Abstract
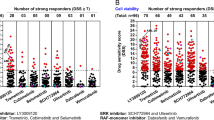
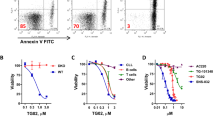
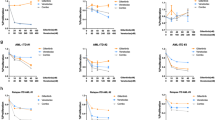
Imatinib represents at present the most attractive therapy for BCR-ABL positive leukemias, even though a percentage of CML patients develop resistance to this compound. For these resistant patients a therapeutic approach based on a combination of drugs is more likely to be effective. In the last years, constitutive NF-κB/Rel activity has been demonstrated in several hematological malignancies. As a result, NFkB/Rel-blocking approaches have been proposed as antineoplastic strategies. Furthermore, the identification of specific kinases within the NF-κB activation pathway offers a selective target to address tailored therapies. In the current study, we show that the IKK inhibitor PS1145 is able to inhibit the proliferation of CML cell lines and primary BM cells. Moreover, the addition of Imatinib increases the effects of PS1145 in resistant cell lines and BM cells from resistant patients, with a further increase of apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation and colony growth. Our data provide the rational for a new therapeutic approach, which combines Imatinib and the IKK inhibitor PS1145 in CML resistant patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kantarjian H, Sawyers C, Hochhaus A, Guilhot F, Schiffer C, Gambacorti-Passerini C et al. International STI571 CML Study Group. Hematologic and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 645–652.
O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F et al. IRIS Investigators. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 994–1004.
Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE, O'Brien S, Giles F, Garcia-Manero G, Faderl S et al. Imatinib mesylate therapy in newly diagnosed patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia: high incidence of early complete and major cytogenetic responses. Blood 2003; 101: 97–100.
Kantarjian HM, Cortes J, O'Brien S, Giles FJ, Albitar M, Rios MB et al. Imatinib mesylate (STI571) therapy for Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast phase. Blood 2002; 99: 3547–3553.
Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian H, Resta DJ, Reese SF, Ford JM et al. Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 1038–1042.
Gambacorti-Passerini CB, Gunby RH, Piazza R, Galietta A, Rostagno R, Scapozza L . Molecular mechanism of resistance to Imatinib in Philadelphia-chromosome-positive leukemias. Lancet Oncol 2003; 4: 75–85.
Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN et al. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 2001; 293: 876–880.
Branford S, Rudzki Z, Walsh S, Parkinson I, Grigg A, Szer J et al. Detection of BCR-ABL mutations in patients with CML treated with imatinib is virtually always accompanied by clinical resistance, and mutations in the ATP phosphate-binding loop (P-loop) are associated with a poor prognosis. Blood 2003; 102: 276–283.
Ghosh S, Karin M . Missing pieces in the NF-κB puzzle. Cell 2002; 109: 81–96.
Lin A, Karin M . NF-κB in cancer: a merked target. Semin Cancer Biol 2003; 13: 107–114.
Garg A, Aggarwal BB . Nuclear transcription factor-kB as a target for cancer drug development. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1053–1068.
Turco MC, Romano MF, Petrella A, Bisogni R, Tassone P, Venuta S . NF-κB/Rel-mediated regulation of apoptosis in hematologic malignancies and normal hematopoietic progenitors. Leukemia 2003; 18: 1–7.
Guzman ML, Neering SJ, Upchurch D, Grimes B, Howard DS, Rizzieri DA et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood 2001; 98: 2301–2307.
Bueso-Ramos CE, Rocha FC, Shishodia S, Medeiros LJ, Kantarjian HM, Vadhan-Raj S et al. Expression of constitutively active nuclear-kappa B RelA transcription factor in blasts of acute myeloid leukemia. Hum Pathol 2004; 35: 246–253.
Baumgartner B, Weber M, Quirling M, Fischer C, Page S, Adam M et al. Increased IkappaB kinase activity is associated with activated NF-kappaB in acute myeloid blasts. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2062–2071.
