Abstract
Objective
To compare macular choroidal thickness between cigarette smokers, those with a history of smoking, and nonsmokers in patients over 65 years of age with early-atrophic age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and normals.
Methods
Prospective, consecutive, observational case series. Enhanced depth imaging spectral domain optical coherence tomography 12-line radial scans were performed and choroidal thickness manually quantified at 84 points in the central 3 mm of the macula. Data of normals, soft drusen alone, and soft drusen with additional features of early AMD were compared. A multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) model, controlling for age, was constructed to evaluate the effect of smoking history and AMD features on choroidal thickness.
Results
A history of smoking was significantly associated with a thinner choroid across all patients via logistic regression (P=0.004; O.R.=12.4). Mean macular choroidal thickness was thinner for smokers (148±63 μm) than for nonsmokers (181±65 μm) among all diagnosis categories (P=0.003). Subgroup analysis of patients with AMD features revealed a similar decreased choroidal thickness in smokers (121±41 μm) compared with nonsmokers (146±46 μm, P=0.006). Bivariate analysis revealed an association between increased pack-years of smoking and a thin choroid across all patients (P<0.001) and among patients with features of early AMD (P<0.001). Both the presence of features of macular degeneration (P<0.001) and a history of smoking (P=0.024) were associated with decreased choroidal thickness in a MANOVA model.
Conclusion
Chronic cigarette smoke exposure may be associated with decreased choroidal thickness. There may be an anatomic sequelae to chronic tobacco smoke exposure that underlies previously reported AMD risk.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a degenerative macular condition with both atrophic and neovascular subtypes and is the most common cause of severe vision impairment in adults over 65 years of age in the United States and Europe. Multiple risk factors including age, dietary antioxidant intake,1 genotype,2 and smoking have been identified in several large cohorts of affected patients.3, 4 Cigarette smoking is a highly prevalent modifiable risk factor for many pulmonary, cardiovascular, and additional systemic diseases. Smoking may be related to the development of AMD,5, 6, 7 and has consistently been shown to lead to increased risk of all late forms of AMD.1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 Smoking has also been demonstrated to increase the risk of choroidal neovascularization owing to polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy,14 or ocular histoplasmosis.15 There is little direct evidence for the specific mechanism by which smoking leads to increased risk in AMD, however oxidative stress and vascular injury have been proposed.
Recently, particularly with the advent of enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography (EDI),16, 17 there have been many reports of choroidal thickness and morphology in retinal diseases. Known factors affecting choroidal thickness are age,18, 19 axial length,19, 20 specific medications,21 and chorioretinal disorders such as central serous chorioretinopathy.22 Patients with high myopia,18, 23 diabetic retinopathy,24 and age-related choroidal atrophy25 appear to have a particularly thin choroid.
Consistent with some previous reports,26, 27 we have recently observed decreased choroidal thickness among patients with typical soft drusen, subretinal drusenoid deposits, and early-atrophic age-related macular degeneration compared with normals.28 Cigarette smoking has been linked to many vascular alterations, including experimental evidence of altered retinal29 and choroidal30, 31 blood flow, and endothelial reactivity. Smokers may also be at higher risk for the development and severity of choroidal neovascularization.7, 32 We hypothesized that smokers may have distinct choroidal anatomic features that may include an overall thin choroid. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate central macular choroidal thickness among patients with drusen, early-atrophic AMD, and normals.
Materials and methods
This prospective, consecutive, observational case series conformed to the tenets set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki and was performed in accordance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. The study was approved by the institutional review board of the University of Tennessee, Memphis Health Sciences Center. All patients were seen and examined at the Charles Retina Institute, Memphis, TN.
Patients
Consecutive patients were recruited at a regularly scheduled office visit for EDI SD-OCT examination after meeting the following inclusion criteria:
-
1
Age greater than 65 years.
-
2
No previous eye disease other than refractive error, cataract extraction with intact posterior capsule, drusen, or early-atrophic macular degeneration.
-
3
No history of diabetes or uncontrolled hypertension; no additional uncontrolled systemic disease; blood pressure measurement on day of EDI <140 systolic and <90 diastolic.
-
4
Spherical equivalent (autorefraction of either phakic patients or measured before cataract extraction) ±2.00 diopters.
-
5
No anti-VEGF therapy in fellow eye for at least 3 months before EDI.
