Abstract
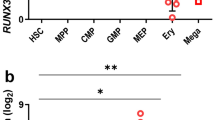
Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells were induced to undergo granulocytic differentiation by treatment with retinoic acid (RA, 10 μM, 1–5 days). The steady-state level of nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA decreased during the RA-induced differentiation. There was also decrease in the level of total cellular nucleophosmin/B23 protein during the RA-induced differentiation. Stabilization and nuclear run-on assays indicate that the decrease in nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA in RA-treated HL-60 cells was transcriptionally regulated. Unlike c-myc mRNA, there was virtually no decline of nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA during the growth arrest by serum-starvation. The decrease in nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA expression in HL-60 cells subsequent to retinoic acid treatment can thus be attributed to cellular differentiation rather than the growth arrest induced by RA. Nucleophosmin/B23 antisense oligomer treatment significantly potentiated RA-induced cellular differentiation. Results of this study suggest that nucleophosmin/B23 is one of the key elements in the down-regulation of nucleolar function for cellular differentiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, C., Yung, B. Down-regulation of nucleophosmin/B23 during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Oncogene 16, 915–923 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201615
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201615
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nucleocapsid Interacts with NPM1 and Protects it from Proteolytic Cleavage, Enhancing Cell Survival, and is Involved in PEDV Growth
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Estrogen stimulates the proliferation of human endometrial cancer cells by stabilizing nucleophosmin/B23 (NPM/B23)
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2013)
-
Sex differences in the response of the alveolar macrophage proteome to treatment with exogenous surfactant protein-A
Proteome Science (2012)
-
In vivo rescue of alveolar macrophages from SP-A knockout mice with exogenous SP-A nearly restores a wild type intracellular proteome; actin involvement
Proteome Science (2011)
-
Altered nucleophosmin transport in acute myeloid leukaemia with mutated NPM1: molecular basis and clinical implications
Leukemia (2009)