Abstract
Objective: To study the long-term impact of stunting during infancy on maturation, growth and fat distribution in adolescence.
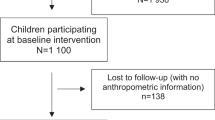
Design: A cohort of 406 Senegalese adolescent girls of rural origin underwent clinical and growth assessments every year from 1995 to 1999.
Subjects: Mean coverage rate was 82% at each round. Adolescent girls were 11.4±0.5 y of age in 1995 and 15.5±0.5 y of age in 1999. Their growth status during infancy was known. About 20% of the girls had a height–age (H–age) below −2 Z-scores (chronic malnutrition or stunting) when they were 6–18 months of age. As adolescents, the girls were divided into two groups on the basis of H–age: those stunted and those non-stunted during infancy.
Measurements: Sexual maturation was assessed by stage of breast development and menarche. Height, body mass, sitting height, bi-iliac and bi-acromial diameters, and six skinfolds were measured.
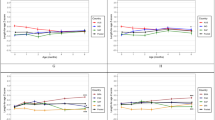
Results: Differences in sexual maturation between previously stunted and non-stunted girls were not significant. Girls stunted at infancy caught up in body weight and subcutaneous fat mass during puberty, but they did not catch up on stature, sitting height or skeletal breadths (bi-acromial and bi-iliac diameters) until the final observation in 1999. Stunted girls did not have less subcutaneous fat (sum of six skinfolds) or a lower BMI. Regional variation in subcutaneous fat distribution (Z-score profile) indicated greater accretion at the biceps and subscapular sites in stunted compared to the non-stunted girls. Regional fat distribution was also assessed by principal component analysis (PCA) performed on the residuals of the six skinfolds measured during the final round (1999). PCA identified three components. Stunted and non-stunted girls were similar for the first (trunk–extremity contrast) and second (anterior–posterior contrast) components. However, there was a difference for the third component: stunted girls tended to accumulate more subcutaneous fat on the upper part of the body (trunk or arms) than non-stunted girls.
Conclusion: Stunted Senegalese girls have a potential for catching up in growth during puberty. The greater accumulation of subcutaneous fat on the upper body in stunted girls may be a consequence of complex hormonal adjustments at the onset of puberty.
Sponsorship: Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD anciennement ORSTOM) and the Nestlé Foundation.
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2001) 55, 50–58
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor: E Bénéfice.
Contributors: EB was the leading contributor, at all stages, to the study. DG, KBS and RMM were contributors. DG carried out the second part of the study; KBS was responsible for the 1995 round. All contributors participated in the analysis, and in writing the paper.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bénéfice, E., Garnier, D., Simondon, K. et al. Relationship between stunting in infancy and growth and fat distribution during adolescence in Senegalese girls. Eur J Clin Nutr 55, 50–58 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601121
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601121
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association between anthropometric criteria and body composition among children aged 6–59 months with severe acute malnutrition: a cross-sectional assessment from India
BMC Nutrition (2022)
-
Body composition of children with moderate and severe undernutrition and after treatment: a narrative review
BMC Medicine (2019)
-
Are stunted young Indonesian children more likely to be overweight, thin, or have high blood pressure in adolescence?
International Journal of Public Health (2017)
-
Paternal under-nutrition programs metabolic syndrome in offspring which can be reversed by antioxidant/vitamin food fortification in fathers
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Should public health interventions aimed at reducing childhood overweight and obesity be gender-focused?
BMC Public Health (2010)