Abstract
Objective:
It was determined whether a combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus) 74-2 and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp lactis DGCC 420 (B. lactis 420) affect the faecal microbiota as well as immunological parameters and blood lipids in healthy adults.
Design:
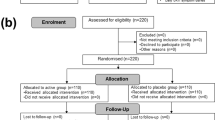
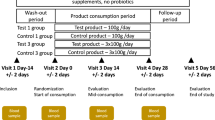
A placebo-controlled, double-blinded, randomized crossover trial was conducted.
Subjects:
Twenty-six healthy volunteers (mean age 25 years) were recruited by advertising in academical buildings. All of them completed the study.
Methods:
After 3-week run-in period, half of the volunteers consumed 300 g/day of yoghurt supplement containing probiotic strains L. acidophilus 74-2 and B. lactis 420, and the other half received the placebo product for a period of 5 weeks. The two groups were crossed during the following 5-week period. Blood and faecal samples were collected at the end of each period. The faecal content of probiotic bacteria, faecal short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), serum lipids and plasma immune system biomarkers were evaluated.
Results:
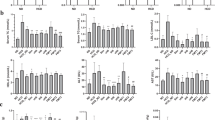
Faecal proportions of L. acidophilus and of B. lactis increased significantly from 0.02 to 0.19 and 0.4 to 1.4% (P<0.05), respectively. Percentages of granulocytes and monocytes showing phagocytic activity were significantly elevated from 92 to 95% during probiotic intervention, whereas their oxidative burst activity and specific immune parameters remained unaffected. Fecal SCFA and serum cholesterol levels were not influenced by the probiotics. However, serum concentrations of triacylglyceroles decreased significantly by 11.6% (P<0.05) in the probiotic supplementation period.
Conclusions:
L. acidophilus and B. lactis were recovered in faeces in significantly elevated numbers after supplementation. They are able to modulate unspecific cellular immune response indicated by the increased phagocytic activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Gawad IA, El-Sayed EM, Hafez SA, El-Zeini HM, Saleh FA (2005). The hypocholesterolaemic effect of soy-yoghurt containing bifidobacteria in rats fed on a cholesterol-enriched diet. Int Dairy J 15, 37–44.
Agerholm-Larsen L, Raben A, Haulrik N, Hansen AS, Manders M, Astrup A (2000). Effect of 8 week intake of probiotic milk products on risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 288–297.
Amann RI, Binder BJ, Olson RJ, Chisholm SW, Devereux R, Stahl DA (1990). Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microb 56, 1919–1925.
Arunachalam K, Gill HS, Chandra RK (2000). Enhancement of natural immune function by dietary consumption of Bifidobacterium lactis (HN019). Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 263–267.
Bartosch S, Woodmansey EJ, Paterson JCM, McMurdo MET, Macfarlane GT (2005). Microbiological effects of consuming a synbiotic containing Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium lactis, and oligofructose in elderly persons, determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction and counting of viable bacteria. Clin Infect Dis 40, 28–37.
Beimfohr C, Krause A, Amann R, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1993). In situ identification of Lactococcci, Enterococci and Streptococci. Syst Appl Microbiol 16, 450–456.
Bertolami MC, Faludi AA, Batluoni M (1999). Evaluation of the effects of a new fermented milk product (Gaio) on primary hypercholesterolemia. Eur J Clin Nutr 53, 97–101.
Brashears MM, Gilliland SE, Buck LM (1998). Bile salt deconjugation and cholesterol removal from media by Lactobacillus casei. J Dairy Sci 81, 2103–2109.
Chiang BL, Sheih YH, Wang LH, Liao CK, Gill HS (2000). Enhancing immunity by dietary consumption of a probiotic lactic acid bacterium (Bifidobacterium lactis HN019): optimization and definition of cellular immune responses. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 849–855.
Cummings JH, Antoine JM, Azpiroz F, Bourdet-Sicard R, Brandtzaeg P, Calder PC et al. (2004). PASSCLAIM-gut health and immunity. Eur J Clin Nutr 43, II/118–II/173.
De Roos NM, Schouten G, Katan MB (1999). Yogurt enriched with Lactobacillus acidophilus does not lower blood lipids in healthy men and women with normal to borderline high serum cholesterol levels. Eur J Clin Nutr 53, 277–280.
De Smet I, De Boever P, Verstrate W (1998). Cholesterol lowering in pigs through enhanced bacterial bile salt hydrolase activity. Br J Nutr 79, 185–194.
De Vrese M, Winkler P, Rautenberg P, Harder T, Noah C, Laue C et al. (2005). Effect of Lactobacillus gasseri PA 16/8, Bifidobacterium longum SP 07/3, B. bifidum MF 20/5 on common cold episodes: A double blind, randomized, controlled trial. Clin Nutr 24, 481–491.
