Abstract
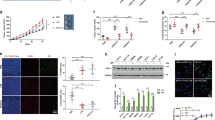
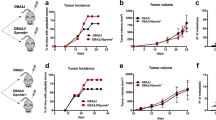
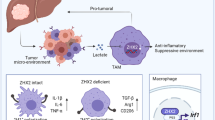
Cancer cells recruit monocytes, macrophages and other inflammatory cells by producing abundant chemoattractants and growth factors, such as macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF/CSF-1) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2), to promote tumor growth and dissemination. An understanding of the mechanisms that target cancer cells and regulate tumor microenvironment is essential in designing anticancer therapies. Here, we showed that serum amyloid-A (SAA) and cathelicidin (LL-37) stimulated M-CSF and MCP-1 expression with or without lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration; conversely, lipoxin-A4 (LXA4) and annexin-A1 (ANXA1) inhibited LPS-induced M-CSF and MCP-1 production by human (HepG2) and mouse (H22) hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HCCs). The effects of LXA4, ANXA1, SAA and LL-37 were dependent on the activation of their mutual cell-surface receptor formyl peptide receptor-2 (FPR2) and subsequent ROS–MAPK–NF-kB signalings. Furthermore, our results indicated that LPS switched macrophages into an IL-10lowIL-12high M1 profile, whereas M-CSF+MCP-1 and FPR2 agonists skewed them into M2 (IL-10highIL-12low). In that respect, through modulating the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3), LXA4 and ANXA1 induced monocyte differentiation into M2a+M2c-like cells and showed antitumorigenetic activities, whereas SAA, LL-37 and M-CSF+MCP-1 led to M2b- or M2d-like polarization, which exacerbated HCC invasion in vitro and in vivo, respectively. Our results suggest that FPR2 has an appreciable pleiotropic regulator role in tumor immunoediting.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C et al. (2009). Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: how intimate is the relationship? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171: 59–76.
Allavena P, Sica A, Solinas G, Porta C, Mantovani A . (2008). The inflammatory micro-environment in tumor progression: the role of tumor-associated macrophages. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 66: 1–9.
Balkwill F, Mantovani A . (2001). Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357: 539–545.
Chiang N, Serhan CN, Dahlen SE, Drazen JM, Hay DW, Rovati GE et al. (2006). The lipoxin receptor ALX: potent ligand-specific and stereoselective actions in vivo. Pharmacol Rev 58: 463–487.
Cocco E, Bellone S, El-Sahwi K, Cargnelutti M, Buza N, Tavassoli FA et al. (2010). Serum amyloid A: a novel biomarker for endometrial cancer. Cancer 116: 843–851.
Coimbra M, Kuijpers SA, van Seters SP, Storm G, Schiffelers RM . (2009). Targeted delivery of anti-inflammatory agents to tumors. Curr Pharm Des 15: 1825–1843.
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C, Mantovani A . (2009). Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 30: 1073–1081.
Craig M, Ying C, Loberg RD . (2008). Co-inoculation of prostate cancer cells with U937 enhances tumor growth and angiogenesis in vivo. J Cell Biochem 103: 1–8.
De Y, Chen Q, Schmidt AP, Anderson GM, Wang JM, Wooters J et al. (2000). LL-37, the neutrophil granule- and epithelial cell-derived cathelicidin, utilizes formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (FPRL1) as a receptor to chemoattract human peripheral blood neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells. J Exp Med 192: 1069–1074.
Duff MD, Mestre J, Maddali S, Yan ZP, Stapleton P, Daly JM . (2007). Analysis of gene expression in the tumor-associated macrophage. J Surg Res 142: 119–128.
Duluc D, Corvaisier M, Blanchard S, Catala L, Descamps P, Gamelin E et al. (2009). Interferon-gamma reverses the immunosuppressive and protumoral properties and prevents the generation of human tumor-associated macrophages. Int J Cancer 125: 367–373.
Duluc D, Delneste Y, Tan F, Moles MP, Grimaud L, Lenoir J et al. (2007). Tumor-associated leukemia inhibitory factor and IL-6 skew monocyte differentiation into tumor-associated macrophage-like cells. Blood 110: 4319–4330.
El Kebir D, Jozsef L, Filep JG . (2008). Opposing regulation of neutrophil apoptosis through the formyl peptide receptor-like 1/lipoxin A4 receptor: implications for resolution of inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 84: 600–606.
