomewide study. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 851–862.
Lundmark F, Duvefelt K, Iacobaeus E, Kockum I, Wallstrom E, Khademi M et al. Variation in interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) influences risk of multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1108–1113.
Gregory SG, Schmidt S, Seth P, Oksenberg JR, Hart J, Prokop A et al. Interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) shows allelic and functional association with multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1083–1091.
Goodwin RG, Lupton S, Schmierer A, Hjerrild KJ, Jerzy R, Clevenger W et al. Human interleukin 7: molecular cloning and growth factor activity on human and murine B-lineage cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989; 86: 302–306.
Korte A, Moricke A, Beyermann B, Kochling J, Taube T, Kebelmann-Betzing C et al. Extensive alternative splicing of interleukin-7 in malignant hematopoietic cells: implication of distinct isoforms in modulating IL-7 activity. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1999; 19: 495–503.
Maeurer MJ, Walter W, Martin D, Zitvogel L, Elder E, Storkus W et al. Interleukin-7 (IL-7) in colorectal cancer: IL-7 is produced by tissues from colorectal cancer and promotes preferential expansion of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol 1997; 45: 182–192.
Vudattu NK, Magalhaes I, Hoehn H, Pan D, Maeurer MJ . Expression analysis and functional activity of interleukin-7 splice variants. Genes Immun 2009; 10: 132–140.
Xing Y, Lee C . Relating alternative splicing to proteome complexity and genome evolution. Adv Exp Med Biol 2007; 623: 36–49.
Irimia M, Rukov JL, Roy SW, Vinther J, Garcia-Fernandez J . Quantitative regulation of alternative splicing in evolution and development. Bioessays 2009; 31: 40–50.
Xing Y . Genomic analysis of RNA alternative splicing in cancers. Front Biosci 2007; 12: 4034–4041.
Garcia-Blanco MA, Baraniak AP, Lasda EL . Alternative splicing in disease and therapy. Nat Biotechnol 2004; 22: 535–546.
Makeyev EV, Zhang J, Carrasco MA, Maniatis T . The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 2007; 27: 435–448.
Smirnova L, Grafe A, Seiler A, Schumacher S, Nitsch R, Wulczyn FG . Regulation of miRNA expression during neural cell specification. Eur J Neurosci 2005; 21: 1469–1477.
Mackall CL, Fry TJ, Bare C, Morgan P, Galbraith A, Gress RE . IL-7 increases both thymic-dependent and thymic-independent T-cell regeneration after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2001; 97: 1491–1497.
Schluns KS, Kieper WC, Jameson SC, Lefrancois L . Interleukin-7 mediates the homeostasis of naive and memory CD8 T cells in vivo. Nat Immunol 2000; 1: 426–432.
Michaelson MD, Mehler MF, Xu H, Gross RE, Kessler JA . Interleukin-7 is trophic for embryonic neurons and is expressed in developing brain. Dev Biol 1996; 179: 251–263.
Araujo DM, Cotman CW . Trophic effects of interleukin-4, -7 and -8 on hippocampal neuronal cultures: potential involvement of glial-derived factors. Brain Res 1993; 600: 49–55.
Moors M, Cline JE, Abel J, Fritsche E . ERK-dependent and -independent pathways trigger human neural progenitor cell migration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2007; 221: 57–67.
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod JJ, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J et al. Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature 1983; 304: 129–135.
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B . Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 2008; 5: 621–628.
Xu Q, Modrek B, Lee C . Genome-wide detection of tissue-specific alternative splicing in the human transcriptome. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30: 3754–3766.
Kan SH, Mancini G, Gallagher G . Identification and characterization of multiple splice forms of the human interleukin-23 receptor alpha chain in mitogen-activated leukocytes. Genes Immun 2008; 9: 631–639.
Atamas SP, Choi J, Yurovsky VV, White B . An alternative splice variant of human IL-4, IL-4 delta 2, inhibits IL-4-stimulated T cell proliferation. J Immunol 1996; 156: 435–441.
Tan X, Lefrancois L . Novel IL-15 isoforms generated by alternative splicing are expressed in the intestinal epithelium. Genes Immun 2006; 7: 407–416.
Orinska Z, Maurer M, Mirghomizadeh F, Bulanova E, Metz M, Nashkevich N et al. IL-15 constrains mast cell-dependent antibacterial defenses by suppressing chymase activities. Nat Med 2007; 13: 927–934.
Lundmark F, Duvefelt K, Hillert J . Genetic association analysis of the interleukin 7 gene (IL7) in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 2007; 192: 171–173.