Delzenne NM, Williams CM (2002). Prebiotics and lipid metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol 13, 61–67.
Ditscheid B, Keller S, Jahreis G (2005). Cholesterol metabolism is affected by calcium phosphate supplementation in humans. J Nutr 135, 1678–1682.
Doncheva NI, Antov GP, Softova EB, Nyagolov YP (2002). Experimental and clinical study on the hypolipidemic and antisclerotic effect of Lactobacillus bulgaricus strain GBN 1 (48). Nutr Res 22, 393–403.
Ewaschuk JB, Dieleman LA (2006). Probiotics and prebiotics in chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 12, 5941–5950.
Franks AH, Harmsen HJ, Raangs GC, Jansen GJ, Schut F, Welling GW (1998). Variations of bacterial populations in human feces measured by fluorescent in situ hybridization with group-specific 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microb 64, 3336–3345.
Fuchs BM, Glöckner FO, Wulf J, Amann R (2000). Unlabeled helper oligonucleotides increase in situ accessibility to 16S rRNA of fluorescently labelled oligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microb 66, 3603–3607.
Glück U, Gebbers JO (2003). Ingested probiotics reduce nasal colonization with pathogenic bacteria /Staphylococcus aureus, Stretococcus pneumoniae, and ß-hemolytic streptococci. Am J Clin Nutr 77, 517–520.
Gmeiner M, Kneifel W, Kube KD, Wouters R, De Boever P, Nollet L (2000). Influence of a synbiotic mixture consisting of L. acidophilus 74-2 and a fructooligosaccharide preparation on the microbial ecology substained in a simulation of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem (SHIME reactor). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53, 219–223.
Gill HS, Cross ML, Rutherfurd KJ, Gopal PK (2001). Dietary probiotic supplementation to enhance cellular immunity in the elderly. Br J Biomed Sci 58, 94–96.
Gilliland SE, Nelson CR, Maxwell C (1985). Assimilation of cholesterol by Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microb 49, 377–381.
Harmsen HJM, Elfferich P, Schut F, Welling GW (1999). A 16S rRNA-targeted probe for detection of lactobacilli and enterococci in faecal samples by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Microb Ecol Health Dis 11, 3–12.
Harmsen HJM, Raangs GC, He T, Degener JE, Welling GW (2002). Extensive set of 16S rRNA based probes for detection of bacteria in human faeces. Appl Environ Microb 68, 2982–2990.
Hatakka K, Savilahti E, Pönka A, Meurman JH, Poussa T, Näse L et al. (2001). Effect of long term consumption of probiotic milk on infections in children attending day care centres: double blind, randomised trial. BMJ 322, 1–5.
Jahreis G, Vogelsang H, Kiessling G, Schubert R, Hammes WP (2002). Influence of probiotic sausage (Lactobacillus paracasei) on blood lipids and immunological parameters of healthy volunteers. Food Res Int 35, 133–138.
Johansson ML, Molin G, Jeppsson B, Nobaek S, Ahrné S, Bengmark S (1993). Administration of different Lactobacillus strains in fermented oatmeal soup: in vivo colonization of human intestinal mucosa and effect on the indigenous flora. Appl Environ Microb 59, 15–20.
Kawase M, Hashimoto H, Hosoda M, Morita M, Hosono A (2001). Effect of fermented milk with Streptococcus thermophilus TMC1543 on serum lipid levels induced by a high-cholesterol diet in adult subjects. Milchwiss 56, 496–499.
Kießling G, Schneider J, Jahreis G (2002). Long term consumption of fermented dairy products over six months increases HDL-cholesterol. Eur J Clin Nutr 56, 843–849.
Kikuchi-Hayakawa H, Shibara-Sone H, Osada K, Onodera-Masuoka N, Ishikawa F, Watanuki M (2000). Lower plasma triglyceride level in syrian hamsters fed on skim milk fermented with Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64, 466–475.
Klaver FAM, Van der Meer R (1993). The assumed assimilation of cholesterol by Lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium bifidum is due to their bile salt-deconjugating activity. Appl Environ Metab 59, 1120–1124.
Kok RG, De Waal A, Schut F, Welling GW, Weenk G, Hellingwerf KJ (1996). Specific detection and analysis of a probiotic Bifidobacterium strain in infant feces. Appl Environ Microb 62, 3668–3672.
Kristensen JH (2002). Probiotic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria. MSc Thesis, The Royal Veterinary and Agricultural University: Copenhagen, Denmark.
Langendijk PS, Schut F, Jansen GJ, Raangs GC, Kamphuis GR, Wilkinson MHF et al. (1995). Quantitative fluorescence in situ hybridisation of Bifidobacterium spp. with genus-specific 16S rRNA-targeted probes and its application in fecal samples. Appl Environ Microb 61, 3069–3075.
