Abstract
Objective: The reproducibility and validity of coffee, decaffeinated coffee and tea intake has not been adequately studied, particularly in Italy, where coffee drinking is peculiar in terms of type and amount of coffee consumed.
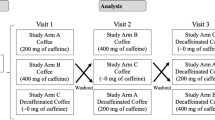
Design: We compared coffee and tea consumption, measured by two interviewer-administered food frequency questionnaires (FFQ), with average intake derived from two 7-day dietary (DD) records (the reference method) on 395 volunteers. The Pearson correlation coefficients (r) were used to assess both reproducibility and validity of information on coffee intake.
Results: A satisfactory level of reproducibility and validity of the pattern consumption was observed for coffee, decaffeinated coffee and tea. The reproducibility for both sex combined showed r of 0.74–0.78 for coffee, 0.57–0.65 for decaffeinated coffee and 0.61–0.67 for tea. The validity was about 0.70 for coffee, around 0.58 for decaffeinated coffee and 0.56–0.60 for tea intake.
Conclusions: The FFQ is a satisfactorily reliable and valid instrument for collecting information on coffee, decaffeinated coffee and tea intake.
Sponsorship: Supported by the Italian Association for Research on Cancer, Milan, Italy, and by the Commission of the European Communities (Contract No.: QLKI-CT-2000-00069).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaton GH (1994): Approaches to analysis of dietary data: relationship between planned analyses and choice of methodology. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 59, 253S–261S.
Bohlscheid-Thomas S, Hoting I, Boeing H & Wahrendorf J (1997): Reproducibility and relative validity of food group intake in a food frequency questionnaire developed for the German part of the EPIC project. Int. J. Epidemiol. 26(Suppl 1), S59–S70.
Brown J, Kreiger N, Darlington GA & Sloan M (2001): Misclassification of exposure: coffee as a surrogate for caffeine intake. Am. J. Epidemiol. 153, 815–820.
D'Amicis A & Viani R (1993) The consumption of coffee. In: Caffeine, Coffee and Health. Monographs of the Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research, ed. S Garattini, pp 1–16. Milan.
D'Avanzo B, La Vecchia C, Katsouyanni K, Negri E & Trichopoulos D (1996): Reliability of information on cigarette smoking and beverage consumption provided by hospital controls. Epidemiology 7, 312–315.
Decarli A, Franceschi S, Ferraroni M, Gnagnarella P, Parpinel MT, La Vecchia C, Negri E, Salvini S, Falcini F & Giacosa A (1996): Validation of a food-frequency questionnaire to assess dietary intakes in cancer studies in Italy. Results for specific nutrients. Ann. Epidemiol. 6, 110–118.
EPIC Group of Spain (1997): Relative validity and reproducibility of a diet history questionnaire in Spain. I. Foods. Int. J. Epidemiol. 26(Suppl 1), S91–S99.
Ferraroni M, Decarli A, Franceschi S, La Vecchia C, Enard L, Negri E, Parpinel MT & Salvini S (1996): Validity and reproducibility of alcohol consumption in Italy. Int. J. Epidemiol. 25, 775–782.
Feskanich D, Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Litin LB & Willett WC (1993): Reproducibility and validity of food intake measurements from a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 93, 790–796.
Franceschi S, Negri E, Salvini S, Decarli A, Ferraroni M, Filiberti R, Giacosa A, Talamini R, Nanni O, Panarello G & La Vecchia C (1993): Reproducibility of an Italian food frequency questionnaire for cancer studies: results for specific food items. Eur. J. Cancer 29A, 2298–2305.
Franceschi S, Barbone F, Negri E, Decarli A, Ferraroni M, Filiberti R, Giacosa A, Gnagnarella P, Nanni O, Salvini S & La Vecchia C (1995): Reproducibility of an Italian food frequency questionnaire for cancer studies. Results for specific nutrients. Ann. Epidemiol. 5, 69–75.
Istituto Centrale di Statistica (ISTAT) (1986): Indagine statistica sulle condizioni di salute della popolazione e sul ricorso ai servizi sanitari—novembre 1983. Note e Relazioni. ISTAT (Roma) 1.
