Abstract
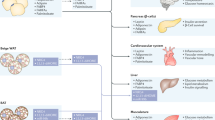
It is now recognized that the low-grade inflammation observed with obesity is associated with the development of a wide range of downstream complications. As such, there is considerable interest in elucidating the regulatory mechanisms underlying the production of inflammatory molecules to improve the prevention and treatment of obesity and its co-morbidities. White adipose tissue is no longer considered a passive reservoir for storing lipids, but rather an important organ influencing energy metabolism, insulin sensitivity and inflammation by the secretion of proteins, commonly referred to as adipokines. Dysregulation of several adipokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and adiponectin, contributes to the low-grade inflammation that is a hallmark of obesity. Evidence now suggests that fatty acids represent a class of molecules that can modulate adipokine production, thereby influencing inflammatory status. Although the precise molecular mechanisms by which dietary fats regulate adipokine production remain unclear, recent findings indicate that diet–gene interactions may have an important role in the transcriptional and secretory regulation of adipokines. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the genes encoding TNF-α, IL-6 and adiponectin can modify circulating levels of these adipokines and, subsequently, obesity-related phenotypes. This genetic variation can also alter the influence of dietary fatty acids on adipokine production. Therefore, the current review will show that it is paramount to consider both genetic information and dietary fat intake to unravel the inter-individual variability in inflammatory response observed in intervention protocols targeting obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajuwon KM, Spurlock ME (2005). Palmitate activates the NF-kappaB transcription factor and induces IL-6 and TNFalpha expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Nutr 135, 1841–1846.
Bessesen DH (2008). Update on obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93, 2027–2034.
Black RA, Rauch CT, Kozlosky CJ, Peschon JJ, Slack JL, Wolfson MF et al. (1997). A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature 385, 729–733.
Bougoulia M, Triantos A, Koliakos G (2006). Plasma interleukin-6 levels, glutathione peroxidase and isoprostane in obese women before and after weight loss. Association with cardiovascular risk factors. Hormones (Athens) 5, 192–199.
Bradley RL, Fisher FF, Maratos-Flier E (2008). Dietary fatty acids differentially regulate production of TNF-alpha and IL-10 by murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16, 938–944.
Bueno AA, Oyama LM, de Oliveira C, Pisani LP, Ribeiro EB, Silveira VL et al. (2008). Effects of different fatty acids and dietary lipids on adiponectin gene expression in 3T3-L1 cells and C57BL/6J mice adipose tissue. Pflugers Arch 455, 701–709.
Cardellini M, Perego L, D'Adamo M, Marini MA, Procopio C, Hribal ML et al. (2005). C-174G polymorphism in the promoter of the interleukin-6 gene is associated with insulin resistance. Diabetes Care 28, 2007–2012.
Caughey GE, Mantzioris E, Gibson RA, Cleland LG, James MJ (1996). The effect on human tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 beta production of diets enriched in n-3 fatty acids from vegetable oil or fish oil. Am J Clin Nutr 63, 116–122.
Cawthorn WP, Heyd F, Hegyi K, Sethi JK (2007). Tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibits adipogenesis via a beta-catenin/TCF4(TCF7L2)-dependent pathway. Cell Death Differ 14, 1361–1373.
Cawthorn WP, Sethi JK (2008). TNF-alpha and adipocyte biology. FEBS Lett 582, 117–131.
Chagnon YC, Perusse L, Lamothe M, Chagnon M, Nadeau A, Dionne FT et al. (1997). Suggestive linkages between markers on human 1p32–p22 and body fat and insulin levels in the Quebec family Study. Obes Res 5, 115–121.
Chandrasekar B, Fernandes G (1994). Decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines and increased antioxidant enzyme gene expression by omega-3 lipids in murine lupus nephritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 200, 893–898.
Clement K, Langin D (2007). Regulation of inflammation-related genes in human adipose tissue. J Intern Med 262, 422–430.
