Summary:
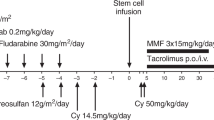
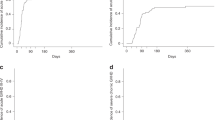
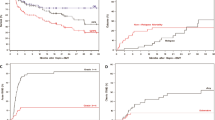
Children with multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) and risk organ involvement who fail to respond to conventional chemotherapy have an extremely poor prognosis. Myeloablative stem cell transplantation (SCT) as a possible salvage approach for these patients has been associated with a high risk of transplant-related mortality. Therefore, allogeneic stem cell transplantation following a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen (RIC-SCT) has recently been performed as an alternative salvage approach. We report on the experience with allogeneic RIC-SCT in nine pediatric high-risk LCH patients. Conditioning regimen included fludarabine in all patients, melphalan in eight patients, total lymphoid irradiation in six patients, total body irradiation in two, antithymocyte globulin in five, and Campath in four patients. RIC-SCT was well tolerated with regard to common procedure-related complications. Two patients died 50 and 69 days after RIC-SCT, respectively. Seven out of the nine patients survived and showed no signs of disease activity (including one with nonengraftment and full autologous hematopoietic recovery) after median follow-up of 390 days post-SCT. Based on this observation, we conclude that RIC-SCT is a feasible procedure with low transplant-related morbidity and mortality and a promising new salvage approach for high-risk LCH patients with resistant risk organ involvement.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arceci RJ . The histiocytoses: the fall of the Tower of Babel. Eur J Cancer 1999; 35: 747–767; discussion 767–769.
Egeler RM, Favara BE, van Meurs M et al. Differential in situ cytokine profiles of Langerhans-like cells and T cells in Langerhans cell histiocytosis: abundant expression of cytokines relevant to disease and treatment. Blood 1999; 94: 4195–4201.
Favara BE, Jaffe R, Egeler RM . Macrophage activation and hemophagocytic syndrome in langerhans cell histiocytosis: report of 30 cases. Pediatr Dev Pathol 2002; 5: 130–140.
Gadner H, Heitger A, Grois N et al. Treatment strategy for disseminated Langerhans cell histiocytosis. DAL HX-83 Study Group. Med Pediatr Oncol 1994; 23: 72–80.
Gadner H, Grois N, Arico M et al. A randomized trial of treatment for multisystem Langerhans' cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr 2001; 138: 728–734.
Minkov M, Grois N, Heitger A et al. Response to initial treatment of multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis: an important prognostic indicator. Med Pediatr Oncol 2002; 39: 581–585.
Gadner H . Langerhans' cell histiocytosis – still an unsolved problem. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1999; 16: 489–493.
Minkov M, Grois N, Broadbent V et al. Cyclosporine A therapy for multisystem langerhans cell histiocytosis. Med Pediatr Oncol 1999; 33: 482–485.
Ringden O, Ahstrom L, Lonnqvist B et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in a patient with chemotherapy-resistant progressive histiocytosis X. N Engl J Med 1987; 316: 733–735.
Stoll M, Freund M, Schmid H et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for Langerhans' cell histiocytosis. Cancer 1990; 66: 284–288.
Greinix HT, Storb R, Sanders JE, Petersen FB . Marrow transplantation for treatment of multisystem progressive Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Bone Marrow Transplant 1992; 10: 39–44.
Frost JD, Wiersma SR . Progressive Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an infant with Klinefelter syndrome successfully treated with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1996; 18: 396–400.
Conter V, Reciputo A, Arrigo C et al. Bone marrow transplantation for refractory Langerhans' cell histiocytosis. Haematologica 1996; 81: 468–471.
Broadbent V, Ladisch S . Results of the Histiocyte Society BMT salvage therapy questionnaire. Med Pediatr Oncol 1998; 31: 45 (abstr.).
Egeler RM, Anderson RA, Wolff JEA et al. Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Med Pediatr Oncol 1999; 32: 238 (abstr.).
Ayas M, Mustafa M, Al-Mahr M, Solh H . Bone marrow transplantation as a salvage therapy for refractory disseminated Langerhans histiocytosis. Med Pediatr Oncol 1999; 32: 238 (abstr.).
Kinugawa N, Imashuku S, Hirota Y et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) in Japan. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 935–938.
