Abstract
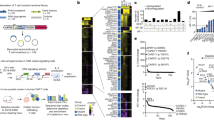
The serine/threonine kinase Akt, a downstream effector of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), is known to play an important role in antiapoptotic signaling and has been implicated in the aggressiveness of a number of different human cancers including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The progression of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs) to AML is thought to be associated with abrogation of apoptotic control mechanisms. However, little is known about signal transduction pathways which may be involved in enhanced survival of MDS cells. In this report, we have performed immunocytochemical and flow cytometric analysis to evaluate the levels of activated Akt in bone marrow or peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients diagnosed with MDS. We observed high levels of Ser473 phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) staining in 90% of the cases (n=22) diagnosed as high-risk MDS, whereas mononuclear cells from normal bone marrow or low-risk MDS patients showed low or absent Ser473 p-Akt staining. Furthermore, all high-risk MDS patients also demonstrated high expression of the Class I PI3K p110δ catalytic subunit and a decreased expression of PTEN. Taken together, our results suggest that Akt activation might be one of the factors contributing to the decreased apoptosis rate observed in patients with high-risk MDS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steelman LS, Pohnert SC, Shelton JG, Franklin RA, Bertrand FE, McCubrey JA . JAK/STAT, Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/Akt and BCR-ABL in cell cycle progression and leukemogenesis. Leukemia 2004; 18: 189–218.
Woodgett JR . Recent advances in the protein kinase B signaling pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2005; 17: 150–157.
van der Geer P, Hunter T, Lindberg RA . Receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and their signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1994; 10: 251–337.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL . The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 489–501.
Vanhaesebroeck B, Welham MJ, Kotani K, Stein R, Warne PH, Zvelebil MJ et al. P110delta, a novel phosphoinositide 3-kinase in leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 4330–4335.
Toker A, Cantley LC . Signalling through the lipid products of phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase. Nature 1997; 387: 673–676.
Brazil DP, Yang ZZ, Hemmings BA . Advances in protein kinase B signalling: AKTion on multiple fronts. Trends Biochem Sci 2004; 29: 233–242.
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC, Toker A . Direct regulation of the Akt proto-oncogene product by phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate. Science 1997; 275: 665–668.
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG . The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal 2002; 14: 381–395.
Kelekar A, Chang BS, Harlan JE, Fesik SW, Thompson CB . Bad is a BH3 domain-containing protein that forms an inactivating dimer with Bcl-XL. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 7040–7046.
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS et al. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 1999; 96: 857–868.
Yamada KM, Araki M . Tumor suppressor PTEN: modulator of cell signaling, growth, migration and apoptosis. J Cell Sci 2001; 114: 2375–2382.
Sun H, Lesche R, Li DM, Liliental J, Zhang H, Gao J et al. PTEN modulates cell cycle progression and cell survival by regulating phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5,-trisphosphate and Akt/protein kinase B signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 6199–6204.
Steelman LS, Bertrand FE, McCubrey JA . The complexity of PTEN: mutation, marker and potential target for therapeutic intervention. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2004; 8: 537–550.
Xu Q, Simpson SE, Scialla TJ, Bagg A, Carroll M . Survival of acute myeloid leukemia cells requires PI3 kinase activation. Blood 2003; 102: 972–980.
Min YH, Eom JI, Cheong JW, Maeng HO, Kim JY, Jeung HK et al. Constitutive phosphorylation of Akt/PKB protein in acute myeloid leukemia: its significance as a prognostic variable. Leukemia 2003; 17: 995–997.
Martelli AM, Tazzari PL, Tabellini G, Bortul R, Billi AM, Manzoli L et al. A new selective AKT pharmacological inhibitor reduces resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs, TRAIL, all-trans-retinoic acid, and ionizing radiation of human leukemia cells. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1794–1805.
Zhao S, Konopleva M, Cabreira-Hansen M, Xie Z, Hu W, Milella M et al. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase dephosphorylates BAD and promotes apoptosis in myeloid leukemias. Leukemia 2004; 18: 267–275.
Kouides PA, Bennett JM . Understanding the myelodysplastic syndromes. Oncologist 1997; 2: 389–401.
Ma L, Delforge M, van Duppen V, Verhoef G, Emanuel B, Boogaerts M et al. Circulating myeloid and lymphoid precursor dendritic cells are clonally involved in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1451–1456.
Greenberg PL . Apoptosis and its role in the myelodysplastic syndromes: implications for disease natural history and treatment. Leuk Res 1998; 22: 1123–1136.
Parker JE, Mufti GJ, Rasool F, Mijovic A, Devereux S, Pagliuca A . The role of apoptosis, proliferation, and the Bcl-2-related proteins in the myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia secondary to MDS. Blood 2000; 96: 3932–3938.
Parker JE, Mufti GJ . The myelodysplastic syndromes: a matter of life or death. Acta Haematol 2004; 111: 78–99.
Sujobert P, Bardet V, Cornillet-Lefebvre P, Hayflick JS, Prie N, Verdier F et al. Essential role for the p110delta isoform in phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation and cell proliferation in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005; 106: 1063–1066.
Tazzari PL, Cappellini A, Grafone T, Mantovani I, Ricci F, Billi AM et al. Detection of serine 473 phosphorylated Akt in acute myeloid leukaemia blasts by flow cytometry. Br J Haematol 2004; 126: 675–681.
Sato N, Kishi K, Toba K, Watanabe K, Itoh H, Narita M et al. Simultaneous expression of CD13, CD22 and CD25 is related to the expression of Fc epsilon R1 in non-lymphoid leukemia. Leuk Res 2004; 28: 691–698.
