Abstract
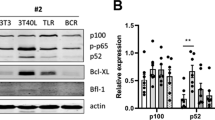
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells circulating in peripheral blood (PB) differ from the leukemic fraction in lymph nodes (LNs) with respect to cell division and drug sensitivity. CD40 stimulation of PB CLL cells in vitro results in chemoresistance and provides a partial model for the LN microenvironment. The TLR9 ligand CpG induces proliferation in immunoglobulin variable heavy-chain-unmutated CLL, but apoptosis in immunoglobulin variable heavy-chain-mutated CLL. To juxtapose proliferative with antiapoptotic signals, we investigated the effects of CpG in the context of CD40 ligation in mutated versus unmutated CLL cells in this study. Prolonged CD40 ligation induced classical, followed by alternative nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), activity in both subgroups, correlating with enhanced Bfl-1 and Bcl-XL levels, respectively. A dichotomy in NF-κB signaling occurred on combined CD40/TLR9 triggering. This induced declining p52 and Bcl-XL levels, and reversed chemoresistance only in mutated cells, whereas unmutated cells proliferated, maintained p52 and Bcl-XL and remained chemoresistant. The pivotal contribution of Bcl-XL to chemoresistance was shown by the BH3 mimetic ABT-737 and RNA interference. Finally, in ex vivo LN samples, p52, p65 and Bcl-XL levels were highly expressed, corroborating the in vitro findings. Thus, a distinction in NF-κB activation and drug susceptibility in mutated versus unmutated (LN-like) CLL cells was uncovered, which was causally linked to Bcl-XL levels.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caligaris-Cappio F . (2003). Role of the microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 123: 380–388.
Caligaris-Cappio F, Ghia P . (2008). Novel insights in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: are we getting closer to understanding the pathogenesis of the disease? J Clin Oncol 26: 4497–4503.
Chen L, Apgar J, Huynh L, Dicker F, Giago-McGahan T, Rassenti L et al. (2005). ZAP-70 directly enhances IgM signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 105: 2036–2041.
Chiorazzi N . (2007). Cell proliferation and death: forgotten features of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 20: 399–413.
Compagno M, Lim WK, Grunn A, Nandula SV, Brahmachary M, Shen Q et al. (2009). Mutations of multiple genes cause deregulation of NF-kappaB in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 459: 717–721.
Damle RN, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Albesiano E, Fais F, Yan XJ et al. (2002). B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells express a surface membrane phenotype of activated, antigen-experienced B lymphocytes. Blood 99: 4087–4093.
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. (1999). Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 94: 1840–1847.
Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lenz G, Tolar P, Young RM, Romesser PB et al. (2010). Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 463: 88–92.
Decker T, Peschel C . (2001). Effect of immunostimulatory CpG-oligonucleotides in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Leuk Lymphoma 42: 301–307.
Decker T, Schneller F, Sparwasser T, Tretter T, Lipford GB, Wagner H et al. (2000). Immunostimulatory CpG-oligonucleotides cause proliferation, cytokine production, and an immunogenic phenotype in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood 95: 999–1006.
Endo T, Nishio M, Enzler T, Cottam HB, Fukuda T, James DF et al. (2007). BAFF and APRIL support chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cell survival through activation of the canonical NF-kappaB pathway. Blood 109: 703–710.
Fais F, Ghiotto F, Hashimoto S, Sellars B, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. (1998). Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express restricted sets of mutated and unmutated antigen receptors. J Clin Invest 102: 1515–1525.
Furman RR, Asgary Z, Mascarenhas JO, Liou HC, Schattner EJ . (2000). Modulation of NF-kappa B activity and apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. J Immunol 164: 2200–2206.
Ghia P, Circosta P, Scielzo C, Vallario A, Camporeale A, Granziero L et al. (2005). Differential effects on CLL cell survival exerted by different microenvironmental elements. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 294: 135–145.
Granziero L, Ghia P, Circosta P, Gottardi D, Strola G, Geuna M et al. (2001). Survivin is expressed on CD40 stimulation and interfaces proliferation and apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 97: 2777–2783.
Hallaert DY, Jaspers A, van Noesel CJ, van Oers MH, Kater AP, Eldering E . (2008). c-Abl kinase inhibitors overcome CD40-mediated drug resistance in CLL: implications for therapeutic targeting of chemoresistant niches. Blood 112: 5141–5149.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . (2008). Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 132: 344–362.