-
6
Intraocular pressure between 11 and 19 mm Hg as measured by Goldmann applanation tonometry on the day of EDI examination.
-
7
Willing to undergo informed consent for study participation.
The spectrum of early AMD was divided to include those with drusen alone as well as those with drusen plus additional features of early AMD such as subretinal drusenoid deposits and RPE hyperpigmentation. Early-atrophic AMD was defined as the presence of large-macular soft drusen with RPE hyperpigmentation as seen by ophthalmoscopy and fundus photography. Subretinal drusenoid deposits and focal areas of outer retinal atrophy on SD-OCT were considered part of the atrophic AMD group. Patients with Snellen best-corrected visual acuity less than 20/200 in the study eye or any geographic atrophy were excluded. Patients with a history of choroidal neovascularization in the fellow eye were not specifically excluded. The drusen group had the presence of macular soft drusen greater than 125 μm without evidence of hyperpigmentation or RPE atrophy on fundus photography, and no evidence of outer retinal or RPE atrophy on SD-OCT. Patients in the drusen and AMD group must have had an available fluorescein angiogram within the past 6 months, and patients with any evidence of neovascularization or geographic atrophy in the study eye were excluded. Thus, rather than using a traditional classification system,4, 33 we modified this using combined fundus photographic, angiographic, and SD-OCT criteria. Normals were recruited from patients presenting for fundus examination with a unilateral disease process or no eye disease.
Imaging
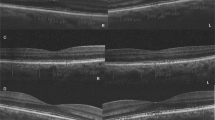
The EDI protocol performed in the present study has been previously described.28 Briefly, all images were obtained by a single experienced ophthalmic photographer, and quantifications were performed independently by two observers (authors EJS and JCR). Spectralis (Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany) 12-line radial raster scan pattern was performed using the enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography (EDI) function with 20 scans averaged per raster. A single observer (author EJS.) initially screened scans for image quality and the absence of exclusion criteria. Autorefraction was performed on the day of each SD-OCT and entered into the Spectralis patient data entry window before each scan. Computer randomization with equal allocation ratio was used to determine which eye would be included for patients with bilateral AMD or drusen. Gray scale, brightness scan (b-scan) images were viewed on the device console. Only scans with a signal strength of at least 8/10 were included. Four scans were initially excluded owing to the low-signal strength secondary to media opacity or ocular surface disorder. The device caliper tool (Heidelberg Eye Explorer, Heidelberg Engineering) was used to perform all measurements. Initially, a single subfoveal choroidal thickness was obtained by extending the caliper tool from the inner aspect of the Bruch’s membrane (outer border of RPE) to the inner scleral border. The caliper was then used to sequentially measure 500 μm distances in both radial directions and a new measurement was obtained at each location. This was performed for three radial positions in each direction for each raster, for a total of seven choroidal measurements in each raster, including the central 3 mm of the macula (84 measurements per eye). All values were then combined and averaged for the recorded overall macular CT. Representative EDI images for diagnosis categories in smokers and nonsmokers are presented in Figure 1.
Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of smokers and nonsmokers with early age-related macular degeneration and normal. (a) Normal control 72 year-old demonstrating normal retina and choroidal anatomy with mean central macular choroidal thickness (CMCT), 204 μm; (b) Normal 75 year-old with 18 pack-year history of smoking and mean CMCT, 91 μm; (c) 72 year-old nonsmoker with drusen and CMCT, 176 μm; (d) 76 year-old with 17 pack-year history of smoking and CMCT, 86 μm; (e) 78 year-old with drusen, pigmentary alteration, and subretinal drusenoid deposits and CMCT, 143 μm; (f) 77 year-old with drusen, pigmentary alteration, and subretinal drusenoid deposits as well as a 34 pack-year history of smoking with CMCT, 43 μm.
Data analysis
The data used for the present study was a subset of an ongoing prospective study, the Choroidal Thickness in Age-related Eye Disease Study, with additional details reported elsewhere.28 For the present study, smoking history was categorized as either no history of regular cigarette smoking, current smoker, or former smoker if the patient reported at least 1 year of habitual smoking but at least 1 year free of cigarette use. Additional categorical variables including history of hypertension and history of hypercholesterolemia were also recorded. Pack-years of cigarette smoking were similarly recorded. All data was analyzed using JMP Pro 10 (SAS, Cary, NC, USA).
