Abstract
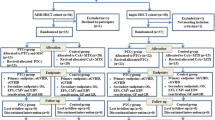
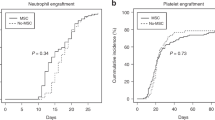
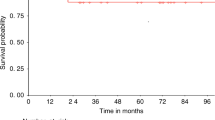
Seven patients underwent treatment with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), together with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). MSCs were given to three patients for graft failure and four patients were included in a pilot study. HSCT donors were three human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-identical siblings, three unrelated donors and one cord blood unit. The conditioning was myeloablative in four patients and reduced in three patients. MSC donors were HLA-identical siblings in three cases and haploidentical in four cases. Neutrophil counts >0.5 × 109/l was reached at a median of 12 (range 10–28) days. Platelet counts >30 × 109/l was achieved at a median of 12 (8–36) days. Acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) grade 0–I was seen in five patients. Two patients developed grade II, which in one patient evolved into chronic GVHD. One severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) patient died of aspergillosis, the others are alive and well. One patient, diagnosed with aplastic anemia had graft failure after her first transplantation and severe Henoch–Schönlein Purpura (HSP). After retransplantation of MSCs and HSCs, she recovered from both the HSP and aplasia. Thus, co-transplantation of MSC resulted in fast engraftment of absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and platelets and 100% donor chimerism, even in three patients regrafted for graft failure/rejection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, Frolova GP . Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation 1968; 6: 230–247.
Erices A, Conget P, Minguell JJ . Mesenchymal progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Br J Haematol 2000; 109: 235–242.
Campagnoli C, Roberts IA, Kumar S, Bennett PR, Bellantuono I, Fisk NM . Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow. Blood 2001; 98: 2396–2402.
Noort WA, Kruisselbrink AB, in't Anker PS, Kruger M, van Bezooijen RL, de Paus RA et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote engraftment of human umbilical cord blood-derived CD34(+) cells in NOD/SCID mice. Exp Hematol 2002; 30: 870–878.
De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A, Alfonso Z, Zuk PA, Zhu M et al. Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow. Cells Tissues Organs 2003; 174: 101–109.
Haynesworth SE, Goshima J, Goldberg VM, Caplan AI . Characterization of cells with osteogenic potential from human marrow. Bone 1992; 13: 81–88.
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999; 284: 143–147.
Galotto M, Berisso G, Delfino L, Podesta M, Ottaggio L, Dallorso S et al. Stromal damage as consequence of high-dose chemo/radiotherapy in bone marrow transplant recipients. Exp Hematol 1999; 27: 1460–1466.
Awaya N, Rupert K, Bryant E, Torok-Storb B . Failure of adult marrow-derived stem cells to generate marrow stroma after successful hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Exp Hematol 2002; 30: 937–942.
Almeida-Porada G, Porada CD, Tran N, Zanjani ED . Cotransplantation of human stromal cell progenitors into preimmune fetal sheep results in early appearance of human donor cells in circulation and boosts cell levels in bone marrow at later time points after transplantation. Blood 2000; 95: 3620–3627.
in't Anker PS, Noort WA, Kruisselbrink AB, Scherjon SA, Beekhuizen W, Willemze R et al. Nonexpanded primary lung and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells promote the engraftment of umbilical cord blood-derived CD34(+) cells in NOD/SCID mice. Exp Hematol 2003; 31: 881–889.
Maitra B, Szekely E, Gjini K, Laughlin MJ, Dennis J, Haynesworth SE et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells support unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cells and suppress T-cell activation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 597–604.
Angelopoulou M, Novelli E, Grove JE, Rinder HM, Civin C, Cheng L et al. Cotransplantation of human mesenchymal stem cells enhances human myelopoiesis and megakaryocytopoiesis in NOD/SCID mice. Exp Hematol 2003; 31: 413–420.
Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M, Ferrer K, McIntosh K, Patil S et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo. Exp Hematol 2002; 30: 42–48.
Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, Milanesi M, Longoni PD, Matteucci P et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood 2002; 99: 3838–3843.
