Abstract
Data sources
Pubmed was searched using the term ‘oral submucous fibrosis' (OSF). Additional searches of the Indian and Chinese literature were conducted manually.
Study selection
Randomised controlled studies (RCTs), observational studies, or case series reports that included individuals of any age with confirmed diagnosis, by clinical examination and/or biopsy of OSF. Types of interventions included habit intervention, surgical procedures, medical treatments (i.e. systemic, submucosal injection or topical agents), or physical therapy. Primary outcomes were objective change or improvement in maximal jaw opening, subjective change in severity of oral/mucosal burning pain, subjective change in quality of life using any questionnaire, and reduction in the rate of malignant transformation.
Data extraction and synthesis
Studies selected were evaluated independently by three reviewers using a data extraction form. Due to the heterogeneity of the studies synthesis was not conducted. The overall quality of evidence of RCTs for each outcome was assessed and reported using the GRADE approach.
Results
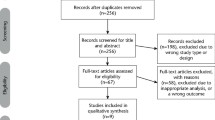
50 studies were identified for inclusion. Only four of these were RCTs. The likely bias associated with these was thought to be high and therefore the authors urged caution in interpreting their conclusions. Interventions included oral pentoxifylline versus multivitamins; oral lycopene, oral lycopene with intralesional corticosteroids or an oral placebo; oral levamisole, an oral antioxidant, or oral levamisole; physiotherapy, injections with combination hyaluronidase/steroids, and a control group. Various objective and subjective outcomes improved with intervention.
Conclusions
The current evidence for the benefit of current interventions to manage OSF is weak.
Similar content being viewed by others
Commentary
This review addresses a significant question as to whether current medical interventions are effective for management of OSF by critically evaluating the RCTs using the GRADE approach. The results are not really surprising and corroborate the conclusions of previous two reviews.1, 2 A total of 27 studies involving medical intervention using a variety of agents including nutritional supplements, steroids, antioxidants, physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory agents, immune-modulators etc were assessed, out of which only four studies satisfied the criteria for RCT. An important point raised by this review was that cessation of areca nut use alone has not been studied and a minority of studies include advice to quit the habit. This underlines the importance of this aspect, which requires due consideration, and the authors advocate use of serum markers for areca nut metabolites for objective assessment. This review identifies significant limitations of the RCTs and substantiates the ambiguity in the management of OSMF. The important concerns expressed were regarding the poor design of studies (randomisation and blinding in allocation of participants), small sample size, highly variable outcome measures, lack of validated instruments for estimation of subjective outcomes, insufficient follow up and inconsistent reporting which emphasises the need for uniformity in conducting and reporting of clinical trials.
The main message is for researchers, and the authors' suggestions for future research on this disease are commendable. The recommendations include conduct of research in areas where areca nut use is prevalent, particularly in Asian countries, evaluation of interventions in early and intermediate stages, inclusion of varying age groups, different areca nut preparations and assessment of cessation of habit along with other interventions. High quality RCTs would be the ideal, with power calculation to determine sample size being crucial. Newer drugs like anti-inflammatory agents, molecular targets like TGF-β, αvβ6 integrin and curcumin can be examined. The outcome measures should include a qualitative appraisal of patient improvement along with evaluation of morbidity and functional status associated with the intervention. Targeted education and legislative amendments for eliminating areca nut dependence still remains an irrevocable part in the management of OSMF.
In conclusion, it is an insightful and well written paper on an intriguing disease with relevant future research directives.
Practice points
-
There is scant evidence that current interventions can benefit patients with OSMF.
-
Future research should follow strict guidelines to obtain valid and applicable results.
References
Jiang X, Jing Hu . Drug Treatment of oral submucous fibrosis: a review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009; 67: 1510–1515.
Fedorowicz Z, Chan Shih-Yen E, Dorri M, Naseer M, Newton T, Shi L . Interventions for the management of oral submucous fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008 Issue 4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Address for correspondence: Professor Saman Warnakulasuriya, Department of Oral Medicine, King's College London Dental Institute, Denmark Hill Campus, Caldecot Road, London SE5 9RW, UK. E-mail: s.warne@kcl.ac.uk
Kerr AR, Warnakulasuriya S, Mighell AJ, et al. A systematic review of medical interventions for oral submucous fibrosis, and future research opportunities. Oral Dis 2011; 17 Suppl 1: 42–57.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angadi, P. Little evidence that current interventions can benefit patients with OSMF. Evid Based Dent 12, 43 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ebd.6400789
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ebd.6400789
This article is cited by
-
The Efficacy of ErCr:YSGG Laser Fibrotomy in Management of Moderate Oral Submucous Fibrosis: A Preliminary Study
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery (2014)