Abstract
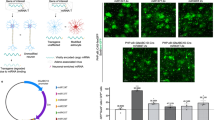
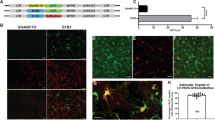
The subventricular zone (SVZ) is one of the neurogenic niches in the adult mammalian brain. The SVZ is of interest for studies on neurogenesis and stem cell therapy. Here, we report specific transduction of ependyma and/or astrocytes by recombinant adeno-associated virus type 4 (AAV4) viral vectors. AAV4 vectors encoding β-galactosidase or eGFP were injected into the lateral ventricles of neonatal and adult C57BL/6 mouse brains. In addition, SVZ injections were conducted on adult mice. AAV4 vectors show a characteristic transduction of the ependyma independent of delivery route. However, AAV4 virus injected into the SVZ targeted GFAP positive astrocytes forming the glial tube in the SVZ and rostral migratory stream (RMS). Our results introduce AAV4 as a new tool by which to manipulate glial cells in the RMS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gage FH . Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 2000; 287: 1433–1438.
Taupin P, Gage FH . Adult neurogenesis and neural stem cells of the central nervous system in mammals. J Neurosci Res 2002; 69: 745–749.
Alvarez-Buylla A, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Tramontin AD . A unified hypothesis on the lineage of neural stem cells. Nat Rev Neurosci 2001; 2: 287–293.
Doetsch F, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A . Cellular composition and three-dimensional organization of the subventricular germinal zone in the adult mammalian brain. J Neurosci 1997; 17: 5046–5061.
Falk A et al. Gene delivery to adult neural stem cells. Exp Cell Res 2002; 279: 34–39.
Yoon SO et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene delivery into neuronal precursors of the adult mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 11974–11979.
Consiglio A et al. Robust in vivo gene transfer into adult mammalian neural stem cells by lentiviral vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 14835–14840.
Hughes SM, Moussavi-Harami F, Sauter SL, Davidson BL . Viral-mediated gene transfer to mouse primary neural progenitor cells. Mol Therapy 2002; 5: 16–24.
Wu P, Ye Y, Svendsen CN . Transduction of human neural progenitor cells using recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors. Gene Therapy 2002; 9: 245–255.
Passini MA, Lee EB, Heuer GG, Wolfe JH . Distribution of a lysosomal enzyme in the adult brain by axonal transport and by cells of the rostral migratory stream. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 6437–6446.
Davidson BL et al. Recombinant adeno-associated type 2, 4 and 5 vectors: transduction of variant cell types and regions in the mammalian CNS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3428–3432.
Peretto P, Merighi A, Fasolo A, Bonfanti L . The subependymal layer in rodents: a site of structural plasticity and cell migration in the adult mammalian brain. Brain Res Bull 1999; 49: 221–243.
Peretto P, Merighi A, Fasolo A, Bonfanti L . Glial tubes in the rostral migratory stream of the adult rat. Brain Res Bull 1997; 42: 9–21.
Luskin MB . Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron 1993; 11: 173–189.
Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A . Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 1994; 264: 1145–1148.
Tramontin AD, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Lim DA, Alvarez-Buylla A . Postnatal development of radial glia and the ventricular zone (VZ): a continuum of the neural stem cell compartment. Cereb Cortex 2003; 13: 580–587.
Spassky N et al. Adult ependymal cells are postmitotic and are derived from radial glial cells during embryogenesis. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 10–18.
Merkle FT, Tramontin AD, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A . Radial glia give rise to adult neural stem cells in the subventricular zone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 17528–17532.
Anthony TE, Klein C, Fishell G, Heintz N . Radial glia serve as neuronal progenitors in all regions of the central nervous system. Neuron 2004; 41: 881–890.
Johansson CB et al. Identification of a neural stem cell in the adult mammalian central nervous system. Cell 1999; 96: 25–34.
Doetsch F et al. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell 1999; 97: 703–716.
Laywell ED et al. Identification of a multipotent astrocytic stem cell in the immature and adult mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 13883–13888.
Chiasson BJ, Tropepe V, Morshead CM, van der Kooy D . Adult mammalian forebrain ependymal and subependymal cells demonstrate proliferative potential, but only subependymal cells have neural stem cell characteristics. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 4462–4471.
Capela A, Temple S . LeX/ssea-1 is expressed by adult mouse CNS stem cells, identifying them as nonependymal. Neuron 2002; 35: 865–875.
Soria JM et al. Defective postnatal neurogenesis and disorganization of the rostral migratory stream in absence of the Vax1 homeobox gene. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 11171–11181.
Lim DA et al. Noggin antagonizes BMP signaling to create a niche for adult neurogenesis. Neuron 2000; 28: 713–726.
Craig CG et al. In vivo growth factor expansion of endogenous subependymal neural precursor cell populations in the adult mouse brain. J Neurosci 1996; 16: 2649–2658.
Benraiss A et al. Adenoviral brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces both neostriatal and olfactory neuronal recruitment from endogenous progenitor cells in the adult forebrain. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 6718–6731.
Emsley JG, Hagg T . Endogenous and exogenous ciliary neurotrophic factor enhances forebrain neurogenesis in adult mice. Exp Neurol 2003; 183: 298–310.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the Davidson Laboratory for critical discussion, Stephanie M Hughes for assisting with early studies, Colleen S Stein for reviewing the manuscript and Christine McLennan for manuscript preparation. This work was supported by the NIH (HD 33531) and the University of Iowa Graduate Program in Neuroscience (GL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Martins, I., Chiorini, J. et al. Adeno-associated virus type 4 (AAV4) targets ependyma and astrocytes in the subventricular zone and RMS. Gene Ther 12, 1503–1508 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302554
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302554
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Destination Brain: the Past, Present, and Future of Therapeutic Gene Delivery
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2017)
-
Glymphatic distribution of CSF-derived apoE into brain is isoform specific and suppressed during sleep deprivation
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2016)
-
Targeted gene transfer into ependymal cells through intraventricular injection of AAV1 vector and long-term enzyme replacement via the CSF
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Global CNS gene delivery and evasion of anti-AAV-neutralizing antibodies by intrathecal AAV administration in non-human primates
Gene Therapy (2013)