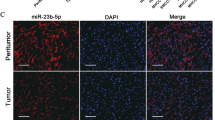
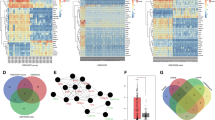
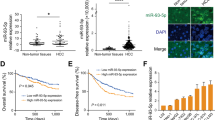
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNAs that can act as oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes in human cancer. Emerging evidence indicates that deregulation of miRNAs contributes to the hepatocarcinogenesis. In the present study, we demonstrated that the levels of miR-520e were dramatically decreased in examined hepatoma cell lines and clinical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues. Moreover, we found that DNA hypermethylation in the upstream region of miR-520e resulted in the downregulation of miR-520e. Next, we demonstrated that introduction of miR-520e dramatically suppressed the growth of hepatoma cells in vitro and in vivo, whereas silencing the expression of miR-520e by anti-miR-520e resulted in a promoted cell proliferation, suggesting that miR-520e may be a novel tumor suppressor. Further studies revealed that NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) was one of the direct target genes of miR-520e, as miR-520e directly bound to the 3′untranslated region of NIK, which reduced the expression of NIK at the levels of mRNA and protein. Moreover, silencing of NIK was able to inhibit the growth of hepatoma cells, similar to the effect of miR-520e overexpression on growth of hepatoma cells. Meanwhile, the knockdown of NIK expression reversed the enhanced proliferation mediated by anti-miR-520e. In addition, miR-520e significantly decreased the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) and depressed the transcriptional activity and nuclear translocation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) (p65). These results suggest that miR-520e suppresses the growth of hepatoma cells by targeting NIK involving the NIK/p-ERK1/2/NF-κB signaling pathway. Finally, we showed that the intratumoral injection with miR-520e was able to directly repress the growth of hepatoma cells in the nude mice. Thus, our finding provides new insight into the mechanism of hepatocarcinogenesis, indicating a therapeutic potential of miR-520e in the treatment of HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Bartel DP . (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297.
Bartel DP, Chen CZ . (2004). Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet 5: 396–400.
Brown KD, Claudio E, Siebenlist U . (2008). The roles of the classical and alternative nuclear factor-kappaB pathways: potential implications for autoimmunity and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 10: 212.
Calin GA, Croce CM . (2006). MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 857–866.
Calin GA, Croce CM . (2007). Chromosomal rearrangements and microRNAs: a new cancer link with clinical implications. J Clin Invest 117: 2059–2066.
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP . (2004). MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303: 83–86.
Chen KH, Weng MS, Lin JK . (2007). Tangeretin suppresses IL-1beta-induced cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression through inhibition of p38 MAPK, JNK, and AKT activation in human lung carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 73: 215–227.
Croce CM, Calin GA . (2005). miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 122: 6–7.
Cui W, Zhang Y, Hu N, Shan C, Zhang S, Zhang W et al (2010). miRNA-520b and miR-520e sensitize breast cancer cells to complement attack via directly targeting 3′UTR of CD46. Cancer Biol Ther 10: 232–241.
Datta J, Kutay H, Nasser MW, Nuovo GJ, Wang B, Majumder S et al (2008). Methylation mediated silencing of microRNA-1 gene and its role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 68: 5049–5058.
Dhawan P, Richmond A . (2002). A novel NF-kappa B-inducing kinase-MAPK signaling pathway up-regulates NF-kappa B activity in melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 277: 7920–7928.
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL . (2007). Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 132: 2557–2576.
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z, Zanesi N, Callegari E et al (2007). MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 15805–15810.
Farazi PA, DePinho RA . (2006). Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 674–687.
Fazi F, Racanicchi S, Zardo G, Starnes LM, Mancini M, Travaglini L et al (2007). Epigenetic silencing of the myelopoiesis regulator microRNA-223 by the AML1/ETO oncoprotein. Cancer Cell 12: 457–466.
Foehr ED, Bohuslav J, Chen LF, DeNoronha C, Geleziunas R, Lin X et al (2000). The NF-kappa B-inducing kinase induces PC12 cell differentiation and prevents apoptosis. J Biol Chem 275: 34021–34024.
Gessi M, Zur Muehlen A, Lauriola L, Gardiman MP, Giangaspero F, Pietsch T . (2011). TP53, beta-Catenin and c-myc/N-myc status in embryonal tumours with ependymoblastic rosettes. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37: 406–413.
Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Fornari F, Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Liu CG et al (2007). Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 67: 6092–6099.
Gramantieri L, Fornari F, Callegari E, Sabbioni S, Lanza G, Croce CM et al (2008). MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 12: 2189–2204.
Gregory RI, Shiekhattar R . (2005). MicroRNA biogenesis and cancer. Cancer Res 65: 3509–3512.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . (2008). Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 132: 344–362.
Ji J, Wang XW . (2009). New kids on the block: diagnostic and prognostic microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 8: 1686–1693.
