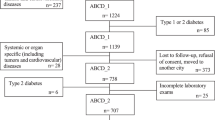
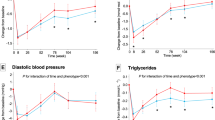
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To examine whether fasting insulin concentrations and markers of first-phase insulin secretion are associated with weight gain and changes in distribution of adiposity over 4.4 y.
DESIGN: Longitudinal prospective population-based cohort study of middle-aged Caucasians.
SUBJECTS: 767 subjects (40–65 y at baseline) were followed up for a mean of 4.4 y.
MEASUREMENTS: 75 g oral glucose tolerance test performed at baseline and follow-up. Insulin was measured at fasting, and 30 and 120 min post-glucose load using a highly specific assay.
RESULTS: Fasting insulin levels were correlated with baseline weight (r=0.32, P<0.001), as was the 30 min insulin incremental response (r=0.17, P<0.001). Mean weight gain over the 4.4 y of follow-up was 2.17 kg (range:−6.17–10.5 kg) for men and 2.49 kg (range:−7.41–12.39 kg) for women. In women, the 30 min insulin incremental response was negatively associated with percentage weight gain (P<0.001), but there was no relationship between fasting insulin levels and weight gain. The baseline fasting insulin was positively correlated with percentage increase in waist–hip ratio (r=0.12, P=0.01). In stratified analysis, this relationship was confined to women over the age of 50 y. However, in men, none of these relationships were demonstrable.
CONCLUSION: In middle-aged women reduced first-phase insulin secretion was associated with an increased risk of future weight gain, whereas fasting hyperinsulinaemia was associated with an increase in waist–hip ratio over time.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gould, A., Williams, D., Byrne, C. et al. Prospective cohort study of the relationship of markers of insulin resistance and secretion with weight gain and changes in regional adiposity. Int J Obes 23, 1256–1261 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801060
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801060
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A longitudinal study of serum insulin and insulin resistance as predictors of weight and body fat gain in African American and Caucasian children
International Journal of Obesity (2017)
-
Insulin Resistance as a Predictor of Gains in Body Fat, Weight, and Abdominal Fat in Nondiabetic Women: A Prospective Study
Obesity (2012)
-
Insulin Sensitivity and Regional Fat Gain in Response to Overfeeding
Obesity (2011)
-
Glucose Metabolism and Diet Predict Changes in Adiposity and Fat Distribution in Weight‐reduced Women
Obesity (2010)
-
Betel Nut Chewing Is Strongly Associated With General and Central Obesity in Chinese Male Middle‐aged Adults
Obesity (2009)