Abstract
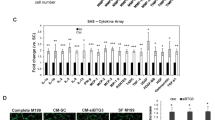
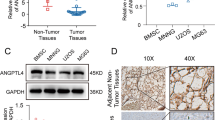
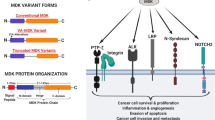
Tumor suppressors with extracellular function are likely to have advantages as targets for cancer therapy, but few are known. Here, we focused on angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4), which is a secreted glycoprotein involved in lipoprotein metabolism and angiogenesis, is methylation-silenced in human cancers, but has unclear roles in cancer development and progression. We found a deletion mutation in its coiled-coil domain at its N-terminal in human gastric cancers, in addition to hypermethylation of the ANGPTL4 promoter CpG islands. Forced expression of wild-type ANGPTL4, but not ANGPTL4 with the deletion, at physiological levels markedly suppressed in vivo tumorigenicity and tumor angiogenesis, indicating that the latter caused the former. Tumor-derived ANGPTL4 suppressed in vitro vascular tube formation and proliferation of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells, partly due to suppression of ERK signaling. These showed that ANGPTL4 is a genetically and epigenetically inactivated secreted tumor suppressor that inhibits tumor angiogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knudson AG . Two genetic hits (more or less) to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2001; 1: 157–162.
Baylin SB, Jones PA . A decade of exploring the cancer epigenome - biological and translational implications. Nat Rev Cancer 2011; 11: 726–734.
Kishore R, Losordo DW . Gene therapy for restenosis: biological solution to a biological problem. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2007; 42: 461–468.
Lane DP, Cheok CF, Lain S . p53-based cancer therapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010; 2: a001222.
Levine AJ, Oren M . The first 30 years of p53: growing ever more complex. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 749–758.
Suzuki H, Watkins DN, Jair KW, Schuebel KE, Markowitz SD, Chen WD et al. Epigenetic inactivation of SFRP genes allows constitutive WNT signaling in colorectal cancer. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 417–422.
Shi Y, He B, You L, Jablons DM . Roles of secreted frizzled-related proteins in cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007; 28: 1499–1504.
Kaneda A, Kaminishi M, Yanagihara K, Sugimura T, Ushijima T . Identification of silencing of nine genes in human gastric cancers. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 6645–6650.
Hattori N, Okochi-Takada E, Kikuyama M, Wakabayashi M, Yamashita S, Ushijima T . Methylation silencing of angiopoietin-like 4 in rat and human mammary carcinomas. Cancer Sci 2011; 102: 1337–1343.
Miida T, Hirayama S . Impacts of angiopoietin-like proteins on lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular events. Curr Opin Lipidol 2010; 21: 70–75.
Yang YH, Wang Y, Lam KS, Yau MH, Cheng KK, Zhang J et al. Suppression of the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling cascade and inhibition of angiogenesis by the carboxyl terminus of angiopoietin-like protein 4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008; 28: 835–840.
Ito Y, Oike Y, Yasunaga K, Hamada K, Miyata K, Matsumoto S et al. Inhibition of angiogenesis and vascular leakiness by angiopoietin-related protein 4. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 6651–6657.
Chomel C, Cazes A, Faye C, Bignon M, Gomez E, Ardidie-Robouant C et al. Interaction of the coiled-coil domain with glycosaminoglycans protects angiopoietin-like 4 from proteolysis and regulates its antiangiogenic activity. FASEB J 2009; 23: 940–949.
Hermann LM, Pinkerton M, Jennings K, Yang L, Grom A, Sowders D et al. Angiopoietin-like-4 is a potential angiogenic mediator in arthritis. Clin Immunol 2005; 115: 93–101.
Ma T, Jham BC, Hu J, Friedman ER, Basile JR, Molinolo A et al. Viral G protein-coupled receptor up-regulates Angiopoietin-like 4 promoting angiogenesis and vascular permeability in Kaposi's sarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 14363–14368.
Li KQ, Li WL, Peng SY, Shi XY, Tang HL, Liu YB . Anti-tumor effect of recombinant retroviral vector-mediated human ANGPTL4 gene transfection. Chin Med J (Engl) 2004; 117: 1364–1369.
Galaup A, Cazes A, Le Jan S, Philippe J, Connault E, Le Coz E et al. Angiopoietin-like 4 prevents metastasis through inhibition of vascular permeability and tumor cell motility and invasiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 18721–18726.
Padua D, Zhang XH, Wang Q, Nadal C, Gerald WL, Gomis RR et al. TGFbeta primes breast tumors for lung metastasis seeding through angiopoietin-like 4. Cell 2008; 133: 66–77.
Zhu P, Tan MJ, Huang RL, Tan CK, Chong HC, Pal M et al. Angiopoietin-like 4 protein elevates the prosurvival intracellular O2-:H2O2 ratio and confers anoikis resistance to tumors. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 401–415.