Initially, continuous variables were compared among diagnostic groups using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Categorical variables were compared using χ2-test or Fisher’s exact test. Univariate logistic regression was used to compare categorical and continuous variables. Bivariate fit-line analysis was used to perform pairwise comparisons among continuous variables. Subgroup analysis was performed separately for normals and for those with features of AMD (drusen and atrophic AMD groups combined). We then constructed a multivariate ANOVA (MANOVA), adjusting for previously identified significant interactions, to evaluate the independent effect of smoking history. This yielded a model including AMD features and cigarette smoking status as categorical variables adjusted for the effect of age on choroidal thickness.
Results
Hundred and forty seven patients were included consisting of 38 with drusen alone, 60 patients with early-atrophic AMD, and 49 normals. A summary of photographic characteristics and smoking history by diagnosis category is presented in Table 1. Of the 147 patients included in the study, 145 patients were Caucasian and two patients were of African American origin. Mean age±standard deviation was 78±7.2 years and was not significantly different among diagnosis categories (P=0.294). Mean spherical equivalent was 0.051±0.02 diopters. There were no significant differences in age among diagnosis categories (P=0.37) or mean refractive error (P=0.44). The patient cohort consisted of 10 current smokers, 57 former smokers, and 80 patients with no smoking history. Of the 147 patients included in the study, 76 of them had controlled hypertension on current medications. Mean pack-year history among smokers was 16.1±14.2 years.
Smoking status was not significantly correlated with diagnosis category (P=0.096). A history of controlled hypertension (P=0.153) or hypercholesterolemia (P=0.213) was not significantly related to choroidal thickness. Graphical analysis of mean choroidal thickness by smoking category is presented in Figure 2. Across all patients, mean choroidal thickness for smoking history (148±63 μm) was significantly thinner than for normals (181±65 μm, P=0.003). Univariate logistic regression revealed a significant association between a history of smoking and a thinner choroid (P=0.004, O.R.=12.4). Subgroup analysis of normals alone revealed a trend for thinner choroidal thickness in smokers (215±54 μm) than nonsmokers (237±50 μm), however the difference did not reach statistical significance (P=0.14). Subgroup analysis among patients with features of AMD (drusen or atrophic AMD) demonstrated a significantly thinner choroid for those with a history of smoking (121±41 μm) than those with no smoking history (146±46 μm; P=0.006). Bivariate fit-line analysis revealed a strong inverse correlation between pack-years of cigarette smoking and mean macular choroidal thickness (P<0.001). Increase in pack-years of smoking was highly correlated with the history of choroidal neovascularization in the fellow eye.(P=0.009) Graphical analysis of pack-year history of smoking and mean macular choroidal thickness is presented in Figure 3.
Comparison of mean macular choroidal thickness (CT) among smoking categories. (a) One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) between lifetime nonsmokers, current smokers, and former smokers; green diamonds vertically centered on mean spanning 1 SD; horizontal width proportional to sample size; mean CT as follows: nonsmokers, 181±65, n=80; current smokers, 147±61, n=10; former smokers, 149±64 μm, n=57; P=0.011; (b) Two-sample t-test subgroup analysis of patients with drusen or early AMD; mean CT is as follows: nonsmokers, 146±46 μm, n=49; history of smoking, 121±41 μm, n=49; P=0.006.
Bivariate analysis of mean macular choroidal thickness by pack-year history of smoking. (a) Fit-line analysis across all patients; red line indicates overall mean, 166 μm; green line indicates fit-line analysis; mean macular choroidal thickness (μm), 186–1.76 (pack-years); (b) Subgroup analysis of patients with drusen or early-atrophic AMD; overall mean, 133 μm; mean macular choroidal thickness (μm), 147–1.02 (pack-years).
Results for the MANOVA whole model test were highly significant (P<0.001). Adjusting for age, drusen (P<0.001), early AMD (P<0.001), and history of smoking (P=0.024) were independently associated with decreased mean choroidal thickness. A subgroup model including only patients with AMD, adjusted for age, revealed a history of smoking (P=0.026) and atrophic macular degeneration (P<0.001) diagnosis as factors associated with a thinner choroid.