Lewis SJ, Burmeister S (2005). A double-blind placebo-controlled study of the effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus on plasma lipids. Eur J Clin Nutr 59, 776–780.
Lu L, Walker A (2001). Pathologic and physiologic interactions of bacteria with the gastrointestinal epithelium. Am J Clin Nutr 73, 1124S–1130S.
Mai V, Katki HA, Harmsen H, Gallaher D, Schatzkin A, Baer DJ et al. (2004). Effect of a controlled diet and black tea drinking on the fecal microflora composition and the fecal bile acid profile of human volunteers in a double-blinded randomized feeding study. J Nutr 134, 473–478.
Manz W, Amann R, Ludwig W, Wagner M, Schleifer KH (1992). Phylogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the major subclasses of proteobacteria: problems and solutions. Syst Appl Microb 15, 593–600.
Marcos A, Wärnberg J, Nova E, Gómez S, Alvarez A, Alvarez R et al. (2004). The effect of milk fermented by yogurt cultures plus Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 on the immene response of subjects under academic examination stress. Eur J Nutr 43, 381–389.
Mättö J, Fondén R, Tolvanen T, von Wright A, Vilpponen-Salmela T, Satokari R et al. (2006). Intestinal survival and persistence of probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains administered in triple-strain yoghurt. Int Dairy J 16, 1174–1180.
Mueller S, Saunier K, Hanisch C, Norin E, Alm L, Midtvedt T et al. (2006). Differences in fecal microbiota in different european study populations in relation to age, gender, and country: a cross-sectional study. Appl Environ Microb 72, 1027–1033.
Olivares M, Paz Díaz-Ropero M, Gómez N, Lara-Villoslada F, Sierra S, Maldonado JA et al. (2006). Oral administration of two probiotic strains Lactobacillus gasseri CECT 5714 and Lactobacillus coryniformis CECT 5711, enhances the intestinal function of healthy adults. Int J Food Microbiol 107, 104–111.
Ouwehand AC, Isolauri E, Kirjavainen PV, Salminen S (1999). Adhesion of four Bifidobacterium strains to human intestinal mucus from subjects in different age groups. FEMS Microbiol Letters 172, 61–64.
Ouwehand AC, Salminen S, Arvola T, Ruuska T, Isolauri E (2004). Microbiota composition of the intestinal mucosa: association with fecal microbiota? Microbiol Immunol 48, 497–500.
Ouwehand AC, Salminen S, Roberts PJ, Ovaska J, Salminen E (2003). Disease-dependent adhesion of lactic acid bacteria to the human intestinal mucosa. Clin Diagn Lab Immun 10, 643–646.
Pereira DIA, Gibson GR (2002). Effects of consumption of probiotics and prebiotics on serum lipid levels in humans. Crit Rev Biochem Molec Biol 37, 259–281.
Pot B, Hertel C, Ludwig W, Descheemaeker P, Kersters K, Schleifer KH (1993). Identification and classification of Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. gasseri, and L. johnsonii strains by SDS-PAGE and rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probe hybridization. J Gen Microb 139, 513–517.
Rochet V, Rogottier-Gois L, Sutren M, Krementscki MN, Andrieux C, Furet JP et al. (2006). Effects of orally administered Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 on the composition or activities of the dominant faecal microbiota in healthy humans. Br J Nutr 95, 421–429.
Salminen S, Bouley C, Boutron-Ruault MC, Cummings JH, Franck A, Gibson GR et al. (1998). Functional food science and gastrointestinal physiology and function. Br J Nutr 80, S147–S171.
Schaafsma G, Meulig WJA, Van Dokkum W, Bouley C (1998). Effects of a milk product, fermented by Lactobacillus acidophilus and with fructo-oligosaccharides added, on blood lipids in male volunteers. Eur J Clin Nutr 52, 436–440.
Schiffrin EJ, Brassart D, Servin AL, Rochat F, Donnet-Hughes A (1997). Immune modulation of blood leukocytes in humans by lactic acid bacteria: criteria for strain selection. Am J Clin Nutr 66, 515S–520S.
Sheih YH, Chiang BL, Wang LH, Liao CK, Gill HS (2001). Systemic immunity-enhancing effects in healthy subjects following dietary consumption of the lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001. J Am Coll Nutr 20, 149–156.
Suomalainen T, Lagström H, Mättö J, Saarela M, Arvilommi H, Laitinen I et al. (2006). Influence of whey based fruit juice containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus on intestinal well-being and humoral immune response in healthy adults. Swiss Soc Food Sci Technol 39, 788–795.
St-Onge MP, Farnworth ER, Jones PJH (2000). Consumption of fermented and nonfermented dairy products: effects on cholesterol concentrations and metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr 71, 674–681.