Jiang J, Gusev Y, Aderca I, Mettler TA, Nagorney DM, Brackett DJ et al (2008). Association of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 14: 419–427.
Kent OA, Mendell JT . (2006). A small piece in the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes. Oncogene 25: 6188–6196.
Kim VN . (2005). MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 376–385.
Kim VN, Nam JW . (2006). Genomics of microRNA. Trends Genet 22: 165–173.
Li M, Lee KF, Lu Y, Clarke I, Shih D, Eberhart C et al (2009a). Frequent amplification of a chr19q13.41 microRNA polycistron in aggressive primitive neuroectodermal brain tumors. Cancer Cell 16: 533–546.
Li Q, Wang G, Shan JL, Yang ZX, Wang HZ, Feng J et al (2010). MicroRNA-224 is upregulated in HepG2 cells and involved in cellular migration and invasion. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25: 164–171.
Li S, Fu H, Wang Y, Tie Y, Xing R, Zhu J et al (2009b). MicroRNA-101 regulates expression of the v-fos FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog (FOS) oncogene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 49: 1194–1202.
Liang L, Wong CM, Ying Q, Fan DN, Huang S, Ding J et al (2010). MicroRNA-125b suppressesed human liver cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting oncogene LIN28B2. Hepatology 52: 1731–1740.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al (2005). MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435: 834–838.
Lujambio A, Ropero S, Ballestar E, Fraga MF, Cerrato C, Setien F et al (2007). Genetic unmasking of an epigenetically silenced microRNA in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 67: 1424–1429.
Lyle R, Watanabe D, te Vruchte D, Lerchner W, Smrzka OW, Wutz A et al (2000). The imprinted antisense RNA at the Igf2r locus overlaps but does not imprint Mas1. Nat Genet 25: 19–21.
Mercatelli N, Coppola V, Bonci D, Miele F, Costantini A, Guadagnoli M et al (2008). The inhibition of the highly expressed miR-221 and miR-222 impairs the growth of prostate carcinoma xenografts in mice. PLoS One 3: e4029.
Nishina T, Yamaguchi N, Gohda J, Semba K, Inoue J . (2009). NIK is involved in constitutive activation of the alternative NF-kappaB pathway and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388: 96–101.
Nojima M, Suzuki H, Toyota M, Watanabe Y, Maruyama R, Sasaki S et al (2007). Frequent epigenetic inactivation of SFRP genes and constitutive activation of Wnt signaling in gastric cancer. Oncogene 26: 4699–4713.
Rangaswami H, Bulbule A, Kundu GC . (2004). Nuclear factor-inducing kinase plays a crucial role in osteopontin-induced MAPK/IkappaBalpha kinase-dependent nuclear factor kappaB-mediated promatrix metalloproteinase-9 activation. J Biol Chem 279: 38921–38935.
Roux PP, Blenis J . (2004). ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68: 320–344.
Saito Y, Liang G, Egger G, Friedman JM, Chuang JC, Coetzee GA et al (2006). Specific activation of microRNA-127 with downregulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 9: 435–443.
Sato H, Suzuki H, Toyota M, Nojima M, Maruyama R, Sasaki S et al (2007). Frequent epigenetic inactivation of DICKKOPF family genes in human gastrointestinal tumors. Carcinogenesis 28: 2459–2466.
Selaru FM, Olaru AV, Kan T, David S, Cheng Y, Mori Y et al (2009). MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinoma and regulates programmed cell death 4 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3. Hepatology 49: 1595–1601.
Shan C, Xu F, Zhang S, You J, You X, Qiu L et al (2010). Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes liver cell proliferation via a positive cascade loop involving arachidonic acid metabolism and p-ERK1/2. Cell Res 20: 563–575.
Xu T, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, Ge YY, Yun JP, Zhuang SM . (2009). MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates G1/S transition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 50: 113–121.
Yamaguchi N, Ito T, Azuma S, Ito E, Honma R, Yanagisawa Y et al (2009). Constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappaB is preferentially involved in the proliferation of basal-like subtype breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Sci 100: 1668–1674.
Ying SY, Lin SL . (2005). Intronic microRNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326: 515–520.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2009CB521702) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81071624).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Shan, C., Kong, G. et al. MicroRNA-520e suppresses growth of hepatoma cells by targeting the NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK). Oncogene 31, 3607–3620 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.523
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.523
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
HLF promotes ovarian cancer progression and chemoresistance via regulating Hippo signaling pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Expression study of microRNA cluster on chromosome 19 (C19MC) in tumor tissue and serum of breast cancer patient
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
Nectin-4 promotes osteosarcoma progression and metastasis through activating PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling by down-regulation of miR-520c-3p
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
miR-185-5p response to usnic acid suppresses proliferation and regulating apoptosis in breast cancer cell by targeting Bcl2
Biological Research (2020)
-
The NF-κB signalling pathway in colorectal cancer: associations between dysregulated gene and miRNA expression
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2018)