Jacobsen BK & Bonaa KH (1990): The reproducibility of dietary data from a self-administered questionnaire. The Tromso Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 19, 349–353.
Johansson L, Solvoll K, Opdahl S, Bjorneboe GE & Drevon CA (1997): Response rates with different distribution methods and reward, and reproducibility of a quantitative food frequency questionnaire. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 51, 346–353.
Landis JR & Koch GG (1977): The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33, 159–174.
Liu K, Stamler J, Dyer A, McKeever J & McKeever P (1978): Statistical methods to assess and minimize the role of intra-individual variability in obscuring the relationship between dietary lipids and serum cholesterol. J. Chronic Dis. 31, 399–418.
Männistö S, Virtanen M, Mikkonen T & Pietinen P (1996): Reproducibility and validity of a food frequency questionnaire in a case–control study on breast cancer. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 49, 401–409.
Munger RG, Folsom AR, Kushi LH, Kaye SA & Sellers TA (1992): Dietary assessment of older Iowa women with a food frequency questionnaire: nutrient intake, reproducibility, and comparison with 24-hour dietary recall interviews. Am. J. Epidemiol. 136, 192–200.
Nicoli MC, Dalla Rosa M, Lerici CR & Severini C (1987): Caratteristiche chimiche dell'estatto di caffè. Nota I. Cinetica di estrazione della caffeina e delle sostanze solubili. Ind. Alim. 26, 467–471.
Pagano R, Negri E, Decarli A & La Vecchia C (1988): Coffee drinking and prevalence of bronchial asthma. Chest 94, 386–389.
Pietinen P, Hartman AM, Haapa E, Räsänen L, Haapakoski J, Palmgren J, Albanes D, Virtamo J & Huttunen JK (1988): Reproducibility and validity of dietary assessment instruments. I. A self-administered food use questionnaire with a portion size picture booklet. Am. J. Epidemiol. 128, 655–666.
Salvini S, Hunter DJ, Sampson L, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Rosner B & Willett WC (1989): Food-based validation of a dietary questionnaire: the effects of week-to-week variation in food consumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 18, 858–867.
Snedecor GW & Cochran WG (1980): Statistical Methods, Seventh Edition. Ames, Iowa: The Iowa State University Press.
Subar AF, Frey CM, Harlan LC & Kahle L (1994): Differences in reported food frequency by season of questionnaire administration: the 1987 National Health Interview Survey. Epidemiology 5, 226–233.
Tavani A, Negri E, Ferraroni M, D'Avanzo B, Decarli A, Giacosa A, La Vecchia C, Nanni O, Parpinel MT, Salvini S, Talamini R & Franceschi S (1995): Influence of some covariates on the reproducibility of an Italian semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 4: 319–327.
Venturini M (1984): Dietologia e Dietetica. Roma: Editoriale Italiana.
Willett W (1998): Nutritional Epidemiology, Vol. 30. Monographs in epidemiology and biostatistics. New York: Oxford University Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor: A Tavani.
Contributors: CLV and SF conceived and coordinated the study. MF, EN and AD managed and analysed data. AT wrote the paper. MP gave valuable contribution on nutrition.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferraroni, M., Tavani, A., Decarli, A. et al. Reproducibility and validity of coffee and tea consumption in Italy. Eur J Clin Nutr 58, 674–680 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601864
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601864
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association between lifetime coffee consumption and late life cerebral white matter hyperintensities in cognitively normal elderly individuals
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Coffee consumption and risk of hypertension: a systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of cohort studies
Journal of Human Hypertension (2018)
-
Population attributable risks of oral cavity cancer to behavioral and medical risk factors in France: results of a large population-based case–control study, the ICARE study
BMC Cancer (2015)
-
Coffee consumption and risk of lung cancer: the ICARE study
European Journal of Epidemiology (2015)
-
A meta-analysis of prospective studies of coffee consumption and mortality for all causes, cancers and cardiovascular diseases
European Journal of Epidemiology (2013)