Hewamana S, Alghazal S, Lin TT, Clement M, Jenkins C, Guzman ML et al. (2008). The NF-kappaB subunit Rel A is associated with in vitro survival and clinical disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and represents a promising therapeutic target. Blood 111: 4681–4689.
Homig-Holzel C, Hojer C, Rastelli J, Casola S, Strobl LJ, Muller W et al. (2008). Constitutive CD40 signaling in B cells selectively activates the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway and promotes lymphomagenesis. J Exp Med 205: 1317–1329.
Kater AP, Evers LM, Remmerswaal EB, Jaspers A, Oosterwijk MF, van Lier RA et al. (2004). CD40 stimulation of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells enhances the anti-apoptotic profile, but also Bid expression and cells remain susceptible to autologous cytotoxic T-lymphocyte attack. Br J Haematol 127: 404–415.
Kato M, Sanada M, Kato I, Sato Y, Takita J, Takeuchi K et al. (2009). Frequent inactivation of A20 in B-cell lymphomas. Nature 459: 712–716.
Keating MJ, Chiorazzi N, Messmer B, Damle RN, Allen SL, Rai KR et al. (2003). Biology and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 5: 153–175.
Kipps TJ . (2007). The B-cell receptor and ZAP-70 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 20: 415–424.
Klein U, Tu Y, Stolovitzky GA, Mattioli M, Cattoretti G, Husson H et al. (2001). Gene expression profiling of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia reveals a homogeneous phenotype related to memory B cells. J Exp Med 194: 1625–1638.
Klinman DM . (2004). Immunotherapeutic uses of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 249–258.
Lankester AC, van Schijndel GM, van der Schoot CE, van Oers MH, van Noesel CJ, van Lier RA . (1995). Antigen receptor nonresponsiveness in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood 86: 1090–1097.
Lee HH, Dadgostar H, Cheng Q, Shu J, Cheng G . (1999). NF-kappaB-mediated up-regulation of Bcl-x and Bfl-1/A1 is required for CD40 survival signaling in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 9136–9141.
Longo PG, Laurenti L, Gobessi S, Petlickovski A, Pelosi M, Chiusolo P et al. (2007). The Akt signaling pathway determines the different proliferative capacity of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells from patients with progressive and stable disease. Leukemia 21: 110–120.
Lopez-Guerra M, Roue G, Perez-Galan P, Alonso R, Villamor N, Montserrat E et al. (2009). p65 activity and ZAP-70 status predict the sensitivity of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to the selective IkappaB kinase inhibitor BMS-345541. Clin Cancer Res 15: 2767–2776.
Messmer BT, Messmer D, Allen SL, Kolitz JE, Kudalkar P, Cesar D et al. (2005). In vivo measurements document the dynamic cellular kinetics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. J Clin Invest 115: 755–764.
Munk P, Reed J . (2004). Microenvironmental interactions and survival of CLL B-cells. Leuk Lymphoma 45: 2365–2372.
Nedellec S, Renaudineau Y, Bordron A, Berthou C, Porakishvili N, Lydyard PM et al. (2005). B cell response to surface IgM cross-linking identifies different prognostic groups of B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. J Immunol 174: 3749–3756.
Nishio M, Endo T, Tsukada N, Ohata J, Kitada S, Reed JC et al. (2005). Nurselike cells express BAFF and APRIL, which can promote survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via a paracrine pathway distinct from that of SDF-1alpha. Blood 106: 1012–1020.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. (2005). An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435: 677–681.
Oscier DG, Gardiner AC, Mould SJ, Glide S, Davis ZA, Ibbotson RE et al. (2002). Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in CLL: clinical stage, IGVH gene mutational status, and loss or mutation of the p53 gene are independent prognostic factors. Blood 100: 1177–1184.
Pleyer L, Egle A, Hartmann TN, Greil R . (2009). Molecular and cellular mechanisms of CLL: novel therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6: 405–418.
Ramakrishnan P, Wang W, Wallach D . (2004). Receptor-specific signaling for both the alternative and the canonical NF-kappaB activation pathways by NF-kappaB-inducing kinase. Immunity 21: 477–489.
Rifkin IR, Leadbetter EA, Busconi L, Viglianti G, Marshak-Rothstein A . (2005). Toll-like receptors, endogenous ligands, and systemic autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev 204: 27–42.