Combs TP, Berg AH, Obici S, Scherer PE, Rossetti L (2001). Endogenous glucose production is inhibited by the adipose-derived protein Acrp30. J Clin Invest 108, 1875–1881.
Davis JE, Gabler NK, Walker-Daniels J, Spurlock ME (2008). Tlr-4 deficiency selectively protects against obesity induced by diets high in saturated fat. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16, 1248–1255.
DiGirolamo M, Fine JB, Tagra K, Rossmanith R (1998). Qualitative regional differences in adipose tissue growth and cellularity in male Wistar rats fed ad libitum. Am J Physiol 274, R1460–R1467.
Divoux A, Tordjman J, Lacasa D, Veyrie N, Hugol D, Aissat A et al. (2010). Fibrosis in human adipose tissue: composition, distribution and link with lipid metabolism and fat mass loss. Diabetes 59, 2817–2825.
Eder K, Baffy N, Falus A, Fulop AK (2009). The major inflammatory mediator interleukin-6 and obesity. Inflamm Res 58, 727–736.
Endres S, Ghorbani R, Kelley VE, Georgilis K, Lonnemann G, van der Meer JW et al. (1989). The effect of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by mononuclear cells. N Engl J Med 320, 265–271.
Fernandez-Real JM, Vendrell J, Ricart W (2005). Circulating adiponectin and plasma fatty acid profile. Clin Chem 51, 603–609.
Ferrucci L, Cherubini A, Bandinelli S, Bartali B, Corsi A, Lauretani F et al. (2006). Relationship of plasma polyunsaturated fatty acids to circulating inflammatory markers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91, 439–446.
Fessler MB, Rudel LL, Brown JM (2009). Toll-like receptor signaling links dietary fatty acids to the metabolic syndrome. Curr Opin Lipidol 20, 379–385.
Flachs P, Mohamed-Ali V, Horakova O, Rossmeisl M, Hosseinzadeh-Attar MJ, Hensler M et al. (2006). Polyunsaturated fatty acids of marine origin induce adiponectin in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetologia 49, 394–397.
Fontaine-Bisson B, El-Sohemy A (2008). Genetic polymorphisms of tumor necrosis factor-alpha modify the association between dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and plasma high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol concentrations in a population of young adults. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics 1, 215–223.
Fontaine-Bisson B, Wolever TM, Chiasson JL, Rabasa-Lhoret R, Maheux P, Josse RG et al. (2007). Tumor necrosis factor alpha −238G>A genotype alters postprandial plasma levels of free fatty acids in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 56, 649–655.
Fumeron F, Aubert R, Siddiq A, Betoulle D, Pean F, Hadjadj S et al. (2004). Adiponectin gene polymorphisms and adiponectin levels are independently associated with the development of hyperglycemia during a 3-year period: the epidemiologic data on the insulin resistance syndrome prospective study. Diabetes 53, 1150–1157.
Gable DR, Matin J, Whittall R, Cakmak H, Li KW, Cooper J et al. (2007). Common adiponectin gene variants show different effects on risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes in European subjects. Ann Hum Genet 71, 453–466.
Galic S, Oakhill JS, Steinberg GR (2010). Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol Cell Endocrinol 316, 129–139.
Garcia-Escobar E, Rodriguez-Pacheco F, Garcia-Serrano S, Gomez-Zumaquero JM, Haro-Mora JJ, Soriguer F et al. (2010). Nutritional regulation of interleukin-6 release from adipocytes. Int J Obes (London) 34, 1328–1332.
Gonzalez-Sanchez JL, Zabena CA, Martinez-Larrad MT, Fernandez-Perez C, Perez-Barba M, Laakso M et al. (2005). An SNP in the adiponectin gene is associated with decreased serum adiponectin levels and risk for impaired glucose tolerance. Obes Res 13, 807–812.
Good M, Newell FM, Haupt LM, Whitehead JP, Hutley LJ, Prins JB (2006). TNF and TNF receptor expression and insulin sensitivity in human omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue—influence of BMI and adipose distribution. Diab Vasc Dis Res 3, 26–33.
