Abstract
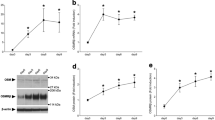
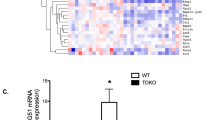
We previously identified a novel transcript, mouse (m)IL-20R1a, generated by alternative splicing of the mIL-20R1 gene and studied its possible in vitro functions. However, the function of mIL-20R1a in vivo is unknown. Overexpression of mIL-20R1a in transgenic FvB/N mice resulted in the pathological change of excess calcium deposited in the kidneys. The interplay between renal epithelial cells and calcium oxalate (CaOx) was important in the crystallization involved in the formation of renal stones (nephrolithiasis). Thus, we investigated and compared the responses of mouse renal proximal (TKPTS) and collecting (M-1) tubule cell lines to CaOx with or without mIL-20R1a. The renal epithelial cell lines exposed to CaOx in the presence of mIL-20R1a showed significantly increased lactate dehydrogenase release; loss of cell viability through apoptosis; increased CaOx internalization; higher tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, MCP-1 and RANTES expression; and higher reactive oxygen species production. Interleukin-6, TNF-α and MCP-1 were also upregulated in the kidneys of mIL-20R1a transgenic mice. These effects of mIL-20R1a on CaOx-exposed renal epithelial cells showed that mIL-20R1a functioned as an aggravating factor in promoting calcium deposition in kidney of mice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gallagher G, Dickensheets H, Eskdale J, Izotova LS, Mirochnitchenko OV, Peat JD et al. Cloning, expression and initial characterization of interleukin-19 (IL-19), a novel homologue of human interleukin-10 (IL-10). Genes Immun 2000; 1: 442–450.
Blumberg H, Conklin D, Xu WF, Grossmann A, Brender T, Carollo S et al. Interleukin 20: discovery, receptor identification, and role in epidermal function. Cell 2001; 104: 9–19.
Dumoutier L, Van Roost E, Colau D, Renauld JC . Human interleukin-10-related T cell-derived inducible factor: molecular cloning and functional characterization as an hepatocyte-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 10144–10149.
Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB . Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene 1995; 11: 2477–2486.
Knappe A, Hor S, Wittmann S, Fickenscher H . Induction of a novel cellular homolog of interleukin-10, AK155, by transformation of T lymphocytes with herpesvirus saimiri. J Virol 2000; 74: 3881–3887.
Parrish-Novak J, Xu W, Brender T, Yao L, Jones C, West J et al. Interleukins 19, 20, and 24 signal through two distinct receptor complexes. Differences in receptor-ligand interactions mediate unique biological functions. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 47517–47523.
Hsing CH, Hsieh MY, Chen WY, Cheung So E, Cheng BC, Chang MS . Induction of interleukin-19 and interleukin-22 after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg 2006; 81: 2196–2201.
Otkjaer K, Kragballe K, Funding AT, Clausen JT, Noerby PL, Steiniche T et al. The dynamics of gene expression of interleukin-19 and interleukin-20 and their receptors in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 2005; 153: 911–918.
Li HH, Lin YC, Chen PJ, Hsiao CH, Lee JY, Chen WC et al. Interleukin-19 upregulates keratinocyte growth factor and is associated with psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 2005; 153: 591–595.
Hsieh MY, Chen WY, Jiang MJ, Cheng BC, Huang TY, Chang MS . Interleukin-20 promotes angiogenesis in a direct and indirect manner. Genes Immun 2006; 7: 234–242.
Hsing CH, Ho CL, Chang LY, Lee YL, Chuang SS, Chang MS . Tissue microarray analysis of interleukin-20 expression. Cytokine 2006; 35: 44–52.
Hsu YH, Li HH, Hsieh MY, Liu MF, Huang KY, Chin LS et al. Function of interleukin-20 as a proinflammatory molecule in rheumatoid and experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 2722–2733.