Suminoe A, Matsuzaki A, Hattori H et al. Unrelated cord blood transplantation for an infant with chemotherapy-resistant progressive Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2001; 23: 633–636.
Nagarajan R, Neglia J, Ramsay N, Baker KS . Successful treatment of refractory Langerhans cell histiocytosis with unrelated cord blood transplantation. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2001; 23: 629–632.
Hale GA, Bowman LC, Woodard JP et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for children with histiocytic disorders: use of TBI and omission of etoposide in the conditioning regimen. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 981–986.
Akkari V, Donadieu J, Piguet C et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with severe Langerhans cell histiocytosis and hematological dysfunction: experience of the French Langerhans Cell Study Group. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 1097–1103.
Amrolia P, Gaspar HB, Hassan A et al. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation for congenital immunodeficiencies. Blood 2000; 96: 1239–1246.
Jacobsohn DA, Duerst R, Tse W, Kletzel M . Reduced intensity haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation for treatment of non-malignant diseases in children. Lancet 2004; 364: 156–162.
Meyer-Wentrup F, Foell J, Wawer A, Burdach S . Unrelated cord blood transplantation in an infant with severe multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis: clinical outcome, engraftment and culture of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 875–876.
Histiocytosis syndromes in children. Writing Group of the Histiocyte Society. Lancet 1987; 1: 208–209.
Broadbent V, Gadner H, Komp DM, Ladisch S . Histiocytosis syndromes in children: II. Approach to the clinical and laboratory evaluation of children with Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Clinical Writing Group of the Histiocyte Society. Med Pediatr Oncol 1989; 17: 492–495.
Broadbent V, Gadner H . Current therapy for Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am 1998; 12: 327–338.
Slavin S, Nagler A, Naparstek E et al. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation and cell therapy as an alternative to conventional bone marrow transplantation with lethal cytoreduction for the treatment of malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases. Blood 1998; 91: 756–763.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974; 18: 295–304.
Lansky SB, List MA, Lansky LL et al. The measurement of performance in childhood cancer patients. Cancer 1987; 60: 1651–1656.
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Egeler RM, Favara BE, Laman JD, Claassen E . Abundant expression of CD40 and CD40-ligand (CD154) in paediatric Langerhans cell histiocytosis lesions. Eur J Cancer 2000; 36: 2105–2110.
Kannourakis G, Abbas A . The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Br J Cancer Suppl 1994; 23: S37–40.
Nezelof C, Basset F . An hypothesis Langerhans cell histiocytosis: the failure of the immune system to switch from an innate to an adaptive mode. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2004; 42: 398–400.
Rao K, Nanduri V, Brock P et al. Bone marrow transplant as salvage for multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2004; 43: 196 (abstr.).
Matthes-Martin S, Lion T, Haas OA et al. Lineage-specific chimaerism after stem cell transplantation in children following reduced intensity conditioning: potential predictive value of NK cell chimaerism for late graft rejection. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1934–1942.
Jordan MB, McClain KL, Xiaotian Y et al. Anti-CD52 antibody, alemtuzumab, binds to Langerhans cells in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2005; 44: 251–254.
Henter JI, Karlen J, Calming U et al. Successful treatment of Langerhans'-cell histiocytosis with etanercept. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 1577–1578.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr G Surico and Dr P Muggeo, II Pediatric Clinic, University of Bari, Italy, and Dr D Koliouskas, Ippokration Hospital, Thessaloniki, Greece, for referring their patients to our institution. We also thank Dr J Foell, University Hospital Halle, Germany, for his assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steiner, M., Matthes-Martin, S., Attarbaschi, A. et al. Improved outcome of treatment-resistant high-risk Langerhans cell histiocytosis after allogeneic stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning. Bone Marrow Transplant 36, 215–225 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705015
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705015
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nationwide retrospective review of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children with refractory Langerhans cell histiocytosis
International Journal of Hematology (2020)
-
Pediatric Langerhans cell histiocytosis: the impact of mutational profile on clinical progression and late sequelae
Annals of Hematology (2019)
-
Successful treatment of adult Langerhans cell histiocytosis with intensified chemotherapy
International Journal of Hematology (2015)
-
Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: A Single Centre Experience
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (2014)
-
Histiocytose agressive à cellules de Langerhans 20 ans après un cancer du sein : à propos d’un cas
Journal Africain du Cancer / African Journal of Cancer (2013)