Tannock GW, Munro K, Harmsen HJM, Welling GW, Smart J, Gopal PK (2000). Analysis of the fecal microflora of human subjects consuming a probiotic product containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus DR20. Appl Environ Microb 66, 2578–2588.
Taranto MP, Medici M, Perdigon G, Ruiz-Holgado AP, Valdez GF (1998). Evidence for hypocholesterolemic effect of Lactobacillus reuteri in hypercholesterolemic mice. J Dairy Sci 81, 2336–2340.
Turchet P, Laurenzano M, Auboiron S, Antoine JM (2003). Effect of fermented milk containing the probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 on winter infections in free-living elderly subjects: a randomised, controlled pilot study. J Nutr Health Aging 7, 75–77.
Valeur N, Engel P, Carbajal N, Connolly E, Ladefoged K (2004). Colonization and immunmodulation by Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 in the human gastrointestinal tract. Appl Environ Microb 70, 1176–1181.
Van der Waaij LA, Harmsen HJM, Madjipour M, Kroese FGM, Zwiers M, Dullemen HM et al. (2005). Bacterial population analysis of human colon and terminal ileum biopsies with 16 S rRNA-based fluorescent probes: commensal bacteria live in suspension and have no direct contact with epithelial cells. Inflamm Bowel Dis 11, 865–871.
Viljanen M, Savilahti E, Haahtela T, Juntunen-Backman K, Korpela R, Poussa T et al. (2005). Probiotics in the treatment of atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome in infants: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Allergy 60, 494–500.
Wallner G, Amann R, Beisker W (1993). Optimizing fluorescent in situ hybridisation of suspend cells with rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes for the flow cytometric identification of microorganisms. Cytometry 14, 136–143.
Wang KY, Li SN, Liu CS, Perng DS, Su YC, Wu DC et al. (2004). Effects of ingesting Lactobacillus- and Bifidobacterium-containing yogurt in subjects with colonized Helicobacter pylori. Am J Clin Nutr 80, 737–741.
Welling GW, Wildeboer-Veloo ACM, Lemmers NWM, Tian R, Gao Q, Raangs GC et al. (2002). Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) as a tool in intestinal bacteriology. Biosci Microflora 20, 115–120.
Welling GW, Wildeboer-Veloo L, Raangs GC, Franks AH, Jansen GJ, Tonk RHJ et al. (2000). Variations of bacterial populations in human faeces measured by FISH with group-specific 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotid probes. Biosci Microflora 19, 79–84.
Weston S, Halbert H, Richmond P, Prescott SL (2005). Effects of probiotics on atopic dermatitis: a randomised controlled trial. Arch Dis Child 90, 892–897.
Wildt S, Munck LK, Vinter-Jensen L, Fischer Hansen B, Nordgaard-Lassen I, Christensen N et al. (2006). Probiotic treatment of collagenous colitis: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial with Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp lactis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 12, 395–401.
Xiao JZ, Kondo S, Takahashi N, Miyaji K, Oshida K, Hiramatsu A et al. (2003). Effects of milk products fermented by Bifidobacterium longum on blood lipids in rats and healthy adult male volunteers. J Dairy Sci 86, 2452–2461.
Yamano T, Iino H, Takada M, Blum S, Rochat F, Fukushima Y (2006). Improvement of the human intestinal flora by ingestion of the probiotic strain Lactobacillus johnsonii La1. Br J Nutr 95, 303–312.
Acknowledgements
We thank U Helms and P Möckel for technical assistance and R Schubert for advise on statistical analysis. In addition, we thank all volunteers for providing serum and faecal samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guarantor: G Jahreis.
Contributors: AK and GJ were responsible for the study design. AK conducted the study and was responsible for data acquisition and analysis. AK performed the statistical analysis and drafted the manuscript. UF established the FISH methodology and validated the oligonucleotide probes. HV performed the immunological analysis. GJ was responsible for obtaining funding and acted as adviser throughout the study. UF and GJ were responsible for the critical review of the manuscript. None of the authors had any personal or financial conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klein, A., Friedrich, U., Vogelsang, H. et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus 74-2 and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp lactis DGCC 420 modulate unspecific cellular immune response in healthy adults. Eur J Clin Nutr 62, 584–593 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602761
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602761
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bifidobacteria in Fermented Dairy Foods: A Health Beneficial Outlook
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins (2023)
-
Impact of processing degree on fermentation profile and chemopreventive effects of oat and waxy barley in LT97 colon adenoma cells
European Food Research and Technology (2021)
-
Gut Microbiome and Precision Nutrition in Heart Failure: Hype or Hope?
Current Heart Failure Reports (2021)
-
The effect of synbiotics supplementation on anthropometric indicators and lipid profiles in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled trial
Lipids in Health and Disease (2020)
-
A review of probiotic supplementation in healthy adults: helpful or hype?
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2019)