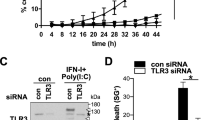
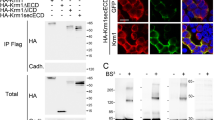
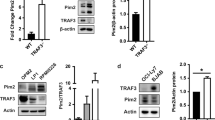
Abstract
Survival signalling by ligand-activated tyrosine kinase receptors plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance between cell viability and apoptosis in multicellular organisms. To identify receptor domains and pathways involved in survival signalling, the nerve growth factor receptor TrkA was expressed in Rat-1/MycERTM fibroblasts. We demonstrate that wt-TrkA receptor delays c-Myc-, U.V.- and Cycloheximide-induced apoptosis and activates targets such as the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) Erk2 and the serine/threonine kinase Akt/PKB, both of which have been implicated in survival signalling. TrkA mutated within its SHC binding site (Y490F) delays c-Myc-induced apoptosis without activating endogenous Akt/PKB. In contrast, the TrkA Y490F mutant receptor does not delay U.V.-induced apoptosis whilst TrkA mutated at its PLC-γ binding site (Y785F) is capable of protecting from apoptosis induced by c-Myc or U.V. treatment. The double mutant TrkA YY490/785FF fails to block either of these two apoptotic stimuli. While PI3-kinase inhibitors LY294002 and Wortmannin competely block survival signalling following U.V. treatment, neither drug affects the ability of TrkA to block c-Myc-induced apoptosis. We show that the Akt/PKB pathway is essential for NGF stimulated TrkA survival signalling in the case of U.V.-induced apoptosis, but that apoptosis induced by c-Myc is also blocked by a novel, Akt/PKB-independent, pathway. These observations suggest that TrkA can activate different survival signalling pathways, which can interfere with specific apoptotic pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulrich, E., Duwel, A., Kauffmann-Zeh, A. et al. Specific TrkA survival signals interfere with different apoptotic pathways. Oncogene 16, 825–832 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201842
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201842
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Control of TrkA-Induced Cell Death by JNK Activation and Differential Expression of TrkA upon DNA Damage
Molecules and Cells (2010)
-
Cholinergic receptor pathways involved in apoptosis, cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation
Cell Communication and Signaling (2009)
-
Nerve Growth Factor Potentiates p53 DNA Binding but Inhibits Nitric Oxide-Induced Apoptosis in Neuronal PC12 Cells
Neurochemical Research (2007)
-
The Trk tyrosine kinase inhibitor K252a regulates growth of lung adenocarcinomas
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2007)
-
Biological activity of the thyroid TRK-T3 oncogene requires signalling through Shc
British Journal of Cancer (2002)