Emoto M, Danbara H, Yoshikai Y . (1992). Induction of gamma/delta T cells in murine salmonellosis by an avirulent but not by a virulent strain of Salmonella choleraesuis. J Exp Med 176: 363–372.
Fan S, Gao M, Meng Q, Laterra JJ, Symons MH, Coniglio S et al. (2005). Role of NF-kappaB signaling in hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-mediated cell protection. Oncogene 24: 1749–1766.
Fiore S, Ryeom SW, Weller PF, Serhan CN . (1992). Lipoxin recognition sites. Specific binding of labeled lipoxin A4 with human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 267: 16168–16176.
Fujimoto H, Sangai T, Ishii G, Ikehara A, Nagashima T, Miyazaki M et al. (2009). Stromal MCP-1 in mammary tumors induces tumor-associated macrophage infiltration and contributes to tumor progression. Int J Cancer 125: 1276–1284.
Gao JL, Murphy PM . (1993). Species and subtype variants of the N-formyl peptide chemotactic receptor reveal multiple important functional domains. J Biol Chem 268: 25395–25401.
Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, Roberts HR, Williams AC, Paraskeva C et al. (2009). The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis 30: 377–386.
Janssen-Heininger YM, Macara I, Mossman BT . (1999). Cooperativity between oxidants and tumor necrosis factor in the activation of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB: requirement of Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinases in the activation of NF-kappaB by oxidants. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 20: 942–952.
Kortylewski M, Xin H, Kujawski M, Lee H, Liu Y, Harris T et al. (2009). Regulation of the IL-23 and IL-12 balance by Stat3 signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 15: 114–123.
Kuninaka S, Yano T, Yokoyama H, Fukuyama Y, Terazaki Y, Uehara T et al. (2000). Direct influences of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IL-6) on the proliferation and cell-surface antigen expression of cancer cells. Cytokine 12: 8–11.
Lawrence T . (2007). Inflammation and cancer: a failure of resolution? Trends Pharmacol Sci 28: 162–165.
Li Y, Ye D . (2010). Cancer therapy by targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 10: 782–796.
Li YS, Wu P, Zhou XY, Chen JG, Cai L, Wang F et al. (2008). Formyl-peptide receptor like 1: a potent mediator of the Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ current ICRAC. Arch Biochem Biophys 478: 110–118.
Martinez FO, Sica A, Mantovani A, Locati M . (2008). Macrophage activation and polarization. Front Biosci 13: 453–461.
McMahon B, Stenson C, McPhillips F, Fanning A, Brady HR, Godson C . (2000). Lipoxin A4 antagonizes the mitogenic effects of leukotriene D4 in human renal mesangial cells. Differential activation of MAP kinases through distinct receptors. J Biol Chem 275: 27566–27575.
Miao T, Wu D, Zhang Y, Bo X, Subang MC, Wang P et al (2006). Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 suppresses the ability of activated signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 to stimulate neurite growth in rat primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci 26: 9512–9519.
Mills CD, Kincaid K, Alt JM, Heilman MJ, Hill AM . (2000). M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J Immunol 164: 6166–6173.
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, Timans JC, Xu Y, Hunte B et al. (2000). Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 13: 715–725.
Panzer U, Steinmetz OM, Turner JE, Meyer-Schwesinger C, von Ruffer C, Meyer TN et al. (2009). Resolution of renal inflammation: a new role for NF-kappaB1 (p50) in inflammatory kidney diseases. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297: F429–F439.
Peng J, Yang XO, Chang SH, Yang J, Dong C . (2010). IL-23 signaling enhances Th2 polarization and regulates allergic airway inflammation. Cell Res 20: 62–71.
Pepinsky RB, Sinclair LK, Browning JL, Mattaliano RJ, Smart JE, Chow EP et al. (1986). Purification and partial sequence analysis of a 37-kDa protein that inhibits phospholipase A2 activity from rat peritoneal exudates. J Biol Chem 261: 4239–4246.
Perretti M, Chiang N, La M, Fierro IM, Marullo S, Getting SJ et al. (2002a). Endogenous lipid- and peptide-derived anti-inflammatory pathways generated with glucocorticoid and aspirin treatment activate the lipoxin A4 receptor. Nat Med 8: 1296–1302.
