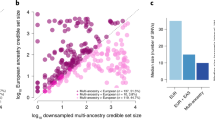
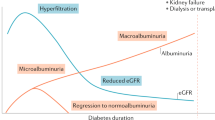
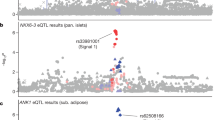
Abstract
The Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium (T1DGC) is an international, multicenter research program with two primary goals. The first goal is to identify genomic regions and candidate genes whose variants modify an individual's risk of type I diabetes (T1D) and help explain the clustering of the disease in families. The second goal is to make research data available to the research community and to establish resources that can be used by, and that are fully accessible to, the research community. To facilitate the access to these resources, the T1DGC has developed a Consortium Agreement (http://www.t1dgc.org) that specifies the rights and responsibilities of investigators who participate in Consortium activities. The T1DGC has assembled a resource of affected sib-pair families, parent–child trios, and case–control collections with banks of DNA, serum, plasma, and EBV-transformed cell lines. In addition, both candidate gene and genome-wide (linkage and association) studies have been performed and displayed in T1DBase (http://www.t1dbase.org) for all researchers to use in their own investigations. In this supplement, a subset of the T1DGC collection has been used to investigate earlier published candidate genes for T1D, to confirm the results from a genome-wide association scan for T1D, and to determine associations with candidate genes for other autoimmune diseases or with type II diabetes that may be involved with β-cell function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rich SS . Mapping genes in diabetes: a genetic epidemiological perspective. Diabetes 1990; 39: 1315–1319.
Pociot F, McDermott MF . Genetics of type 1 diabetes mellitus (review). Genes Immun 2002; 3: 235–249.
Concannon P, Erlich HA, Julier C, Morahan G, Nerup J, Pociot F et al. Type 1 diabetes. Evidence for susceptibility loci from four genome-wide linkage scans in 1,435 multiplex families. Diabetes 2005; 54: 2995–3001.
Concannon P, Chen W-M, Julier C, Morahan G, Akolkar B, Erlich HA et al. Genome-wide scan for linkage to type 1 diabetes in 2,496 multiplex families from the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Diabetes 2009; 58: 1018–1022.
Fine mapping of the MHC region for Type 1 Diabetes Genes: proceedings of the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium MHC Fine Mapping Workshop, Washington, DC, 27–28 August 2007. Diab Obes Metab 2009; 11 (Suppl 1): 1–109.
Brown WM, Pierce JJ, Hilner JE, Perdue LH, Lohman K, Lu L et al. and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Overview of the Rapid Response data. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S5–S15.
Julier C, Akolkar B, Concannon P, Morahan G, Nierras C, Pugliese A and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. The Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium ‘Rapid Response’ family-based candidate gene study: strategy, genes selection, and main outcome. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S121–S127.
Erlich HA, Lohman K, Mack SJ, Valdes AM, Julier C, Mirel D et al. for the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Association analysis of SNPs in the IL4R locus with type I diabetes. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S33–S41.
Podolsky R, Prasad Linga-Reddy MV, She J-X and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Analyses of multiple single nucleotide polymorphisms in the SUMO4/IDDM5 region in affected sib-pair families with type I diabetes. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S16–S20.
Qu H-Q, Bradfield JP, Grant SFA, Hakonarson H, Polychronakos C and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Remapping the type I diabetes association of the CTLA4 locus. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S27–S32.
Qu H-Q, Bradfield JP, Bélisle A, Grant SFA, Hakonarson H, Polychronakos C and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. The type I diabetes association of the IL2RA locus. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S42–S48.
Steck AK, Baschal EE, Jasinski JM, Boehm BO, Bottini N, Concannon P et al. and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. rs2476601 T allele (R620W) defines high-risk PTPN22 type I diabetes-associated haplotypes with preliminary evidence for an additional protective haplotype. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S21–S26.
Bergholdt R, Brorsson C, Boehm B, Morahan G, Pociot F and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. No association of the IRS1 and PAX4 genes with type I diabetes. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S49–S53.
Erlich HA, Valdes AM, Julier C, Mirel D, Noble JA and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Evidence for association of the TCF7 locus with type I diabetes. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S54–S59.
Kahles H, Morahan G, Todd JA, Badenhoop K and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Association analyses of the vitamin D receptor gene in 1654 families with type I diabetes. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S60–S63.
Morahan G, McKinnon E, Berry J, Browning B, Julier C, Pociot F et al. and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Evaluation of IL12B as a candidate type I diabetes susceptibility gene using data from the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S64–S68.
Qu H-Q, Polychronakos C and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Reassessment of the type I diabetes association of the OAS1 locus. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S69–S73.
Howson JMM, Walker NM, Smyth DJ, Todd JA and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Analysis of 19 genes for association with type I diabetes in the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium families. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S74–S84.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007; 447: 661–678.
Todd JA, Walker NM, Cooper JD, Smyth DJ, Downes K, Plagnol V et al. Robust associations of four new chromosome regions from genome-wide analyses of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 857–864.
Cooper JD, Walker NM, Smyth DJ, Downes K, Healy BC, Todd JA and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Follow-up of 1715 SNPs from the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium genome-wide association study in type I diabetes families. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S85–S94.
Criswell LA, Pfeiffer KA, Lum RF, Gonzales B, Novitzke J, Kern M et al. Analysis of families in the multiple autoimmune disease genetics consortium (MADGC) collection: the PTPN22 620W allele associates with multiple autoimmune phenotypes. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 561–571.
Zeggini E, Scott LJ, Saxena R, Voight BF, Marchini JL, Hu T et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data and large-scale replication identifies additional susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 638–645.
Cooper JD, Walker NM, Healy BC, Smyth DJ, Downes K, Todd JA and the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Analysis of 55 autoimmune disease and type II diabetes loci: further confirmation of chromosomes 4q27, 12q13.2 and 12q24.13 as type I diabetes loci, and support for a new locus, 12q13.3–q14.1. Genes Immun 2009; 10 (Suppl 1): S95–S120.
Barrett JC, Clayton DG, Concannon P, Akolkar B, Cooper JD, Erlich HA et al. Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 703–707.
Acknowledgements
This research uses resources provided by the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium, a collaborative clinical study sponsored by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), and Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation International (JDRF) and supported by U01 DK062418. Further support was provided by a grant from the NIDDK (DK46635) to PC and a joint JDRF and Wellcome Trust grant to the Diabetes and Inflammation Laboratory at Cambridge, which also received support from the National Institute for Health Research Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre. Genotyping was performed by the Center for Inherited Disease Research (CIDR). CIDR is fully funded through a federal contract from the National Institutes of Health to the Johns Hopkins University, contract no. N01-HG-65403.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rich, S., Akolkar, B., Concannon, P. et al. Overview of the Type I Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Genes Immun 10 (Suppl 1), S1–S4 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.84
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.84
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nine residues in HLA-DQ molecules determine with susceptibility and resistance to type 1 diabetes among young children in Sweden
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Type 1 diabetes genetic risk score is discriminative of diabetes in non-Europeans: evidence from a study in India
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Autoimmunity plays a role in the onset of diabetes after 40 years of age
Diabetologia (2020)
-
Early-life factors contributing to type 1 diabetes
Diabetologia (2019)
-
Type 1 diabetes mellitus
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2017)