Caligiuri G, Kaveri SV, Nicoletti A . IL-20 and atherosclerosis: another brick in the wall. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006; 26: 1929–1930.
Chen WY, Cheng BC, Jiang MJ, Hsieh MY, Chang MS . IL-20 is expressed in atherosclerosis plaques and promotes atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006; 26: 2090–2095.
Wei CC, Hsu YH, Li HH, Wang YC, Hsieh MY, Chen WY et al. IL-20: biological functions and clinical implications. J Biomed Sci 2006; 13: 601–612.
Wei CC, Chen WY, Chen PJ, Lee YJ, Wang DH, Chen WC et al. Detection of IL-20 and its receptors on psoriasis skin. Clin Immunol 2005; 117: 65–72.
Zhao L, Dong A, Gu J, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Zhang W et al. The antitumor activity of TRAIL and IL-24 with replicating oncolytic adenovirus in colorectal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 1011–1022.
Miyahara R, Banerjee S, Kawano K, Efferson C, Tsuda N, Miyahara Y et al. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 (mda-7)/interleukin (IL)-24 induces anticancer immunity in a syngeneic murine model. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 753–761.
Chen WY, Cheng YT, Lei HY, Chang CP, Wang CW, Chang MS . IL-24 inhibits the growth of hepatoma cells in vivo. Genes Immun 2005; 6: 493–499.
Saito Y, Miyahara R, Gopalan B, Litvak A, Inoue S, Shanker M et al. Selective induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells through adenoviral transfer of the melanoma differentiation-associated -7 (mda-7)/interleukin-24 (IL-24) gene. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 238–247.
Yacoub A, Mitchell C, Lebedeva IV, Sarkar D, Su ZZ, McKinstry R et al. mda-7 (IL-24) Inhibits growth and enhances radiosensitivity of glioma cells in vitro via JNK signaling. Cancer Biol Ther 2003; 2: 347–353.
Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Lebedeva IV, Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Valerie K et al. mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 10054–10059.
Wei CC, Chang MS . A novel transcript of mouse interleukin-20 receptor acts on glomerular mesangial cells as an aggravating factor in lupus nephritis. Genes Immun 2008; 9: 668–679.
Pak CY, Poindexter JR, Adams-Huet B, Pearle MS . Predictive value of kidney stone composition in the detection of metabolic abnormalities. Am J Med 2003; 115: 26–32.
Lieske JC, Deganello S . Nucleation, adhesion, and internalization of calcium-containing urinary crystals by renal cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999; 10 (Suppl 14): S422–S429.
Khan SR, Hackett RL . Retention of calcium oxalate crystals in renal tubules. Scanning Microsc 1991; 5: 707–711; discussion 711–702.
Khan SR, Byer KJ, Thamilselvan S, Hackett RL, McCormack WT, Benson NA et al. Crystal-cell interaction and apoptosis in oxalate-associated injury of renal epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999; 10 (Suppl 14): S457–S463.
Khan SR . Crystal-induced inflammation of the kidneys: results from human studies, animal models, and tissue-culture studies. Clin Exp Nephrol 2004; 8: 75–88.
Byer K, Khan SR . Citrate provides protection against oxalate and calcium oxalate crystal induced oxidative damage to renal epithelium. J Urol 2005; 173: 640–646.
Khan SR . Calcium oxalate crystal interaction with renal tubular epithelium, mechanism of crystal adhesion and its impact on stone development. Urol Res 1995; 23: 71–79.
Khan SR . Role of renal epithelial cells in the initiation of calcium oxalate stones. Nephron 2004; 98: e55–e60.
Koul HK . Role of p38 MAP kinase signal transduction in apoptosis and survival of renal epithelial cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 2003; 1010: 62–65.
Chaturvedi LS, Koul S, Sekhon A, Bhandari A, Menon M, Koul HK . Oxalate selectively activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signal transduction pathways in renal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 13321–13330.
Knoll T, Steidler A, Trojan L, Sagi S, Schaaf A, Yard B et al. The influence of oxalate on renal epithelial and interstitial cells. Urol Res 2004; 32: 304–309.