Discussion
The results of the present study indicate that a history of cigarette smoking is associated with decreased central macular choroidal thickness among Caucasian adults over 65 years of age. Results from the univariate analysis of the Beijing Eye Study demonstrated a similar association with subfoveal choroidal thickness among adults over 50,34 however the statistical significance was not present in the multivariate model adjusted for age and additional covariates. The present study differed in both patient demographics and method of macular choroidal thickness measurement. While Wei et al34 reported results from a single subfoveal choroidal thickness, we obtained the average of 84 points per eye in the central 3 mm of the macula. In addition, their series examined patients over 50, a generally younger cohort than our series. These factors likely account for the observed differences in results. In the subgroup analysis, we demonstrated a significantly thinner choroid in smokers with features of early AMD, but the result was not present for normals alone. This is likely accounted for the smaller sample size and resultant reduced power for the normals alone. While features of early AMD appear to be a better predictor of reduced choroidal thickness, a history of chronic cigarette smoke exposure appears to remain a significant influential factor in the present series. AMD diagnosis was not specifically related to a history of smoking in the present series; the study was underpowered to detect this association, and the proportion of smokers in each diagnosis category was similar. We did not find a history of hypertension associated with differences in mean choroidal thickness, but included only treated patients with no history of uncontrolled hypertension. The 52% of patients with chronic, controlled hypertension is consistent with reported rates for the general population.35
There are many potential mechanisms by which chronic cigarette smoke may influence choroidal vasculature. Cigarette smoke contains a myriad of potential toxic and systemic vasoconstrictive substances36, 37, 38 including nicotine.39, 40 Experimental evidence indicates that smoking induces multiple acute influences on cerebral vasculature, with vasoconstriction predominating during chronic exposure.41 Smoking appears to impair endothelial cell function in many vascular regions, and evidence supports long-term vasoconstriction and altered endothelial response37, 42, 43 to various vasoactive mediators in tobacco smoke.40, 44, 45 Human studies indicate abnormal choroidal vascular reactivity to carbogen (high oxygen) inhalation in chronic smokers.30 Substances in cigarette smoke have additionally been demonstrated to induce direct oxidative damage to endothelium.46, 47 We hypothesize that chronic cigarette smoke exposure contributes to specific structural changes to the choroid which might manifest as an overall thinner than average appearance on EDI. These manifestations may result from chronic vasoconstriction, coupled with direct oxidative damage to endothelium, leading to vascular dropout. Pack-years of smoking appear to be associated with a thinner choroid in the present study, which indicates a probable dose-dependent effect. Previous reports have indicated an increase risk and severity of choroidal neovascularization in smokers,5, 7, 32 which may be related to nicotine-induced increase in retinal pigment epithelial vascular endothelial growth factor.48, 49 Similarly we observed a strong correlation between increased pack-years and a history of choroidal neovascularization in fellow eyes of those with chronic tobacco smoke exposure, indicating a dose-dependent increased risk of late AMD in smokers. Smoking has also been associated with increased risk of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV), a process typically demonstrating a thicker than normal choroid.32 However, it may be difficult to accurately assess choroidal thickness in the context of a neovascular process, since type 1 neovascularization adds to choroidal thickness. Additional smoking related factors may be important in PCV, such as complement factor, and VEGF alterations.
The significance of choroidal thickness in AMD remains unknown. With recent advances in SD-OCT, this parameter has become a clinically measurable anatomic variable in patients with various retinal conditions. We have recently observed a thinner choroid in patients with signs of early AMD, which is consistent with some previous reports.26, 27 Both smoking history and the presence of early AMD are associated with the development of late AMD, including both geographic atrophy and choroidal neovascularization.1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 32 Therefore, choroidal thickness may be an additional useful clinical variable in assessing risk of AMD progression or the development of late AMD, particularly considering its apparent anatomic association with these two well-known risk factors. While a thin choroid is not necessarily related to blood flow or overall function,50 there is evidence of regional choroidal blood flow alterations in AMD,51, 52, 53, 54, 55 which may involve an overall decrease in blood flow and regional volume.52, 53, 56
The present study is limited by small to moderate sample size, single-center study location, and predominantly Caucasian subjects. Although we made every effort to control for known variables that affect choroidal thickness, there remain many additional potentially unrecognized confounding factors. We used a classification system that included ophthalmoscopic, angiographic, and SD-OCT features to identify features of early AMD, that may differ from additional centers. We conclude that there is an apparent relationship between chronic cigarette smoke exposure and a relatively thin choroid in Caucasian patients with features of early AMD who are over 65 years of age, which is likely present in normals as well. This may be an anatomic feature underlying the increased risk of progression to late AMD in patients with a history of chronic cigarette smoking.