Goyenechea E, Collins LJ, Parra D, Abete I, Crujeiras AB, O'Dell SD et al. (2009). The −11391 G/A polymorphism of the adiponectin gene promoter is associated with metabolic syndrome traits and the outcome of an energy-restricted diet in obese subjects. Horm Metab Res 41, 55–61.
Goyenechea E, Dolores Parra M, Alfredo Martinez J (2006). Weight regain after slimming induced by an energy-restricted diet depends on interleukin-6 and peroxisome-proliferator-activated-receptor-gamma2 gene polymorphisms. Br J Nutr 96, 965–972.
Greenberg AS, Nordan RP, McIntosh J, Calvo JC, Scow RO, Jablons D (1992). Interleukin 6 reduces lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose tissue of mice in vivo and in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: a possible role for interleukin 6 in cancer cachexia. Cancer Res 52, 4113–4116.
Grimble RF, Howell WM, O'Reilly G, Turner SJ, Markovic O, Hirrell S et al. (2002). The ability of fish oil to suppress tumor necrosis factor alpha production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in healthy men is associated with polymorphisms in genes that influence tumor necrosis factor alpha production. Am J Clin Nutr 76, 454–459.
Guerreiro CS, Ferreira P, Tavares L, Santos PM, Neves M, Brito M et al. (2009). Fatty acids, IL6, and TNFalpha polymorphisms: an example of nutrigenetics in Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol 104, 2241–2249.
Gustafson B (2010). Adipose tissue, inflammation and atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 17, 332–341.
Hamid YH, Urhammer SA, Jensen DP, Glumer C, Borch-Johnsen K, Jorgensen T et al. (2004). Variation in the interleukin-6 receptor gene associates with type 2 diabetes in Danish whites. Diabetes 53, 3342–3345.
Harkins JM, Moustaid-Moussa N, Chung YJ, Penner KM, Pestka JJ, North CM et al. (2004). Expression of interleukin-6 is greater in preadipocytes than in adipocytes of 3T3-L1 cells and C57BL/6J and ob/ob mice. J Nutr 134, 2673–2677.
He K, Liu K, Daviglus ML, Jenny NS, Mayer-Davis E, Jiang R et al. (2009). Associations of dietary long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and fish with biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial activation (from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis [MESA]). Am J Cardiol 103, 1238–1243.
Hotamisligil GS, Peraldi P, Budavari A, Ellis R, White MF, Spiegelman BM (1996). IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-alpha- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Science 271, 665–668.
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993). Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259, 87–91.
Huth C, Illig T, Herder C, Gieger C, Grallert H, Vollmert C et al. (2009). Joint analysis of individual participants' data from 17 studies on the association of the IL6 variant −174G>C with circulating glucose levels, interleukin-6 levels, and body mass index. Ann Med 41, 128–138.
Junyent M, Parnell LD, Lai CQ, Arnett DK, Tsai MY, Kabagambe EK et al. (2009). ADAM17_i33708A>G polymorphism interacts with dietary n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids to modulate obesity risk in the Genetics of Lipid Lowering Drugs and Diet Network study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 20, 698–705.
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T (2005). Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr Rev 26, 439–451.
Kanety H, Feinstein R, Papa MZ, Hemi R, Karasik A (1995). Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Possible mechanism for suppression of insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J Biol Chem 270, 23780–23784.
Karastergiou K, Mohamed-Ali V (2010). The autocrine and paracrine roles of adipokines. Mol Cell Endocrinol 318, 69–78.
Kim J, Choi YS, Lim S, Yea K, Yoon JH, Jun DJ et al. (2010). Comparative analysis of the secretory proteome of human adipose stromal vascular fraction cells during adipogenesis. Proteomics 10, 394–405.
Klipstein-Grobusch K, Mohlig M, Spranger J, Hoffmann K, Rodrigues FU, Sharma AM et al. (2006). Interleukin-6 g.−174G>C promoter polymorphism is associated with obesity in the EPIC-Potsdam Study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14, 14–18.
