Abstract
Background: The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increasing with an epidemic growth rate. Animal studies with taurine supplementation have shown increased insulin secretion and action, suggesting that taurine supplementation may have a potential to prevent T2DM.
Objective: To assess the effect of taurine treatment on insulin secretion and action, and on plasma lipid levels in overweight men with a positive history of T2DM.
Design: 20 nondiabetic subjects were included in a double-blinded, randomized, crossover study, receiving a daily supplementation of 1.5 g taurine or placebo for two periods of 8 weeks. The subjects were overweight first-degree relatives of T2DM patients. An intravenous glucose tolerance test (IVGTT) was used to measure first-phase insulin secretory response, and a euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp was used to determine peripheral insulin action.
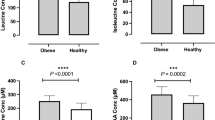
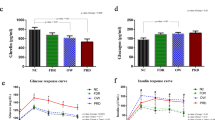
Results: Mean plasma taurine concentration was 39±7 (s.d.) μmol/l after placebo and 131±62 μmol/l after taurine intervention (P<0.0001). There was no significant difference after taurine intervention compared to placebo in incremental insulin response (Insincr.) neither during the IVGTT, nor in insulin-stimulated glucose disposal during the clamp. Insulin secretion, adjusted for insulin sensitivity, was also unchanged. There was no significant effect of taurine supplementation on blood lipid levels as well.
Conclusion: Daily supplementation with 1.5 g taurine for 8 weeks had no effect on insulin secretion or sensitivity, or on blood lipid levels. These findings in persons with an increased risk of T2DM are in contrast to those from animal studies, and do not support the assumption that dietary supplementation with taurine can be used to prevent the development of T2DM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anuradha CV & Balakrishnan SD (1999): Taurine attenuates hypertension and improves insulin sensitivity in the fructose-fed rat, an animal model of insulin resistance. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 77, 749–754.
Alberti KGMM & Zimmet PZ (1998): Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetes Med. 15, 539–553.
Beck-Nielsen H & Groop LC (1994): Metabolic and genetic characterization of prediabetic states: sequence of events leading to non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Invest. 94, 1714–1721.
Beck-Nielsen H, Henriksen JE, Hermansen K, Madsen LD, Olivarius NF, Mandrup-Poulsen TR, Pedersen OB, Richelsen B & Schmidtz OE (2000): Klaringsrapport. Type 2-diabetes og det metaboliske syndrom — diagnostik og behandling 6, 1–36.
Cherif H, Reusens B, Ahn MT, Hoet JJ & Remacle C (1998): Effects of taurine on the insulin secretion of rat fetal islets from dams fed a low-protein diet. J. Endocrinol. 159, 341–348.
DeFronzo RA & Ferrannini E (1991): Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 14, 173–194.
DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD & Andres R (1979): Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am. J. Physiol. 237, E214–E223.
De Luca G, Calpona PR, Caponetti A, Romano G, Di Benedetto A, Cucinotta D & Di Giorgio RM (2001a): Taurine and osmoregulation: platelet taurine content, uptake, and release in type 2 diabetic patients. Metab. Clin. Exp. 50, 60–64.
De Luca G, Calpona PR, Caponetti A, Macaione V, Di Benedetto A, Cucinotta D & Di Giorgio RM (2001b): Amino acid profile in platelets of diabetic patients. Metab. Clin. and Exp. 50, 739–741.
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA & Nathan DM (2002): Diabetes-Prevention PRG. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 393–403.
Elizarova EP & Nedosugova LV (1996): First experiments in taurine administration for diabetes mellitus. The effect on erythrocyte membranes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 403, 583–588.
Ferrannini E (1988): The theoretical bases of indirect calorimetry: a review. Metabolism 37, 287–301.
Franconi F, Bennardini F, Mattana A, Miceli M, Ciuti M, Mian M, Gironi A, Anichini R & Seghieri G (1995): Plasma and platelet taurine are reduced in subjects with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: effects of taurine supplementation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 61, 1115–1119.
Franconi F, Miceli M, Fazzini A, Seghieri G, Caputo S, DiLeo MA, Lepore D & Ghirlanda G (1996): Taurine and diabetes. Humans and experimental models. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 403, 579–582.
Frayn KN (1983): Calculation of substrate oxidation rates in vivo from gaseous exchange. J. Appl. Physiol. 55, 628–634.
Granner DK & O’Brien RM (1992): Molecular physiology and genetics of NIDDM. Importance of metabolic staging. Diabetes Care 15, 369–395.
Haas T, Svacina S, Pav J, Hovorka R, Sucharda P & Sonka J (1994): Risk calculation of type 2 diabetes. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 41, 297–303.
Hales CN & Barker DJP (1992): Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: the thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Diabetologia 35, 595–601.
Hansen SH (2001): The role of taurine in diabetes and the development of diabetic complications. Diabetes-Metab. Res. Rev. 17, 330–346.
Harris MI (1998): Diabetes in America: epidemiology and scope of the problem. Diabetes Care 21, C11–C14.
Hayes KC & Sturman JA (1981): Taurine in metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1, 401–425.
Hubbard RW, Chambers JG, Sanchez A, Slocum R & Lee P (1988): Amino acid analysis of plasma: studies in sample preparation. J. Chromatogr. 431, 163–169.
King H, Aubert RE & Herman WH (1998): Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care 21, 1414–1431.
Kibayashi E, Yokogoshi H, Mizue H, Miura K, Yoshita K, Nakagawa H, Naruse Y, Sokejima S & Kagamimori S (2000): Daily dietary taurine intake in Japan. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 483, 137–142.