References
SanGiovanni JP, Chew EY, Clemons TE, Ferris FL 3rd, Gensler G, Lindblad AS et al. The relationship of dietary carotenoid and vitamin A, E, and C intake with age-related macular degeneration in a case-control study: AREDS Report No. 22. Arch Ophthalmol 2007; 125 (9): 1225–1232.
Seddon JM, Reynolds R, Rosner B . Associations of smoking, body mass index, dietary lutein, and the LIPC gene variant rs10468017 with advanced age-related macular degeneration. Mol Vis 2010; 16: 2412–2424.
AREDS. Risk factors associated with age-related macular degeneration. A case-control study in the age-related eye disease study: age-related eye disease study report number 3. Ophthalmology 2000; 107 (12): 2224–2232.
AREDS. A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of high-dose supplementation with vitamins C and E, beta carotene, and zinc for age-related macular degeneration and vision loss: AREDS report no. 8. Arch Ophthalmol 2001; 119 (10): 1417–1436.
Khan JC, Thurlby DA, Shahid H, Clayton DG, Yates JR, Bradley M et al. Smoking and age related macular degeneration: the number of pack years of cigarette smoking is a major determinant of risk for both geographic atrophy and choroidal neovascularisation. Br J Ophthalmol 2006; 90 (1): 75–80.
Chakravarthy U, Wong TY, Fletcher A, Piault E, Evans C, Zlateva G et al. Clinical risk factors for age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Ophthalmol 2010; 10: 31.
Chakravarthy U, Augood C, Bentham GC, de Jong PT, Rahu M, Seland J et al. Cigarette smoking and age-related macular degeneration in the EUREYE Study. Ophthalmology 2007; 114 (6): 1157–1163.
Mitchell P, Wang JJ, Smith W, Leeder SR . Smoking and the 5-year incidence of age-related maculopathy: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Arch Ophthalmol 2002; 120 (10): 1357–1363.
Dandekar SS, Jenkins SA, Peto T, Bird AC, Webster AR . Does smoking influence the type of age related macular degeneration causing visual impairment? Br J Ophthalmol 2006; 90 (6): 724–727.
DeAngelis MM, Ji F, Kim IK, Adams S, Capone A Jr, Ott J et al. Cigarette smoking, CFH, APOE, ELOVL4, and risk of neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol 2007; 125 (1): 49–54.
Delcourt C, Delyfer MN, Rougier MB, Amouyel P, Colin J, Le Goff M et al. Associations of complement factor H and smoking with early age-related macular degeneration: the ALIENOR study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011; 52 (8): 5955–5962.
Seddon JM, Reynolds R, Shah HR, Rosner B . Smoking, dietary betaine, methionine, and vitamin D in monozygotic twins with discordant macular degeneration: epigenetic implications. Ophthalmology 2011; 118 (7): 1386–1394.
Klein R, Cruickshanks KJ, Nash SD, Krantz EM, Nieto FJ, Huang GH et al. The prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and associated risk factors. Arch Ophthalmol 2010; 128 (6): 750–758.
Kabasawa S, Mori K, Horie-Inoue K, Gehlbach PL, Inoue S, Awata T et al. Associations of cigarette smoking but not serum fatty acids with age-related macular degeneration in a Japanese population. Ophthalmology 2011; 118 (6): 1082–1088.
Chheda LV, Ferketich AK, Carroll CP, Moyer PD, Kurz DE, Kurz PA . Smoking as a risk factor for choroidal neovascularization secondary to presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome. Ophthalmology 2012; 119 (2): 333–338.
Margolis R, Spaide RF . A pilot study of enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in normal eyes. Am J Ophthalmol 2009; 147 (5): 811–815.
Spaide RF . Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of retinal pigment epithelial detachment in age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol 2009; 147 (4): 644–652.
Manjunath V, Taha M, Fujimoto JG, Duker JS . Choroidal thickness in normal eyes measured using Cirrus HD optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 2010; 150 (3): 325–329.
Goldenberg D, Moisseiev E, Goldstein M, Loewenstein A, Barak A . Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography: choroidal thickness and correlations with age, refractive error, and axial length. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging 2012; 43 (4): 296–301.
