Abstract
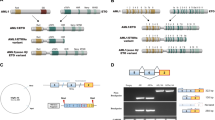
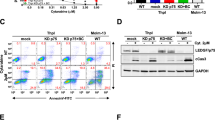
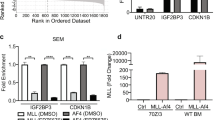
The AML1 and CBFβ subunits of core binding factor (CBF) are involved in several chromosomal abnormalities frequently associated with acute leukemias. As a result, the CBFβ-SMMHC, AML1-ETO and AML1-MDS1/EVI1 fusion proteins are expressed in subsets of acute myeloid leukemia, and TEL-AML1 is expressed in B-lineage acute lymphocytic leukemia. These CBF oncoproteins likely contribute to leukemogenesis in part by inhibiting endogenous CBF. As a result they are expected to inhibit differentiation and perhaps apoptosis. In addition, the domains unique to each fusion protein may also contribute to leukemogenesis via unique mechanisms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedman, A. Leukemogenesis by CBF oncoproteins. Leukemia 13, 1932–1942 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401590
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401590
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pathogenic Mechanisms in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2022)
-
C/EBPα in normal and malignant myelopoiesis
International Journal of Hematology (2015)
-
ETV6/RUNX1 abrogates mitotic checkpoint function and targets its key player MAD2L1
Oncogene (2010)
-
Identification of a region on the outer surface of the CBFβ-SMMHC myeloid oncoprotein assembly competence domain critical for multimerization
Oncogene (2006)
-
CBFβ-SMMHC slows proliferation of primary murine and human myeloid progenitors
Leukemia (2005)