Tse WT, Pendleton JD, Beyer WM, Egalka MC, Guinan EC . Suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation by human marrow stromal cells: implications in transplantation. Transplantation 2003; 75: 389–397.
Lazarus HM, Haynesworth SE, Gerson SL, Rosenthal NS, Caplan AI . Ex vivo expansion and subsequent infusion of human bone marrow-derived stromal progenitor cells (mesenchymal progenitor cells): implications for therapeutic use. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 16: 557–564.
Koç ON, Gerson SL, Cooper BW, Dyhouse SM, Haynesworth SE, Caplan AI et al. Rapid hematopoietic recovery after coinfusion of autologous-blood stem cells and culture-expanded marrow mesenchymal stem cells in advanced breast cancer patients receiving high-dose chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 307–316.
Le Blanc K, Tammik L, Sundberg B, Haynesworth SE, Ringdén O . Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit and stimulate mixed lymphocyte cultures and mitogenic responses independently of the major histocompatibility complex. Scand J Immunol 2003; 57: 11–20.
Lazarus HM, Koc ON, Devine SM, Curtin P, Maziarz RT, Holland HK et al. Cotransplantation of HLA-identical sibling culture-expanded mesenchymal stem cells and hematopoietic stem cells in hematologic malignancy patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 389–398.
Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, Götherström C, Hassan M, Uzunel M et al. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet 2004; 363: 1439–1441.
Ringden O, Uzunel M, Rasmusson I, Remberger M, Sundberg B, Lonnies H et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of therapy-resistant graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation 2006; 81: 1390–1397.
Olerup O, Zetterquist H . HLA-DR typing by PCR amplification with sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP) in 2 h: an alternative to serological DR typing in clinical practice including donor-recipient matching in cadaveric transplantation. Tissue Antigens 1992; 39: 225–235.
Ringden O, Remberger M, Runde V, Bornhauser M, Blau IW, Basara N et al. Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors: a comparison with marrow transplantation. Blood 1999; 94: 455–464.
Remberger M, Svahn BM, Mattsson J, Ringden O . Dose study of thymoglobulin during conditioning for unrelated donor allogeneic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation 2004; 78: 122–127.
Ringden O, Ruutu T, Remberger M, Nikoskelainen J, Volin L, Vindelov L et al. A randomized trial comparing busulfan with total body irradiation as conditioning in allogeneic marrow transplant recipients with leukemia: a report from the Nordic Bone Marrow Transplantation Group. Blood 1994; 83: 2723–2730.
Svenberg P, Remberger M, Svennilson J, Mattsson J, Leblanc K, Gustafsson B et al. Allogenic stem cell transplantation for nonmalignant disorders using matched unrelated donors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2004; 10: 877–882.
Rao K, Amrolia PJ, Jones A, Cale CM, Naik P, King D et al. Improved survival after unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation in children with primary immunodeficiency using a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen. Blood 2005; 105: 879–885.
Storb R, Deeg HJ, Fisher L, Appelbaum F, Buckner CD, Bensinger W et al. Cyclosporine v methotrexate for graft-v-host disease prevention in patients given marrow grafts for leukemia: long-term follow-up of three controlled trials. Blood 1988; 71: 293–298.
Cutler C, Kim HT, Hochberg E, Ho V, Alyea E, Lee SJ et al. Sirolimus and tacrolimus without methotrexate as graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis after matched related donor peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2004; 10: 328–336.
Ringden O, Remberger M, Persson U, Ljungman P, Aldener A, Andstrom E et al. Similar incidence of graft-versus-host disease using HLA-A, -B and -DR identical unrelated bone marrow donors as with HLA-identical siblings. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 619–625.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974; 18: 295–304.
Mattsson J, Uzunel M, Tammik L, Aschan J, Ringden O . Leukemia lineage-specific chimerism analysis is a sensitive predictor of relapse in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1976–1985.
Ringden O, Remberger M, Lehmann S, Hentschke P, Mattsson J, Klaesson S et al. N-acetylcysteine for hepatic veno-occlusive disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 993–996.