Perretti M, Ingegnoli F, Wheller SK, Blades MC, Solito E, Pitzalis C . (2002b). Annexin 1 modulates monocyte–endothelial cell interaction in vitro and cell migration in vivo in the human SCID mouse transplantation model. J Immunol 169: 2085–2092.
Pollard JW . (2004). Tumour-educated macrophages promote tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 71–78.
Sandri S, Rodriguez D, Gomes E, Monteiro HP, Russo M, Campa A . (2008). Is serum amyloid A an endogenous TLR4 agonist? J Leukoc Biol 83: 1174–1180.
Serhan CN, Hamberg M, Samuelsson B . (1984). Lipoxins: novel series of biologically active compounds formed from arachidonic acid in human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 5335–5339.
Serhan CN, Yacoubian S, Yang R . (2008). Anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators. Annu Rev Pathol 3: 279–312.
Sironi M, Martinez FO, D'Ambrosio D, Gattorno M, Polentarutti N, Locati M et al. (2006). Differential regulation of chemokine production by Fcgamma receptor engagement in human monocytes: association of CCL1 with a distinct form of M2 monocyte activation (M2b, Type 2). J Leukoc Biol 80: 342–349.
Spite M, Serhan CN . (2010). Novel lipid mediators promote resolution of acute inflammation: impact of aspirin and statins. Circ Res 107: 1170–1184.
Su SB, Gong W, Gao JL, Shen W, Murphy PM, Oppenheim JJ et al. (1999). A seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor, FPRL1, mediates the chemotactic activity of serum amyloid A for human phagocytic cells. J Exp Med 189: 395–402.
Teng MW, Andrews DM, McLaughlin N, von Scheidt B, Ngiow SF, Moller A et al. (2010). IL-23 suppresses innate immune response independently of IL-17A during carcinogenesis and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 8328–8333.
Varney ML, Olsen KJ, Mosley RL, Bucana CD, Talmadge JE, Singh RK . (2002). Monocyte/macrophage recruitment, activation and differentiation modulate interleukin-8 production: a paracrine role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor angiogenesis. in vivo 16: 471–477.
Wang Q, Ni H, Lan L, Wei X, Xiang R, Wang Y . (2010). Fra-1 protooncogene regulates IL-6 expression in macrophages and promotes the generation of M2d macrophages. Cell Res 20: 701–712.
Ye RD, Boulay F, Wang JM, Dahlgren C, Gerard C, Parmentier M et al. (2009). International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIII. Nomenclature for the formyl peptide receptor (FPR) family. Pharmacol Rev 61: 119–161.
Zhang L, Wu P, Jin SW, Yuan P, Wan JY, Zhou XY et al. (2007). Lipoxin A4 negatively regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced differentiation of RAW264.7 murine macrophages into dendritic-like cells. Chin Med J (Engl) 120: 981–987.
Zhang T, Ma Z, Wang R, Wang Y, Wang S, Cheng Z et al. (2010a). Thrombin facilitates invasion of ovarian cancer along peritoneum by inducing monocyte differentiation toward tumor-associated macrophage-like cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59: 1097–1108.
Zhang Z, Huang L, Zhao W, Rigas B . (2010b). Annexin 1 induced by anti-inflammatory drugs binds to NF-kappaB and inhibits its activation: anticancer effects in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 70: 2379–2388.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Charles N Serhan for helpful comments about FPR2. We also appreciate all anonymous reviewers for helpful suggestions on quality improvement of the paper. This work was supported by China Scholarship Council Fellowship No. 2009616073 and National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants 30570726 and 30772154.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Cai, L., Wang, H. et al. Pleiotropic regulation of macrophage polarization and tumorigenesis by formyl peptide receptor-2. Oncogene 30, 3887–3899 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.112
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.112
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Chicken cathelicidin-2 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages
Veterinary Research (2022)
-
Lipoxin alleviates oxidative stress: a state-of-the-art review
Inflammation Research (2022)
-
FPR2 participates in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) progression through RhoA-mediated M2 macrophage polarization
Journal of Ovarian Research (2021)
-
Inflammation and tumor progression: signaling pathways and targeted intervention
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)
-
Peritoneal macrophages are impaired in cathelicidin-deficient mice systemically challenged with Escherichia coli
Cell and Tissue Research (2021)