Summary:
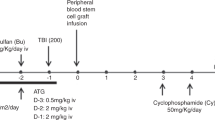
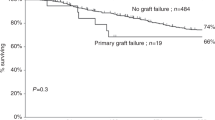
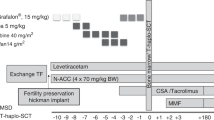
Both increased graft rejection and increased graft vs host disease (GVHD) remain obstacles to success for unrelated donor (URD) BMT for patients with SAA. Partial T cell depletion (PTCD) may decrease the risk of severe GVHD, while still maintaining sufficient donor T lymphocytes to ensure engraftment. We report on 12 patients with SAA who underwent PTCD URD BMT. All patients had failed medical therapy or relapsed following initial responses, and were transfusion dependent. The median age was 6 years, and there were five males. Donors were matched for four patients, and mismatched for eight. All patients received total body irradiation with either Ara-C or thiotepa and cyclophosphamide. PTCD was accomplished using monoclonal antibody T10B9 or OKT3 and complement. All patients engrafted, with a median time of 18 days to ANC >500. Only one patient had greater than grade II acute GVHD; two patients had limited and one patient extensive chronic GVHD. Nine patients are alive and transfusion independent at a median months post BMT. Three patients died from infection or renal failure. This series suggests that an aggressive immunosuppressive conditioning regimen with PTCD results in successful engraftment and minimal GVHD in pediatric patients with SAA, even with HLA mismatched donors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacigalupo A, Bruno B, Saracco P et al. Antilymphocyte globulin, cyclosporine, prednisolone, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for severe aplastic anemia: an update of the GITMO/EBMT study on 100 patients. Blood 2000; 95: 1931–1934.
Bunin N, Leahey A, Kamani N, August C . Bone marrow transplantation in pediatric patients with severe aplastic anemia: cyclophosphamide and anti-thymocyte globulin conditioning followed by recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage stimulating factor. Am J Pediatri Hematol/Oncol 1996; 18: 68–71.
Gillio A, Boulad F, Small T et al. Comparison of long-term outcome of children with severe aplastic anemia treated with immunosuppression vs bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood and Marrow Transplant 1997; 3: 18–24.
Sanders J, Storb R, Anasetti C et al. Marrow transplant experience for children with severe aplastic anemia. Am J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol 1994; 16: 43–49.
Bacigalupo A, Broccia G, Corda G et al. Antilymphocyte globulin, cyclosporin, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with acquired severe aplastic anemia (SAA): a pilot study of the EBMT SAA Working Party. Blood 1995; 85: 1348–1353.
Kernan NA, Bartsch G, Ash RC et al. Analysis of 462 transplantations from unrelated donors facilitated by the National Marrow Donor Program. N Engl J Med 1993; 328: 593–602.
Kojima S, Matsuyama T, Kato S et al. Outcome of 154 patients with severe aplastic anemia who received transplants from unrelated donors: the Japan Marrow Donor Program. Blood 2002; 100: 799–803.
Hurley C, Maiers M, Ng J et al. Large-scale DNA-based typing of HLA-A and HLA-B at low resolution is highly accurate, specific and reliable. Tissue Antigens 2000; 55: 352–358.
Deeg H, Storb R . Graft-versus-host disease: pathophysiological and clinical aspects. Ann Rev Med 1984; 3: 11–24.
Bunin N, Leahey A, Dunn S . Related donor liver transplant for veno-occlusive disease following T-depleted unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation. Transplant 1996; 61: 664–666.
Godder K, Pati A, Abhyankar S et al. De novo chronic graft-versus-host disease presenting as hemolytic anemia following partially mismatched related donor bone marrow transplant. Bone Marrow Tranplant 1997; 19: 813–817.
Gluckman E, Socie G, Devergie A et al. Bone marrow transplantation in 107 patients with severe aplastic anemia using cyclophosphamide and thoraco-abdominal irradiation for conditioning: long-term follow-up. Blood 1991; 78: 2451–2455.
McGlave P, Haake R, Miller W et al. Therapy of severe aplastic anemia in young adults and children with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1987; 70: 1325–1330.
Storb R, Etzioni R, Anasetti C et al. Cyclophosphamide combined with antithymocyte globulin in preparation for allogeneic marrow transplants in patients with aplastic anemia. Blood 1994; 84: 941–949.
Rosenfeld S, Kimball J, Vining D, Young N . Intensive immunosuppression with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine as treatment for severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood 1995; 85: 3058–3065.
Kojima S, Horibe K, Inaba J et al. Long-term outcome of acquired aplastic anaemia in children: comparison between immunosuppressive therapy and bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 321–328.
Ohara A, Kojima S, Hamajima N et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myelogenous leukemia as a late clonal complication in children with acquired aplastic anemia. Blood 1997; 90: 1009–1013.
Kojima S, Tsuchida M, Kudoh T et al. Risk factors for evolution of acquired aplastic anemia into myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia after immunosuppressive therapy in children. Blood 2002; 100: 786–790.