Chamberlin W, Barone J, Kedo A, Fried W . Lack of recovery of murine hematopoietic stromal cells after irradiation-induced damage. Blood 1974; 44: 385–392.
O'Flaherty E, Sparrow R, Szer J . Bone marrow stromal function from patients after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 207–212.
Carlo-Stella C, Tabilio A, Regazzi E, Garau D, La Tagliata R, Trasarti S et al. Effect of chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia on hematopoietic and fibroblast marrow progenitors. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 20: 465–471.
Le Blanc K, Remberger M, Uzunel M, Mattsson J, Barkholt L, Ringden O . A comparison of nonmyeloablative and reduced-intensity conditioning for allogeneic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation 2004; 78: 1014–1020.
Cilloni D, Carlo-Stella C, Falzetti F, Sammarelli G, Regazzi E, Colla S et al. Limited engraftment capacity of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells following T-cell-depleted hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2000; 96: 3637–3643.
Koç ON, Peters C, Aubourg P, Raghavan S, Dyhouse S, DeGasperi R et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells remain host-derived despite successful hematopoietic engraftment after allogeneic transplantation in patients with lysosomal and peroxisomal storage diseases. Exp Hematol 1999; 27: 1675–1681.
Fouillard L, Bensidhoum M, Bories D, Bonte H, Lopez M, Moseley AM et al. Engraftment of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells in the bone marrow of a patient with severe idiopathic aplastic anemia improves stroma. Leukemia 2003; 17: 474–476.
Mattsson J, Uzunel M, Remberger M, Ringden O . T cell mixed chimerism is significantly correlated to a decreased risk of acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Transplantation 2001; 71: 433–439.
Studeny M, Marini FC, Champlin RE, Zompetta C, Fidler IJ, Andreeff M . Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells as vehicles for interferon-beta delivery into tumors. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 3603–3608.
Chapel A, Bertho JM, Bensidhoum M, Fouillard L, Young RG, Frick J et al. Mesenchymal stem cells home to injured tissues when co-infused with hematopoietic cells to treat a radiation-induced multi-organ failure syndrome. J Gene Med 2003; 5: 1028–1038.
Le Blanc K, Ringden O . Immunobiology of human mesenchymal stem cells and future use in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 321–334.
Ljungman P, Brand R, Einsele H, Frassoni F, Niederwieser D, Cordonnier C . Donor CMV serologic status and outcome of CMV-seropositive recipients after unrelated donor stem cell transplantation: an EBMT megafile analysis. Blood 2003; 102: 4255–4260.
Acknowledgements
We thank Inger Hammarberg and Kristina Gynning-Holmström for secretarial assistance and Maivor Höglund-Lindecrantz for help with data collection. We also thank the staff at Center for Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation, Department of Pediatrics and Hematology, for compassionate and competent patient care. This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Society (0070-B02-16XAC, 4562-B02-02XBB, 4562-B05-05XCC), the Children's Cancer Foundation (2000/067, 01/039, 05/007), the Swedish Research Council (K2003-32X-05971-23A, K2003-32XD-14716-01A, K2006-32X-14716-04-1, K2005-32P-15457-01A), the Cancer Society in Stockholm, the Cancer and Allergy Foundation, the Tobias Foundation, the Swedish Society of Medicine, the Stockholm County Council, the Sven and Ebba-Christina Hagbergs Foundation and Karolinska Institutet.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Blanc, K., Samuelsson, H., Gustafsson, B. et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells to enhance engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 21, 1733–1738 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404777
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404777
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Stem cells for treatment of liver fibrosis/cirrhosis: clinical progress and therapeutic potential
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)
-
Effect of HO-1-modified BMMSCs on immune function in liver transplantation
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Mouse Hair Follicles Reduce Hypertrophic Scarring in a Murine Wound Healing Model
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2022)
-
Efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stem cells co-infusion in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2021)
-
Mesenchymal stromal cells as prophylaxis for graft-versus-host disease in haplo-identical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients with severe aplastic anemia?—a systematic review and meta-analysis
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2021)