Abstract
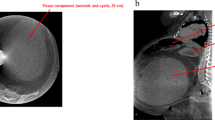
Primary epiploic appendagitis (PEA) is a rare cause of abdominal acute or subacute complaints. Diagnosis of PEA is made when computed tomography (CT) reveals a characteristic lesion. We report on contrast-enhanced CT images of a patient with PEA and regression of inflammation and the reduction in size of the inflamed appendage over the time period of 4 months. Patients with PEA usually recover without medication or surgical treatment within a few weeks. However, due to continuing bloating and irregular bowel movements we investigated carbohydrate malabsorption and diagnosed a fructose malabsorption. Bloating and irregular bowel movements in this patient with PEA were correlated to carbohydrate malabsorption and were treated successfully with a diet free of culprit carbohydrates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schnedl WJ, Krause R, Tafeit E, Tillich M, Lipp RW, Wallner-Liebmann SJ . Insights into epiploic appendagitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 8: 45–49.
Seo AY, Kim N, Oh DH . Abdominal bloating: pathophysiology and treatment. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2013; 19: 433–453.
Singh AK, Gervais DA, Hahn PF, Sagar P, Mueller PR, Novelline RA . CT appearance of acute epiploic appendagitis. Am J Roentgenol 2004; 183: 1303–1307.
Ozdemir S, Gulpinar K, Leventoglu S, Uslu HY, Turkoz E, Ozkay N et al. Torsion of the primary epiploic appendagitis: a case series and review of literature. Am J Surg 2010; 199: 453–458.
Bayat MRH, Maharaj J, Vawda F . Epiploic appendagitis. S Afr Med J 2008; 98: 849–850.
Birjawi GA, Haddad MC, Zantout HM, Uthman SZ . Primary epiploic appendagitis: a report of two cases. J Clin Imag 2000; 24: 207–209.
Sirvanci M, Balci NC, Karaman K, Duran C, Karakas E . Primary epiploic appendagitis: MRI findings. Mag Res Imag 2002; 20: 137–139.
Rioux M., Langis P . Primary epiploic appendagitis: clinical, US, and CT findings in 14 cases. Radiology 1994; 191: 523–526.
Sand M, Gelos M, Bechara FG, Sand D, Wiese TH, Steinstraesser L et al. Epiploic appendagitis – clinical characteristics of an uncommon surgical diagnosis. BMC Surg 2007; 7: 11.
Son HJ, Lee SJ, Lee JH, Kim JS, Kim YH, Rhee PL et al. Clinical diagnosis of primary epiploic appendagitis: differentiation from acute diverticulitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2002; 34: 435–438.
Hiller N, Berelowitz D, Hadas-Halpern I . Primary epiploic appendagitis: clinical and radiological manifestations. IMAJ 2000; 2: 896–898.
Schnedl WJ, Tillich M, Lipp RW . Image of the month. Primary epiploic appendagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010; 8: A16.
Talukdar R, Saikia N, Mazumder S, Gupta C, Khanna S, Chauduri D et al. Epiploic appendagitis: report of two cases. Surg Today 2007; 37: 150–153.
Rao PM, Rhea JT, Wittenberg J, Warshaw AL . Misdiagnosis of primary epiploic appendagitis. Am J Surg 1998; 176: 81–85.
Bastidas JG, Danzy LE, Blackwell L, Bostick PJ, Hayden R . Epiploic appendagitis in a 24-year-old woman. Am J Emerg Med 2008; 26: 838–839.
Sangha S, Soto JA, Becker JM, Farraye FA . Primary epiploic appendagitis: an underappreciated diagnosis. A case series and review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci 2004; 49: 347–350.
Elia M, Cummings JH . Physiological aspects of energy metabolism and gastrointestinal effects of carbohydrates. Eur J Clin Nutr 2007; 61 (Suppl 1): S40–S74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schnedl, W., Lipp, R., Wallner-Liebmann, S. et al. Primary epiploic appendagitis and fructose malabsorption. Eur J Clin Nutr 68, 1359–1361 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.109
This article is cited by
-
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: people without celiac disease avoiding gluten—is it due to histamine intolerance?
Inflammation Research (2018)