Li XQ, Larsen M, Munch IC . Subfoveal choroidal thickness in relation to sex and axial length in 93 Danish university students. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011; 52 (11): 8438–8441.
Lee WJ, Seong M . Sildenafil citrate and choroidal thickness. Retina 2011; 31 (8): 1742 author reply 1742-1743.
Imamura Y, Fujiwara T, Margolis R, Spaide RF . Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 2009; 29 (10): 1469–1473.
Nishida Y, Fujiwara T, Imamura Y, Lima LH, Kurosaka D, Spaide RF . Choroidal thickness and visual acuity in highly myopic eyes. Retina 2012; 32 (7): 1229–1236.
Regatieri CV, Branchini L, Carmody J, Fujimoto JG, Duker JS . Choroidal thickness in patients with diabetic retinopathy analyzed by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Retina 2012; 32 (3): 563–568.
Spaide RF . Age-related choroidal atrophy. Am J Ophthalmol 2009; 147 (5): 801–810.
Kim SW, Oh J, Kwon SS, Yoo J, Huh K . Comparison of choroidal thickness among patients with healthy eyes, early age-related maculopathy, neovascular age-related macular degeneration, central serous chorioretinopathy, and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina 2011; 31 (9): 1904–1911.
Querques G, Querques L, Forte R, Massamba N, Coscas F, Souied EH . Choroidal changes associated with reticular pseudodrusen. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2012; 53 (3): 1258–1263.
Sigler EJ, Randolph JC . Comparison of macular choroidal thickness among patients older than age 65 with early atrophic age-related macular degeneration and normals. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2013; 54 (9): 6307–6313.
Langhans M, Michelson G, Groh MJ . Effect of breathing 100% oxygen on retinal and optic nerve head capillary blood flow in smokers and non-smokers. Br J Ophthalmol 1997; 81 (5): 365–369.
Wimpissinger B, Resch H, Berisha F, Weigert G, Schmetterer L, Polak K . Response of choroidal blood flow to carbogen breathing in smokers and non-smokers. Br J Ophthalmol 2004; 88 (6): 776–781.
Kergoat H, Faucher C . Effects of oxygen and carbogen breathing on choroidal hemodynamics in humans. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999; 40 (12): 2906–2911.
Cackett P, Yeo I, Cheung CM, Vithana EN, Wong D, Tay WT et al. Relationship of smoking and cardiovascular risk factors with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and age-related macular degeneration in Chinese persons. Ophthalmology 2011; 118 (5): 846–852.
Bressler NM, Bressler SB, Fine SL . Age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol 1988; 32 (6): 375–413.
Wei WB, Xu L, Jonas JB, Shao L, Du KF, Wang S et al. Subfoveal choroidal thickness: the beijing eye study. Ophthalmology 2013; 120 (1): 175–180.
Yoon SS, Ostchega Y, Louis T . Recent trends in the prevalence of high blood pressure and its treatment and control, 1999–2008. NCHS data brief 2010; (48): 1–8.
Krupski WC . The peripheral vascular consequences of smoking. Ann Vasc Surg 1991; 5 (3): 291–304.
Fushimi H, Inoue T, Yamada Y, Matsuyama Y, Kameyama M . Profound vasoconstrictive effect of cigarette smoking in diabetics with autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1992; 16 (3): 191–195.
Quillen JE, Rossen JD, Oskarsson HJ, Minor RL Jr, Lopez AG, Winniford MD . Acute effect of cigarette smoking on the coronary circulation: constriction of epicardial and resistance vessels. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993; 22 (3): 642–647.
Lassila R, Seyberth HW, Haapanen A, Schweer H, Koskenvuo M, Laustiola KE . Vasoactive and atherogenic effects of cigarette smoking: a study of monozygotic twins discordant for smoking. BMJ 1988; 297 (6654): 955–957.
Chalon S, Moreno H Jr, Benowitz NL, Hoffman BB, Blaschke TF . Nicotine impairs endothelium-dependent dilatation in human veins in vivo. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2000; 67 (4): 391–397.
Iida M, Iida H, Dohi S, Takenaka M, Fujiwara H . Mechanisms underlying cerebrovascular effects of cigarette smoking in rats in vivo. Stroke 1998; 29 (8): 1656–1665.