Scheid C, Koul H, Hill WA, Luber-Narod J, Kennington L, Honeyman T et al. Oxalate toxicity in LLC-PK1 cells: role of free radicals. Kidney Int 1996; 49: 413–419.
Kaneto H, Fukuzaki A, Ishidoya S, Takeda A, Ogata Y, Sasaki T et al. mRNA expression of chemokines in rat kidneys with ureteral obstruction]. Nippon Hinyokika Gakkai zasshi 2000; 91: 69–74.
Segerer S, Nelson PJ, Schlondorff D . Chemokines, chemokine receptors, and renal disease: from basic science to pathophysiologic and therapeutic studies. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000; 11: 152–176.
Umekawa T, Chegini N, Khan SR . Oxalate ions and calcium oxalate crystals stimulate MCP-1 expression by renal epithelial cells. Kidney Int 2002; 61: 105–112.
Dickman KG, Jacobs WR, Mandel LJ . Renal metabolism and acute renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 1987; 1: 359–366.
Burke TJ, Burnier M, Langberg H, Shanley P, Schrier RW . Renal response to shock. Ann Emerg Med 1986; 15: 1397–1400.
Andreoli SP . The pathophysiology of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 1999; 8: 459–464.
Sarica K, Erbagci A, Yagci F, Bakir K, Erturhan S, Ucak R . Limitation of apoptotic changes in renal tubular cell injury induced by hyperoxaluria. Urol Res 2004; 32: 271–277.
Noiri E, Nakao A, Uchida K, Tsukahara H, Ohno M, Fujita T et al. Oxidative and nitrosative stress in acute renal ischemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2001; 281: F948–F957.
Sharma K, Cook A, Smith M, Valancius C, Inscho EW . TGF-beta impairs renal autoregulation via generation of ROS. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2005; 288: F1069–F1077.
Kuin A, Kruse JJ, Stewart FA . Proteinuria and vascular changes after renal irradiation: the role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and vascular endothelial growth factor (Vegf). Radiat Res 2003; 159: 174–181.
Yamamoto T, Nagase M, Hishida A, Honda N . Interstitial inflammatory and chronic tubulointerstitial lesions in lupus nephritis: comparison with those in IgA nephropathy. Lupus 1993; 2: 261–268.
Kelly KJ . Acute renal failure: much more than a kidney disease. Semin Nephrol 2006; 26: 105–113.
Evevquoz D, Rosman J, Reichenstein T, Garzoni D, Rohrer W, Thiel G . C-reactive protein and early diagnosis of kidney transplant rejection. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 1993; 123: 1837–1842.
Ernest S, Bello-Reuss E . Expression and function of P-glycoprotein in a mouse kidney cell line. Am J Physiol 1995; 269 (2 Part 1): C323–C333.
Wei CC, Li HH, Hsu YH, Hsing CH, Sung JM, Chang MS . Interleukin-20 targets renal cells and is associated with chronic kidney disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 374: 448–453.
Pizzolato P . Histochemical recognition of calcium oxalate. J Histochem Cytochem 1964; 12: 333–336.
Liegler TJ, Hyun W, Yen TS, Stites DP . Detection and quantification of live, apoptotic, and necrotic human peripheral lymphocytes by single-laser flow cytometry. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 1995; 2: 369–376.
Campos AH, Schor N . Mechanisms involved in calcium oxalate endocytosis by Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Braz J Med Biol Res 2000; 33: 111–118.
Wei CC, Chen WY, Wang YC, Chen PJ, Lee JY, Wong TW et al. Detection of IL-20 and its receptors on psoriatic skin. Clin Immunol 2005; 117: 65–72.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the National Science Council (NSC 96-2628-B-006-055-MY3), Taiwan, Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, CC., Chang, MS. Mouse interleukin-20 receptor 1a targets renal epithelial cells and is associated with renal calcium deposition. Genes Immun 10, 237–247 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.93
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.93