Rodriguez A, Martinez N, Camacho FI, Ruiz-Ballesteros E, Algara P, Garcia JF et al. (2004). Variability in the degree of expression of phosphorylated IkappaBalpha in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cases with nodal involvement. Clin Cancer Res 10: 6796–6806.
Romano MF, Lamberti A, Tassone P, Alfinito F, Costantini S, Chiurazzi F et al. (1998). Triggering of CD40 antigen inhibits fludarabine-induced apoptosis in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 92: 990–995.
Rosenwald A, Alizadeh AA, Widhopf G, Simon R, Davis RE, Yu X et al. (2001). Relation of gene expression phenotype to immunoglobulin mutation genotype in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med 194: 1639–1647.
Schneider P . (2005). The role of APRIL and BAFF in lymphocyte activation. Curr Opin Immunol 17: 282–289.
Silke J, Brink R . (2010). Regulation of TNFRSF and innate immune signalling complexes by TRAFs and cIAPs. Cell Death Differ 17: 35–45.
Skaug B, Jiang X, Chen ZJ . (2009). The role of ubiquitin in NF-kappaB regulatory pathways. Annu Rev Biochem 78: 769–796.
Smit LA, Hallaert DY, Spijker R, de GB, Jaspers A, Kater AP et al. (2007). Differential Noxa/Mcl-1 balance in peripheral versus lymph node chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells correlates with survival capacity. Blood 109: 1660–1668.
Sun SC, Ley SC . (2008). New insights into NF-kappaB regulation and function. Trends Immunol 29: 469–478.
Tas SW, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Hajji N, Schuitemaker JH, van der Sluijs KF, May MJ et al. (2007). Noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling in dendritic cells is required for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) induction and immune regulation. Blood 110: 1540–1549.
Vallabhapurapu S, Matsuzawa A, Zhang W, Tseng PH, Keats JJ, Wang H et al. (2008). Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-kappaB signaling. Nat Immunol 9: 1364–1370.
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. (2006). The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 10: 389–399.
van Gent R, Kater AP, Otto SA, Jaspers A, Borghans JA, Vrisekoop N et al. (2008). In vivo dynamics of stable chronic lymphocytic leukemia inversely correlate with somatic hypermutation levels and suggest no major leukemic turnover in bone marrow. Cancer Res 68: 10137–10144.
Vogler M, Butterworth M, Majid A, Walewska RJ, Sun XM, Dyer MJ et al. (2008). Concurrent up-regulation of BCL-XL and BCL2A1 induces approximately 1000-fold resistance to ABT-737 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 113: 4403–4413.
Wierda WG, Johnson MM, Do KA, Manshouri T, Dey A, O'Brien S et al. (2003). Plasma interleukin 8 level predicts for survival in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 120: 452–456.
Willimott S, Baou M, Naresh K, Wagner SD . (2007). CD154 induces a switch in pro-survival Bcl-2 family members in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 138: 721–732.
Zarnegar BJ, Wang Y, Mahoney DJ, Dempsey PW, Cheung HH, He J et al. (2008). Noncanonical NF-kappaB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK. Nat Immunol 9: 1371–1378.
Acknowledgements
We thank professor Carel JM van Noessel and Dr Richard Bende (department of pathology, AMC) for obtaining lymph node material of CLL patients. We are very grateful to the patients for donating blood samples. ABT-737, a BH3 mimetic, was obtained under MTA from Abbott (Abbott Park, courtesy Dr S Rosenberg). This work was supported by the Dutch Cancer Society (KWF), Grant no. UvA 2007-3856.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tromp, J., Tonino, S., Elias, J. et al. Dichotomy in NF-κB signaling and chemoresistance in immunoglobulin variable heavy-chain-mutated versus unmutated CLL cells upon CD40/TLR9 triggering. Oncogene 29, 5071–5082 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.248
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.248
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ibrutinib sensitizes CLL cells to venetoclax by interrupting TLR9-induced CD40 upregulation and protein translation
Leukemia (2023)
-
Progress in understanding the mechanisms of resistance to BCL-2 inhibitors
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
Activation and expansion of T-follicular helper cells in chronic lymphocytic leukemia nurselike cell co-cultures
Leukemia (2022)
-
Regulation of Bcl-XL by non-canonical NF-κB in the context of CD40-induced drug resistance in CLL
Cell Death & Differentiation (2021)
-
Biological significance of monoallelic and biallelic BIRC3 loss in del(11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression
Blood Cancer Journal (2021)