Abstract
Background/objectives:
There is a growing body of evidence that nutritional status influences the morbidity and mortality of children undergoing treatment for cancer. The aim of this paper is to determine if nutritional status is associated with survival post-pediatric bone marrow transplant.
Subjects/methods:
This was a single-center retrospective audit of patients who underwent an autologous or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Patients were divided into three weight categories of underweight, ideal weight and overweight defined by percent ideal body weight. The outcome of interest, overall post transplant survival, was compared between weight categories.
Results:
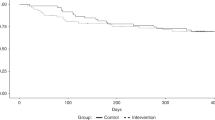
Of 113 patients, 15 (13%) were underweight and 41 (36%) were classified as overweight. After adjustment for age, sex, donor source, conditioning therapy and year of transplant, overweight patients were significantly less likely to survive than ideal-weight patients (hazard ratio (HR) 1.91; 95% confidence interval, 1.10–3.31). There was no significant increase in mortality when underweight patients were compared with ideal-weight patients (HR 1.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.57–3.79).
Conclusions:
Children who are overweight before hematopoietic stem cell transplantation have decreased survival compared with ideal-weight children.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ladas ED, Sacks N, Brophy P, Rogers PC . Standards of nutritional care in pediatric oncology. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2006; 46: 339–344.
Donaldson SS, Wesley MN, DeWys WD, Suskind RM, Jaffe N, vanEys J . A study of the nutritional status of pediatric cancer patients. Am J Dis Child 1981; 135: 1107–1112.
Rogers PC, Meacham LR, Oeffinger KC, Henry DW, Lange BJ . Obesity in pediatric oncology. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2005; 45: 881–891.
Lange BJ, Gerbing RB, Feusner J, Skolnik J, Sacks N, Smith F et al. Mortality in overweight and underweight children with acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA 2005; 293: 203–211.
Butturini AM, Dorey FJ, Lange BJ, Gaynon PS, Fu C, Franklin J et al. Obesity and outcome in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 2063–2069.
Withycombe JS, Post-White JE, Mezza JL, Hawks RG, Smith LM, Sacks N et al. Weight patterns in children with higher risk ALL: a report from the children’s oncology group (COG) for CCG 1961. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2009; 53: 1249–1254.
Woods W, Neudorf S, Gold S, Sanders J, JD Buckley, Barnard DR et al. A comparison of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation, autologous bone marrow transplantation, and aggressive chemotherapy in children with acute myeloid leukemia in remission: a repost from the Children’s Cancer Group. Blood 2001; 97: 56–62.
Robin M, Guardiola P, Dombret H, Baruchel A, Esperou H, Ribaud P et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for acute myeloblastic leukaemia in remission: risk factors for long term morbidity and mortality. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 877–887.
Woolfrey AE, Anasetti C, Storer B, Doney K, Milner LA, Sievers EL et al. Factors associated with outcome after unrelated marrow transplantation for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. Blood 2002; 99: 2002–2008.
White MS, Murphy A, Hastings Y, Shergold J, Lockwood L . Energy expenditure and body composition in children pre-bone marrow transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 775–779.
Hopman GD, Pena EG, Le Cessie S, Van Weel MH, Vossen JM, Mearin ML . Tube feeding and bone marrow transplantation. Med Pediatr Oncol 2003; 40: 375–379.
Muscaritoli M, Grieco G, Capria S, Iori AP, Rossi Fanelli F . Nutritional and metabolic support in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 75: 183–190.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Growth Charts. Developed by the National Center for Health Statistics in Collaboration with the National Centre for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion 2000 Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts.
Elliott L, Molseed LL, McCallum P eds. The Clinical Guide to Oncology Nutrition. 2nd edn Oncology Nutrition Dietetic Group, The American Dietetic Association: Chicago, Illinois, 2006.
Rogers PC, Melnick SJ, Ladas EJ, Halton J, Baillargeon J, Sacks N . Children’s Oncology Group (COG) Nutrition Committee. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2008; 50: 447–450.
Fleming DR, Rayens MK, Garrison J . Impact of obesity on allogeneic stem cell transplant patients: a matched case controlled study. Am J Med 1997; 102: 265–268.
Dickson TM, Kushiwerz-Glaz CR, Blume KG, Negrin RS, Hu WW, Shizuru JA et al. Impact of admission body weight and chemotherapy dose adjustment on the outcome of autologous bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 1999; 5: 299–305.
Meloni G, Proia A, Capria S, Romano A, Trapé G, Trisolini SM et al. Obesity and autologous stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 365–367.
Gibbs JP, Gooley T, Coreau B, Murray G, Stewart P, Appelbaum FR et al. The impact of obesity and disease on busulfan oral clearance in adults. Blood 1999; 93: 4436–4440.
Onuma M, Bub JD, Rummel TL, Iwamoto Y . Prostate cancer cell-adipocyte interaction: leptin mediates androgen0independent prostate cancer cell proliferation through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 42660–42667.
Ladas EJ, Sacks N, Meacham L, Henry D, Enriquez L, Lowry G et al. A multidisciplinary review of nutrition considerations in the pediatric oncology population: a perspective from children’s oncology group. Nutr Clin Prac 2005; 20: 377–393.
Australian Government, Department of Health and Ageing. Australian national children’s nutrition and physical activity survey, 2007.
White MS, Davies PSW, Murphy AJ . Validation of percent body fat indicators in pediatric oncology nutrition assessment. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2008; 30: 124–129.
Murphy AJ, White M, Davies PS . Body composition of children with cancer. Am J Clin Nutr 2010; 92: 55–60.
Van Eys J . Malnutrition in children with cancer: incidence and consequence. Cancer 1979; 43 (5 suppl), 2030–2035.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Children’s Nutrition Research Centre, School of Medicine, The University of Queensland, Nutrition and Dietetics Department and the Queensland Children’s Cancer Centre and the Queensland Children’s Institute of Medical Research, The University of Queensland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
White, M., Murphy, A., Hallahan, A. et al. Survival in overweight and underweight children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Clin Nutr 66, 1120–1123 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2012.109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2012.109
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nutritional status and body mass index before hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and associated outcomes: a rapid review
Supportive Care in Cancer (2024)
-
The European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) roadmap and perspectives to improve nutritional care in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on behalf of the Cellular Therapy and Immunobiology Working Party (CTIWP) and the Nurses Group (NG) of the EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Optimization of nutrition support practices early after hematopoietic cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
High body mass index did not result in poor outcome in Taiwanese children with acute myeloid leukemia: a single-institution experience
International Journal of Hematology (2015)
-
An international survey of nutritional practices in low- and middle-income countries: a report from the International Society of Pediatric Oncology (SIOP) PODC Nutrition Working Group
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2014)