Kordes U, Krappmann D, Heissmeyer V, Ludwig WD, Scheidereit C . Transcription factor NF-kappaB is constitutively activated in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2000; 3: 399–402.
Bailly JD, Skladanowski A, Bettaieb A, Mansat V, Larsen AK, Laurent G . Natural resistance of acute myeloid leukemia cell lines to mitoxantrone is associated with lack of apoptosis. Leukemia 1997; 9: 1523–1532.
Panwalkar A, Verstovsek S, Giles F . Nuclear factor-kappaB modulation as a therapeutic approach in hematologic malignancies. Cancer 2004; 15: 1578–1589.
Umezawa K, Chaicharoenpong C . Molecular design and biological activities of NF-kappaB inhibitors. Mol Cells 2002; 14: 163–167.
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y . Phosphorilation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-κB activity. Annu Rev Immunol 2000; 18: 621–663.
Karin M, Lin A . NF-κB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 221–227.
Senftleben U, Karin M . The IKK/NF-κB pathway. Crit Care Med 2002; 30: 18–26.
Hayashi T, Hideshima T, Anderson KC . Novel therapies for multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 2003; 120: 10–17.
Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Richardson P, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Hayashi T et al. NF-kappa B as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 16639–16647.
Cilloni D, Carlo-Stella C, Falzetti F, Sammarelli G, Regazzi E, Colla S et al. Limited engraftment capacity of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells following T cell depleted hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2000; 96: 3637–3643.
Aradhya S, Nelson DL . NF-κB signaling and human disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2000; 11: 300–306.
Pahl HL . Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 1999; 18: 6853–6866.
Li ZW, Chu W, Hu Y, Delhase M, Deerinck T, Ellisman M et al. The IKK beta subunit of I kappa B kinase B kinase (IKK) is essential for nuclear factor kappa B activatation and prevention of apoptosis. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 1839–1845.
Zandi E, Chen Y, Karin M . Direct phosphorilation of IKappaB by IKKalpha and IKK beta: Discrimination between free and NF-κB bound substrate. Science 1998; 281: 1360–1363.
Delhase M, Hayakawa M, Chen Y, Karin M . Positive and negative regulation of I kappa B kinase activity through IKK beta subunit phosphorylation. Science 1999; 284: 309–313.
Kavai H, Nie L, Yuan ZM . Inactivation of NF-κB dependent cell survival, a novel mechanisn for the proapoptotic function of c-ABL. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 6079–6088.
Shaul Y . c-ABL:activation and nuclear targets. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 10–16.
Pendergast AM . The Abl family kinases: mechanism of regulation and signaling. Adv Cancer Res 2002; 85: 51–100.
Reuther JY, Reuther GW, Cortez D, Pendergast AM, Baldwin AS . A requirement for NF-κB activation in BCR-ABL mediated transformation. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 968–981.
Acknowledgements
Grants and financial support: This work has been supported by grants from AIRC (Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro), CNR (Progetto Finalizzato Oncologia), MURST-COFIN 2003, AIL (Associazione Italiana contro le Leucemie), and by Regione Piemonte. We are indebted to Lami Oyewumi for the revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cilloni, D., Messa, F., Arruga, F. et al. The NF-κB pathway blockade by the IKK inhibitor PS1145 can overcome Imatinib resistance. Leukemia 20, 61–67 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403998
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403998
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
FAM167A is a key molecule to induce BCR-ABL-independent TKI resistance in CML via noncanonical NF-κB signaling activation
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2022)
-
Eliminating chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells by IRAK1/4 inhibitors
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Inhibition of kinase IKKβ suppresses cellular abnormalities induced by the human papillomavirus oncoprotein HPV 18E6
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Inhibition of cystathionine β-synthase promotes apoptosis and reduces cell proliferation in chronic myeloid leukemia
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)
-
Selective activation of TNFR1 and NF-κB inhibition by a novel biyouyanagin analogue promotes apoptosis in acute leukemia cells
BMC Cancer (2016)