Cao L, Xu CB, Zhang Y, Cao YX, Edvinsson L . Secondhand smoke exposure induces Raf/ERK/MAPK-mediated upregulation of cerebrovascular endothelin ETA receptors. BMC Neurosci 2011; 12: 109.
Cao L, Zhang Y, Cao YX, Edvinsson L, Xu CB . Cigarette smoke upregulates rat coronary artery endothelin receptors in vivo. PloS one 2012; 7 (3): e33008.
Kiowski W, Linder L, Stoschitzky K, Pfisterer M, Burckhardt D, Burkart F et al. Diminished vascular response to inhibition of endothelium-derived nitric oxide and enhanced vasoconstriction to exogenously administered endothelin-1 in clinically healthy smokers. Circulation 1994; 90 (1): 27–34.
Moliterno DJ, Willard JE, Lange RA, Negus BH, Boehrer JD, Glamann DB et al. Coronary-artery vasoconstriction induced by cocaine, cigarette smoking, or both. N Engl J Med 1994; 330 (7): 454–459.
Schweitzer KS, Hatoum H, Brown MB, Gupta M, Justice MJ, Beteck B et al. Mechanisms of lung endothelial barrier disruption induced by cigarette smoke: role of oxidative stress and ceramides. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2011; 301 (6): L836–L846.
Edirisinghe I, Rahman I . Cigarette smoke-mediated oxidative stress, shear stress, and endothelial dysfunction: role of VEGFR2. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2010; 1203: 66–72.
Pons M, Marin-Castano ME . Nicotine increases the VEGF/PEDF ratio in retinal pigment epithelium: a possible mechanism for CNV in passive smokers with AMD. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011; 52 (6): 3842–3853.
Nakanishi H, Yamashiro K, Yamada R et al. Joint effect of cigarette smoking and CFH and LOC387715/HTRA1 polymorphisms on polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010; 51 (12): 6183–6187.
Sogawa K, Nagaoka T, Takahashi A, Tanano I, Tani T, Ishibazawa A et al. Relationship between choroidal thickness and choroidal circulation in healthy young subjects. Am J Ophthalmol 2012; 153 (6): 1129–1132 e1121.
Berenberg TL, Metelitsina TI, Madow B, Dai Y, Ying GS, Dupont JC et al. The association between drusen extent and foveolar choroidal blood flow in age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2012; 32 (1): 25–31.
Grunwald JE, Hariprasad SM, DuPont J, Maguire MG, Fine SL, Brucker AJ et al. Foveolar choroidal blood flow in age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1998; 39 (2): 385–390.
Grunwald JE, Metelitsina TI, Dupont JC, Ying GS, Maguire MG . Reduced foveolar choroidal blood flow in eyes with increasing AMD severity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005; 46 (3): 1033–1038.
Ross RD, Barofsky JM, Cohen G, Baber WB, Palao SW, Gitter KA . Presumed macular choroidal watershed vascular filling, choroidal neovascularization, and systemic vascular disease in patients with age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol 1998; 125 (1): 71–80.
Mori F, Konno S, Hikichi T, Yamaguchi Y, Ishiko S, Yoshida A . Pulsatile ocular blood flow study: decreases in exudative age related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol 2001; 85 (5): 531–533.
Boltz A, Luksch A, Wimpissinger B, Maar N, Weigert G, Frantal S et al. Choroidal blood flow and progression of age-related macular degeneration in the fellow eye in patients with unilateral choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010; 51 (8): 4220–4225.
Acknowledgements
This work was Supported in part by an unrestricted grant from Research to Prevent Blindness, Tarrytown, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sigler, E., Randolph, J., Calzada, J. et al. Smoking and choroidal thickness in patients over 65 with early-atrophic age-related macular degeneration and normals. Eye 28, 838–846 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.100
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.100
This article is cited by
-
Prevalence of and factors associated with dilated choroidal vessels beneath the retinal pigment epithelium among the Japanese
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Microvascular contributions to age-related macular degeneration (AMD): from mechanisms of choriocapillaris aging to novel interventions
GeroScience (2019)
-
Long-term Progression and Risk Factors of Fundus Tessellation in the Beijing Eye Study
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Makula-Atrophie bei feuchter altersabhängiger Makuladegeneration
Der Ophthalmologe (2016)
-
Enhanced depth imaging-OCT of the choroid: a review of the current literature
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2014)