Kondo H, Shimomura I, Matsukawa Y, Kumada M, Takahashi M, Matsuda M et al. (2002). Association of adiponectin mutation with type 2 diabetes: a candidate gene for the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes 51, 2325–2328.
Krey G, Braissant O, L'Horset F, Kalkhoven E, Perroud M, Parker MG et al. (1997). Fatty acids, eicosanoids, and hypolipidemic agents identified as ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors by coactivator-dependent receptor ligand assay. Mol Endocrinol 11, 779–791.
Kristiansen OP, Mandrup-Poulsen T (2005). Interleukin-6 and diabetes: the good, the bad, or the indifferent? Diabetes 54 (Suppl 2), S114–S124.
Kyriakou T, Collins LJ, Spencer-Jones NJ, Malcolm C, Wang X, Snieder H et al. (2008). Adiponectin gene ADIPOQ SNP associations with serum adiponectin in two female populations and effects of SNPs on promoter activity. J Hum Genet 53, 718–727.
Lihn AS, Bruun JM, He G, Pedersen SB, Jensen PF, Richelsen B (2004). Lower expression of adiponectin mRNA in visceral adipose tissue in lean and obese subjects. Mol Cell Endocrinol 219, 9–15.
Liu M, Liu F (2009). Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of adiponectin. Biochem J 425, 41–52.
Maeda N, Takahashi M, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Nishizawa H, Kishida K et al. (2001). PPARgamma ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes 50, 2094–2099.
Maury E, Brichard SM (2010). Adipokine dysregulation, adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol 314, 1–16.
Mohamed-Ali V, Goodrick S, Rawesh A, Katz DR, Miles JM, Yudkin JS et al. (1997). Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82, 4196–4200.
Momiyama Y, Ohmori R, Fayad ZA, Kihara T, Tanaka N, Kato R et al. (2010). Associations between plasma C-reactive protein levels and the severities of coronary and aortic atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 17, 460–467.
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Catalan V, Ortega F, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Ricart W, Fruhbeck G et al. (2010). Circulating omentin concentration increases after weight loss. Nutr Metab (London) 7, 27.
Mutch DM, Rouault C, Keophiphath M, Lacasa D, Clement K (2009a). Using gene expression to predict the secretome of differentiating human preadipocytes. Int J Obes (London) 33, 354–363.
Mutch DM, Tordjman J, Pelloux V, Hanczar B, Henegar C, Poitou C et al. (2009b). Needle and surgical biopsy techniques differentially affect adipose tissue gene expression profiles. Am J Clin Nutr 89, 51–57.
Nagao K, Inoue N, Wang YM, Yanagita T (2003). Conjugated linoleic acid enhances plasma adiponectin level and alleviates hyperinsulinemia and hypertension in Zucker diabetic fatty (fa/fa) rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310, 562–566.
Nair S, Lee YH, Rousseau E, Cam M, Tataranni PA, Baier LJ et al. (2005). Increased expression of inflammation-related genes in cultured preadipocytes/stromal vascular cells from obese compared with non-obese Pima Indians. Diabetologia 48, 1784–1788.
Nieters A, Becker N, Linseisen J (2002). Polymorphisms in candidate obesity genes and their interaction with dietary intake of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids affect obesity risk in a sub-sample of the EPIC-Heidelberg cohort. Eur J Nutr 41, 210–221.
Nishizawa H, Shimomura I, Kishida K, Maeda N, Kuriyama H, Nagaretani H et al. (2002). Androgens decrease plasma adiponectin, an insulin-sensitizing adipocyte-derived protein. Diabetes 51, 2734–2741.
Oller do Nascimento CM, Ribeiro EB, Oyama LM (2009). Metabolism and secretory function of white adipose tissue: effect of dietary fat. An Acad Bras Cienc 81, 453–466.
Perez-Matute P, Perez-Echarri N, Martinez JA, Marti A, Moreno-Aliaga MJ (2007). Eicosapentaenoic acid actions on adiposity and insulin resistance in control and high-fat-fed rats: role of apoptosis, adiponectin and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Br J Nutr 97, 389–398.