Deeg H, Amylon M, Harris R et al. Marrow transplantation from unrelated donors for patients with aplastic anemia (AA)-optimisaton of a conditioning regimen. Blood 1999; 94: hash;3147.
Davies S, Wagner J, Defor T et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children and adolescents with aplastic anaemia or myelodysplasia. Br J Haematol 1997; 96: 749–756.
Kojima S, Inaba J, Yoshimi A et al. Unrelated donor marrow transplantation in children with severe aplastic anaemia using cyclophosphamide, anti-thymocyte globulin and total body irradiation. Br J Haematol 2001; 114: 706–711.
Margolis D, Camitta B, Pietryga D et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation to treat severe aplastic anaemia in children and young adults. Br J Haematol 1996; 94: 65–72.
Vassilou G, Webb D, Pamphilon D et al. Improved outcome of alternative donor bone marrow transplantation in children with severe aplastic anaemia using a conditioning regimen containing low-dose total body irradiation, cyclophosphamide and Campath. Br J Haematol 2001; 114: 701–705.
Benesch M, Urban C, Sykora K et al. Transplantation of highly purified CD34+ progenitor cells from alternative donors in children with refractory severe aplastic anemia. Br J Haematol 2004; 125: 58–63.
Woodard P, Cunningham J, Benaim E et al. Effective donor lymphohematopoietic reconstitution after haploidentical CD34+-selected hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children with refractory severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 411–418.
Davies S, Ramsay N, Haake R et al. Comparison of engraftment in recipients of matched sibling or unrelated donor marrow allografts. Bone Marrow Transplantation 1994; 13: 51–57.
Beatty P, Anasetti C, Hansen J et al. Marrow transplantation from unrelated donors for treatment of hematologic malignancies: effect of mismatching for one HLA locus. Blood 1993; 81: 249–253.
Davies S, Shu X, Blazar B et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation: influence of HLA A and B incompatibility on outcome. Blood 1995; 86: 1636–1642.
Champlin R, Passweg J, Zhang M et al. T cell depletion of bone marrow transplants for leukemia from donors other than HLA-identical siblings: advantage of T cell antibodies with narrow specificities. Blood 2000; 95: 3996–4000.
Kernan N, Bordignon C, Heller G et al. Graft failure after T-cell-depleted human leukocyte antigen identical marrow transplants for leukemia: I. Analysis of risk factors and results of secondary transplants. Blood 1989; 74: 2227–2236.
Kernan NA, Collins J, Juliano L et al. Clonable T lymphocytes in T-cell-depleted bone marrow transplants correlate with development of graft-v-host disease. Blood 1986; 68: 770–773.
Walter E, Greenberg P, Gilbert M et al. Reconstitution of cellular immunity against cytomegalovirus in recipients of allogeneic bone marrow by transfer of T cell clones from the donor. New Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1038–1044.
Bacigalupo A, Lamparelli T, Bruzzi P et al. Antithymocyte globulin for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in transplants from unrelated donors: 2 randomized studies from Gruppo Italiano Trapianti Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Blood 2001; 98: 2942–2947.
Burnett A, Hann I, Robertson A et al. Prevention of graft-versus-host disease by ex vivo T-cell-depletion: reduction in graft failure augmented with total body irradiation. Leukemia 1988; 20: 300–303.
Mineishi S, Longo W, Atkinson M et al. Addition of high-dose Ara-C to the BMT conditioning regimen reduces leukemia relapse without an increase in toxicity. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 23: 1217–1222.
Aversa F, Terenzi A, Carotti A et al. Improved outcome with T cell depleted bone marrow transplantation for acute leukemia. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 1545–1550.
Socie G, Henry-Amar M, Cosset J et al. Increased incidence of solid malignant tumors after bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Blood 1991; 78: 277–279.
Bhatia S, Louie A, Bhatia R et al. Solid cancers after bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 464–471.
Deeg H, Anasetti C, Petersdorf E et al. Cyclophosphamide plus ATG conditioning is insufficient for sustained hematopoietic reconstitution in patients with severe aplastic anemia transplanted with marrow from HLA-A, B, DRB matched unrelated donors. Blood 1994; 83: 3417–3418.
Wagner J, Deeg H, Seidel K et al. Bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia from genotypically HLA-nonidentical relatives. An update of the Seattle experience. Transplantation 1996; 61: 54–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bunin, N., Aplenc, R., Iannone, R. et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children with severe aplastic anemia: minimal GVHD and durable engraftment with partial T cell depletion. Bone Marrow Transplant 35, 369–373 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704803
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704803
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Matched Sibling Versus Matched Unrelated Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children with Severe Acquired Aplastic Anemia: Experience of the Polish Pediatric Group for Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (2012)
-
Outcomes of matched sibling and alternative donor stem cell transplantation for 26 children with severe aplastic anemia
International Journal of Hematology (2010)
-
Current European practice in pediatric myeloablative conditioning
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
Unrelated cord blood transplantation in children with idiopathic severe aplastic anemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
Risk-adapted procedures for HSCT from alternative donor in children with severe aplastic anaemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)