Dhodapkar KM, Kaufman JL, Ehlers M, Banerjee DK, Bonvini E, Koenig S et al. Selective blockade of inhibitory Fcgamma receptor enables human dendritic cell maturation with IL-12p70 production and immunity to antibody-coated tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 2910–2915.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Xu Z, Stokoe D, Kane LP, Weiss A . The inducible expression of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN promotes apoptosis and decreases cell size by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway in Jurkat T cells. Cell Growth Differ 2002; 13: 285–296.
Cappellini A, Tabellini G, Zweyer M, Bortul R, Tazzari PL, Billi AM et al. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway regulates cell cycle progression of HL60 human leukemia cells through cytoplasmic relocalization of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) and control of cyclin D1 expression. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2157–2167.
Hsu J, Shi Y, Krajewski S, Renner S, Fisher M, Reed JC et al. The AKT kinase is activated in multiple myeloma tumor cells. Blood 2001; 98: 2853–2855.
Knapp W, Strobl H, Majdic O . Flow cytometric analysis of cell-surface and intracellular antigens in leukemia diagnosis. Cytometry 1994; 18: 187–198.
Wang NM, Chang JG, Liu TC, Lin SF, Peng CT, Tsai FJ et al. Aberrant transcripts of FHIT, TSG101 and PTEN/MMAC1 genes in normal peripheral mononuclear cells. Int J Oncol 2000; 16: 75–80.
Gersuk GM, Beckham C, Loken MR, Kiener P, Anderson JE, Farrand A et al. A role for tumour necrosis factor-alpha, Fas and Fas-Ligand in marrow failure associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol 1998; 103: 176–188.
Wilson HM, Lesnikov V, Plymate SR, Ward J, Deeg HJ . High IGFBP-3 levels in marrow plasma in early-stage MDS: effects on apoptosis and hemopoiesis. Leukemia 2005; 19: 580–585.
Davis RE, Greenberg PL . Bcl-2 expression by myeloid precursors in myelodysplastic syndromes: relation to disease progression. Leuk Res 1998; 22: 767–777.
Bouscary D, De Vos J, Guesnu M, Jondeau K, Viguier F, Melle J et al. Fas/Apo-1 (CD95) expression and apoptosis in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 1997; 11: 839–845.
Gore SD . Inhibitors of signaling in myelodysplastic syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2004; 17: 613–622.
Shih LY, Huang CF, Wang PN, Wu JH, Lin TL, Dunn P et al. Acquisition of FLT3 or N-ras mutations is frequently associated with progression of myelodysplastic syndrome to acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 466–475.
Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE, Singhania N, Thomas DA, Wilson EF et al. Farnesyltransferase inhibitor R115777 in myelodysplastic syndrome: clinical and biologic activities in the phase 1 setting. Blood 2003; 102: 4527–4534.
Birkenkamp KU, Geugien M, Schepers H, Westra J, Lemmink HH, Vellenga E . Constitutive NF-kappaB DNA-binding activity in AML is frequently mediated by a Ras/PI3-K/PKB-dependent pathway. Leukemia 2004; 18: 103–112.
Sanz C, Richard C, Prosper F, Fernandez-Luna JL . Nuclear factor k B is activated in myelodysplastic bone marrow cells. Haematologica 2002; 87: 1005–1006.
Guthridge MA, Barry EF, Felquer FA, McClure BJ, Stomski FC, Ramshaw H et al. The phosphoserine-585-dependent pathway of the GM-CSF/IL-3/IL-5 receptors mediates hematopoietic cell survival through activation of NF-kappaB and induction of bcl-2. Blood 2004; 103: 820–827.
Bortul R, Tazzari PL, Cappellini A, Tabellini G, Billi AM, Bareggi R et al. Constitutively active Akt1 protects HL60 leukemia cells from TRAIL-induced apoptosis through a mechanism involving NF-kappaB activation and cFLIP(L) up-regulation. Leukemia 2003; 17: 379–389.
Fuhler GM, Drayer AL, Vellenga E . Decreased phosphorylation of protein kinase B and extracellular signal-regulated kinase in neutrophils from patients with myelodysplasia. Blood 2003; 101: 1172–1180.
Grandage VL, Gale RE, Linch DC, Khwaja A . PI3-kinase/Akt is constitutively active in primary acute myeloid leukaemia cells and regulates survival and chemoresistance via NF-kappaB, Mapkinase and p53 pathways. Leukemia 2005; 19: 586–594.
Lunghi P, Tabilio A, Lo-Coco F, Pelicci PG, Bonati A . Arsenic trioxide (ATO) and MEK1 inhibition synergize to induce apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2005; 19: 234–244.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from AIRC, Italian MIUR Cofin 2003 and FIRB 2001, ‘Hairshow A.I.L.’, Fondazione del Monte di Bologna e Ravenna.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nyåkern, M., Tazzari, P., Finelli, C. et al. Frequent elevation of Akt kinase phosphorylation in blood marrow and peripheral blood mononuclear cells from high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome patients. Leukemia 20, 230–238 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404057
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404057
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
An mTORC1/2 dual inhibitor, AZD2014, acts as a lysosomal function activator and enhances gemtuzumab ozogamicin-induced apoptosis in primary human leukemia cells
International Journal of Hematology (2019)
-
GEP analysis validates high risk MDS and acute myeloid leukemia post MDS mice models and highlights novel dysregulated pathways
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016)
-
Loss of SHIP-1 protein expression in high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes is associated with miR-210 and miR-155
Oncogene (2012)
-
Activation of nuclear inositide signalling pathways during erythropoietin therapy in low-risk MDS patients
Leukemia (2012)
-
Multiple forms of PKR present in the nuclei of acute leukemia cells represent an active kinase that is responsive to stress
Leukemia (2011)