Petersson H, Lind L, Hulthe J, Elmgren A, Cederholm T, Riserus U (2009). Relationships between serum fatty acid composition and multiple markers of inflammation and endothelial function in an elderly population. Atherosclerosis 203, 298–303.
Poitou C, Lacorte JM, Coupaye M, Bertrais S, Bedel JF, Lafon N et al. (2005). Relationship between single nucleotide polymorphisms in leptin, IL6 and adiponectin genes and their circulating product in morbidly obese subjects before and after gastric banding surgery. Obes Surg 15, 11–23.
Potapov VA, Chistiakov DA, Dubinina A, Shamkhalova MS, Shestakova MV, Nosikov VV (2008). Adiponectin and adiponectin receptor gene variants in relation to type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance-related phenotypes. Rev Diabet Stud 5, 28–37.
Poulain-Godefroy O, Le Bacquer O, Plancq P, Lecoeur C, Pattou F, Fruhbeck G et al. (2010). Inflammatory role of Toll-like receptors in human and murine adipose tissue. Mediators Inflamm 2010, 823486.
Prins JB, Niesler CU, Winterford CM, Bright NA, Siddle K, O'Rahilly S et al. (1997). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces apoptosis of human adipose cells. Diabetes 46, 1939–1944.
Qi L, Doria A, Manson JE, Meigs JB, Hunter D, Mantzoros CS et al. (2006). Adiponectin genetic variability, plasma adiponectin, and cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 55, 1512–1516.
Qi L, Rifai N, Hu FB (2007a). Interleukin-6 receptor gene variations, plasma interleukin-6 levels, and type 2 diabetes in US Women. Diabetes 56, 3075–3081.
Qi L, Zhang C, van Dam RM, Hu FB (2007b). Interleukin-6 genetic variability and adiposity: associations in two prospective cohorts and systematic review in 26 944 individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92, 3618–3625.
Razquin C, Martinez JA, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Salas-Salvado J, Estruch R, Marti A (2009). A 3-year Mediterranean-style dietary intervention may modulate the association between adiponectin gene variants and body weight change. Eur J Nutr 49, 311–319.
Sesti G, Perego L, Cardellini M, Andreozzi F, Ricasoli C, Vedani P et al. (2005). Impact of common polymorphisms in candidate genes for insulin resistance and obesity on weight loss of morbidly obese subjects after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and hypocaloric diet. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90, 5064–5069.
Shah R, Lu Y, Hinkle CC, McGillicuddy FC, Kim R, Hannenhalli S et al. (2009). Gene profiling of human adipose tissue during evoked inflammation in vivo. Diabetes 58, 2211–2219.
Shi H, Kokoeva MV, Inouye K, Tzameli I, Yin H, Flier JS (2006). TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116, 3015–3025.
Sookoian SC, Gonzalez C, Pirola CJ (2005). Meta-analysis on the G-308A tumor necrosis factor alpha gene variant and phenotypes associated with the metabolic syndrome. Obes Res 13, 2122–2131.
Stenholm S, Koster A, Alley DE, Visser M, Maggio M, Harris TB et al. (2009). Adipocytokines and the metabolic syndrome among older persons with and without obesity—the InCHIANTI Study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 73, 55–65.
Stenlof K, Wernstedt I, Fjallman T, Wallenius V, Wallenius K, Jansson JO (2003). Interleukin-6 levels in the central nervous system are negatively correlated with fat mass in overweight/obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88, 4379–4383.
Thorand B, Baumert J, Doring A, Herder C, Kolb H, Rathmann W et al. (2006). Sex differences in the relation of body composition to markers of inflammation. Atherosclerosis 184, 216–224.
Trayhurn P, Wood IS (2004). Adipokines: inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J Nutr 92, 347–355.
Trujillo ME, Scherer PE (2005). Adiponectin—journey from an adipocyte secretory protein to biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. J Intern Med 257, 167–175.
Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Marino MW, Hotamisligil GS (1997). Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature 389, 610–614.
van Dijk SJ, Feskens EJ, Bos MB, Hoelen DW, Heijligenberg R, Bromhaar MG et al. (2009). A saturated fatty acid-rich diet induces an obesity-linked proinflammatory gene expression profile in adipose tissue of subjects at risk of metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 90, 1656–1664.
Vasseur F, Meyre D, Froguel P (2006). Adiponectin, type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: lessons from human genetic studies. Expert Rev Mol Med 8, 1–12.
Vaxillaire M, Dechaume A, Vasseur-Delannoy V, Lahmidi S, Vatin V, Lepretre F et al. (2006). Genetic analysis of ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2 candidate polymorphisms for type 2 diabetes in the Caucasian population. Diabetes 55, 856–861.
Voros G, Maquoi E, Collen D, Lijnen HR (2003). Differential expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, TNF-alpha converting enzyme and ADAMTS family members in murine fat territories. Biochim Biophys Acta 1625, 36–42.
Vozarova B, Weyer C, Hanson K, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C, Pratley RE (2001). Circulating interleukin-6 in relation to adiposity, insulin action, and insulin secretion. Obes Res 9, 414–417.
Wang B, Trayhurn P (2006). Acute and prolonged effects of TNF-alpha on the expression and secretion of inflammation-related adipokines by human adipocytes differentiated in culture. Pflugers Arch 452, 418–427.
Wang P, Mariman E, Renes J, Keijer J (2008). The secretory function of adipocytes in the physiology of white adipose tissue. J Cell Physiol 216, 3–13.
Warodomwichit D, Shen J, Arnett DK, Tsai MY, Kabagambe EK, Peacock JM et al. (2009). ADIPOQ polymorphisms, monounsaturated fatty acids, and obesity risk: the GOLDN study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17, 510–517.
Weldon SM, Mullen AC, Loscher CE, Hurley LA, Roche HM (2007). Docosahexaenoic acid induces an anti-inflammatory profile in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human THP-1 macrophages more effectively than eicosapentaenoic acid. J Nutr Biochem 18, 250–258.
Wilson AG, Symons JA, McDowell TL, McDevitt HO, Duff GW (1997). Effects of a polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter on transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94, 3195–3199.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S et al. (2002). Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med 8, 1288–1295.
Yeop Han C, Kargi AY, Omer M, Chan CK, Wabitsch M, O'Brien KD et al. (2010). Differential effect of saturated and unsaturated free fatty acids on the generation of monocyte adhesion and chemotactic factors by adipocytes: dissociation of adipocyte hypertrophy from inflammation. Diabetes 59, 386–396.
You T, Nicklas BJ (2006). Chronic inflammation: role of adipose tissue and modulation by weight loss. Curr Diabetes Rev 2, 29–37.
Zhao LJ, Xiong DH, Pan F, Liu XG, Recker RR, Deng HW (2008). Polymorphisms of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor 2 gene are associated with obesity phenotypes among 405 Caucasian nuclear families. Hum Genet 124, 171–177.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs David Dyck and William Bettger for their input on this manuscript. DMM is supported by a grant from the Ontario Ministry of Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs (OMAFRA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stryjecki, C., Mutch, D. Fatty acid–gene interactions, adipokines and obesity. Eur J Clin Nutr 65, 285–297 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2010.277
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2010.277
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Allele-specific effect of various dietary fatty acids and ETS1 transcription factor on SCD1 expression
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
A Novel Approach to the Nutrigenetics and Nutrigenomics of Obesity and Weight Management
Current Oncology Reports (2016)
-
Alpha linolenic acid in maternal diet halts the lipid disarray due to saturated fatty acids in the liver of mice offspring at weaning
Lipids in Health and Disease (2015)
-
Fasting and postprandial regulation of the intracellular localization of adiponectin and of adipokines secretion by dietary fat in rats
Nutrition & Diabetes (2015)
-
Inhibition of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes upregulates elongase 6 and downregulates genes affecting triacylglycerol synthesis
International Journal of Obesity (2014)