Pernis A, Gupta S, Yopp J, Garfein E, Kashleva H, Schindler C et al. Gamma chain-associated cytokine receptors signal through distinct transducing factors. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 14517–14522.
Nunnari G, Xu Y, Acheampong EA, Fang J, Daniel R, Zhang C et al. Exogeneous IL-7 induces Fas-mediated human neuronal apoptosis: potential effects during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Neurovirol 2005; 11: 319–328.
De-Fraja C, Conti L, Magrassi L, Govoni S, Cattaneo E . Members of the JAK/STAT proteins are expressed and regulated during development in the mammalian forebrain. J Neurosci Res 1998; 54: 320–330.
He F, Ge W, Martinowich K, Becker-Catania S, Coskun V, Zhu W et al. A positive autoregulatory loop of Jak-STAT signaling controls the onset of astrogliogenesis. Nat Neurosci 2005; 8: 616–625.
Wishcamper CA, Brooks DM, Douglas Coffin J, Lurie DI . Focal cerebral ischemia upregulates SHP-1 in reactive astrocytes in juvenile mice. Brain Res 2003; 974: 88–98.
Wishcamper CA, Coffin JD, Lurie DI . Lack of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 results in decreased numbers of glia within the motheaten (me/me) mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 2001; 441: 118–133.
Okano H, Imai T, Okabe M . Musashi: a translational regulator of cell fate. J Cell Sci 2002; 115 (Pt 7): 1355–1359.
Samuels IS, Karlo JC, Faruzzi AN, Pickering K, Herrup K, Sweatt JD et al. Deletion of ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase identifies its key roles in cortical neurogenesis and cognitive function. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 6983–6995.
Loh YH, Zhang W, Chen X, George J, Ng HH . Jmjd1a and Jmjd2c histone H3 Lys 9 demethylases regulate self-renewal in embryonic stem cells. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 2545–2557.
Helbig I, Matigian NA, Vadlamudi L, Lawrence KM, Bayly MA, Bain SM et al. Gene expression analysis in absence epilepsy using a monozygotic twin design. Epilepsia 2008; 49: 1546–1554.
Wang Y, Ng EL, Tang BL . Rab23: what exactly does it traffic? Traffic 2006; 7: 746–750.
Yoshida E, Atkinson TG, Chakravarthy B . Neuroprotective gene expression profiles in ischemic cortical cultures preconditioned with IGF-1 or bFGF. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2004; 131: 33–50.
Lacombe ML, Milon L, Munier A, Mehus JG, Lambeth DO . The human Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinases. J Bioenerg Biomembr 2000; 32: 247–258.
Seifert M, Welter C, Mehraein Y, Seitz G . Expression of the nm23 homologues nm23-H4, nm23-H6, and nm23-H7 in human gastric and colon cancer. J Pathol 2005; 205: 623–632.
Schuller E, Gulesserian T, Seidl R, Cairns N, Lube G . Brain t-complex polypeptide 1 (TCP-1) related to its natural substrate beta1 tubulin is decreased in Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci 2001; 69: 263–270.
Marciano PG, Brettschneider J, Manduchi E, Davis JE, Eastman S, Raghupathi R et al. Neuron-specific mRNA complexity responses during hippocampal apoptosis after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 2866–2876.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported from Karolinska Institutet and by a grant from Cancerfonden, Sweden to MM. We thank Dr Markus Frericks for help with gene expression analysis and Ali Moshfegh, Karolinska University Hospital (Affymetrix core facility lab). We are indebted to Hanni Höhn and Deshun Pan, Department of Med. Microbiology, University of Mainz, Germany for preparation of recombinant IL-7 proteins and to Michel Morre, Cytheris, Paris, France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website (http://www.nature.com/gene)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moors, M., Vudattu, N., Abel, J. et al. Interleukin-7 (IL-7) and IL-7 splice variants affect differentiation of human neural progenitor cells. Genes Immun 11, 11–20 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.77
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.77
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cytokine profiling of extracellular vesicles isolated from plasma in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome: a pilot study
Journal of Translational Medicine (2020)
-
Flip the coin: IL-7 and IL-7R in health and disease
Nature Immunology (2019)
-
Neutrophils in traumatic brain injury (TBI): friend or foe?
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2018)
-
BDE-47 and 6-OH-BDE-47 modulate calcium homeostasis in primary fetal human neural progenitor cells via ryanodine receptor-independent mechanisms
Archives of Toxicology (2014)
-
Protein expression profiling of inflammatory mediators in human temporal lobe epilepsy reveals co-activation of multiple chemokines and cytokines
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2012)