Nakayama T, Hirakawa H, Shibata K, Abe K, Nagayasu T, Taguchi T . Expression of angiopoietin-like 4 in human gastric cancer: ANGPTL4 promotes venous invasion. Oncol Rep 2010; 24: 599–606.
Issa JP . CpG island methylator phenotype in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 988–993.
Ushijima T . Epigenetic field for cancerization. J Biochem Mol Biol 2007; 40: 142–150.
Hato T, Tabata M, Oike Y . The role of angiopoietin-like proteins in angiogenesis and metabolism. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2008; 18: 6–14.
Oike Y, Akao M, Kubota Y, Suda T . Angiopoietin-like proteins: potential new targets for metabolic syndrome therapy. Trends Mol Med 2005; 11: 473–479.
Ge H, Yang G, Huang L, Motola DL, Pourbahrami T, Li C . Oligomerization and regulated proteolytic processing of angiopoietin-like protein 4. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 2038–2045.
Yin W, Romeo S, Chang S, Grishin NV, Hobbs HH, Cohen JC . Genetic variation in ANGPTL4 provides insights into protein processing and function. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 13213–13222.
Mei R, Galipeau PC, Prass C, Berno A, Ghandour G, Patil N et al. Genome-wide detection of allelic imbalance using human SNPs and high-density DNA arrays. Genome Res 2000; 10: 1126–1137.
Hoglund M, Gorunova L, Andren-Sandberg A, Dawiskiba S, Mitelman F, Johansson B . Cytogenetic and fluorescence in situ hybridization analyses of chromosome 19 aberrations in pancreatic carcinomas: frequent loss of 19p13.3 and gain of 19q13.1-13.2. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1998; 21: 8–16.
Trojan J, Brieger A, Raedle J, Esteller M, Zeuzem S . 5′-CpG island methylation of the LKB1/STK11 promoter and allelic loss at chromosome 19p13.3 in sporadic colorectal cancer. Gut 2000; 47: 272–276.
Sobottka SB, Haase M, Fitze G, Hahn M, Schackert HK, Schackert G . Frequent loss of heterozygosity at the 19p13.3 locus without LKB1/STK11 mutations in human carcinoma metastases to the brain. J Neurooncol 2000; 49: 187–195.
Tanner JE, Forte A, Panchal C . Nucleosomes bind fibroblast growth factor-2 for increased angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Res 2004; 2: 281–288.
Zhu H, Zhang L, Wu S, Teraishi F, Davis JJ, Jacob D et al. Induction of S-phase arrest and p21 overexpression by a small molecule 2[[3-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy) propyl] amino]ethanol in correlation with activation of ERK. Oncogene 2004; 23: 4984–4992.
Asada K, Ando T, Niwa T, Nanjo S, Watanabe N, Okochi-Takada E et al. FHL1 on chromosome X is a single-hit gastrointestinal tumor-suppressor gene and contributes to the formation of an epigenetic field defect. Oncogene 2012; 32: 2140–2149.
Ando T, Yoshida T, Enomoto S, Asada K, Tatematsu M, Ichinose M et al. DNA methylation of microRNA genes in gastric mucosae of gastric cancer patients: its possible involvement in the formation of epigenetic field defect. Int J Cancer 2009; 124: 2367–2374.
Enomoto S, Maekita T, Tsukamoto T, Nakajima T, Nakazawa K, Tatematsu M et al. Lack of association between CpG island methylator phenotype in human gastric cancers and methylation in their background non-cancerous gastric mucosae. Cancer Sci 2007; 98: 1853–1861.
Ota N, Kawakami K, Okuda T, Takehara A, Hiranuma C, Oyama K et al. Prognostic significance of p16INK4a hypermethylation in non-small cell lung cancer is evident by quantitative DNA methylation analysis. Anticancer Res 2006; 26: 3729–3732.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Masabumi Shibuya, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, for his expert advice. This study was supported by the Third-term Comprehensive Cancer Control Strategy from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan and by National Cancer Center Research and Development Fund. YN is a recipient of a Research Resident Fellowships from the Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okochi-Takada, E., Hattori, N., Tsukamoto, T. et al. ANGPTL4 is a secreted tumor suppressor that inhibits angiogenesis. Oncogene 33, 2273–2278 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.174
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.174
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ANGPTL4 accelerates ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma carcinogenesis and angiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment by activating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and interacting with ESM1
Journal of Translational Medicine (2024)
-
ANGPTL4 regulates ovarian cancer progression by activating the ERK1/2 pathway
Cancer Cell International (2024)
-
Suppression of angiopoietin-like 4 reprograms endothelial cell metabolism and inhibits angiogenesis
Nature Communications (2023)
-
High glucose-induced IL-7/IL-7R upregulation of dermal fibroblasts inhibits angiogenesis in a paracrine way in delayed diabetic wound healing
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
ANGPTL4 negatively regulates the progression of osteosarcoma by remodeling branched-chain amino acid metabolism
Cell Death Discovery (2022)