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA & Nathan DM (2002): Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med 346 (6), 393–403.
Köbberling J & Tillil H (1982): Empirical risk figures for first degree relatives of non-insulin dependent diabetics. In eds. J Köbberling & R Tattersall, pp. 201–209 The Genetics of Diabetes Mellitus. London: Academic Press.
Kulakowski EC & Maturo J (1984): Hypoglycemic properties of taurine: not mediated by enhanced insulin release. Biochem Pharmacol 33, 2835–2838.
Laidlaw SA, Shultz TD, Cecchino JT & Kopple JD (1988): Plasma and urine taurine levels in vegans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 47, 660–663.
Lehtovirta M, Forsen B, Gullstrom M, Häggblom M, Eriksson JG, Taskinen MR & Groop L (2001): Metabolic effects of metformin in patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Med. 18, 578–583.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF & Turner RC (1985): Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28, 412–419.
Maturo J & Kulakowski EC (1988): Taurine binding to the purified insulin receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 37, 3755–3760.
Murakami S, Kondo-Ohta Y & Tomisawa K (1999): Improvement in cholesterol metabolism in mice given chronic treatment of taurine and fed a high-fat diet. Life Sci. 64, 83–91.
Murakami S, Kondo Y & Nagate T (2000): Effects of long-term treatment with taurine in mice fed a high-fat diet: improvement in cholesterol metabolism and vascular lipid accumulation by taurine. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 483, 177–186.
Murakami S, Kondo Y, Toda Y, Kitajima H, Kameo K, Sakono M & Fukuda N (2002): Effect of taurine on cholesterol metabolism in hamsters: Up- regulation of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor by taurine. Life Sci. 70, 2355–2366.
Nakaya Y, Minami A, Harada N, Sakamoto S, Niwa Y & Ohnaka M (2000): Taurine improves insulin sensitivity in the Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rat, a model of spontaneous type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71, 54–58.
Nandhini ATA & Anuradha CV (2002): Taurine modulates kallikrein activity and glucose metabolism in insulin resistant rats. Amino Acids 22, 27–38.
Nandhini ATA, Balakrishnan SD & Anuradha CV (2002): Taurine improves lipid profile in rats fed a high fructose- diet. Nutr. Res. 22, 343–354.
Pan XR, Li GW, Hu YH, Wang JX, Yang WY, An ZX, Hu ZX, Lin J, Xiao JZ, Cao HB, Liu PA, Jiang XG, Jiang YY, Wang JP, Zheng H, Zhang H, Bennett PH & Howard BV (1997): Effects of diet and exercise in preventing NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance. The Da Qing IGT and Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 20, 537–544.
Rana SK & Sanders TA (1986): Taurine concentrations in the diet, plasma, urine and breast milk of vegans compared with omnivores. Br. J. Nutr. 56, 17–27.
Sturman JA, Hepner GW, Hofmann AF & Thomas PJ (1975): Metabolism of [35S]taurine in man. J. Nutr. 105, 1206–1214.
Stenson WF (1998): The esophagus and stomach. In (eds.) M Shils, J Olson, M Shike & A Ross, pp. 1125–1133 Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease. Media, PA: Lippencott Williams and Wilkins.
Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hämäläinen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Rastas M, Salminen V, Uusitupa M & Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group (2001): Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 1343–1350.
Vaag A, Henriksen JE & Beck-Nielsen H (1992): Decreased insulin activation of glycogen synthase in skeletal muscles in young nonobese Caucasian first-degree relatives of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Invest. 89, 782–788.
Widen EI, Eriksson JG & Groop LC (1992): Metformin normalizes nonoxidative glucose metabolism in insulin-resistant normoglycemic first-degree relatives of patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 41, 354–358.
Zhao X, Jia J & Lin Y (1998): Taurine content in Chinese food and daily intake of Chinese men. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 442, 501–505.
Acknowledgements
We thank the subjects for their participation, and Marianne Modest, Stella Falster as well as the staff at Steno Diabetes Center for their contribution and hard work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantors: C Brøns and C Spohr.
Contributors: Charlotte Brøns and Camilla Spohr were involved in the design of the study, collection and analysis of data, writing the manuscript. Heidi Storgaard assisted in the collection of data, commenting the article. Jørn Dyerberg and Allan Vaag were involved in design of the study, providing advice, commenting the article.
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was supported by grants from Steno Diabetes Center, Gentofte, Denmark and by Aase and Ejnar Danielsens Foundation, Lyngby, Denmark.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brøns, C., Spohr, C., Storgaard, H. et al. Effect of taurine treatment on insulin secretion and action, and on serum lipid levels in overweight men with a genetic predisposition for type II diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Nutr 58, 1239–1247 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601955
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601955
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Protective and therapeutic effectiveness of taurine supplementation plus low calorie diet on metabolic parameters and endothelial markers in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized, clinical trial
Nutrition & Metabolism (2022)
-
Cardiac remodeling, apoptosis-related process (Bax, Bcl-2), and their ratio (Bax/Bcl-2) in cardiomyocytes of diabetic rats after combined exercise training and taurine supplementation
Comparative Clinical Pathology (2021)
-
Use and abuse of dietary supplements in persons with diabetes
Nutrition & Diabetes (2020)
-
The effects of taurine supplementation on glycemic control and serum lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Amino Acids (2020)
-
Ameliorative effects of taurine against diabetes: a review
Amino Acids (2018)