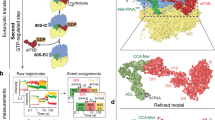
Abstract
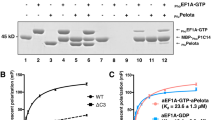
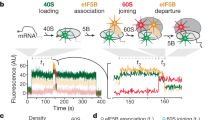
In contrast to prokaryotic elongation factor EF-Tu, which delivers aminoacyl-tRNAs to the ribosomal A-site, eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2 binds methionyl initiator transfer RNA (Met-tRNAiMet) to the P-site of the 40S ribosomal subunit. The results of directed hydroxyl radical probing experiments to map binding of Saccharomyces cerevisiae eIF2 on the ribosome and on Met-tRNAiMet revealed that eIF2γ primarily contacts the acceptor stem of Met-tRNAiMet and identified a key binding interface between domain III of eIF2γ and 18S rRNA helix h44 on the 40S subunit. Whereas the analogous domain III of EF-Tu contacts the T stem of tRNAs, biochemical analyses demonstrated that eIF2γ domain III is important for ribosome, not Met-tRNAiMet. Thus, despite their structural similarity, eIF2 and EF-Tu bind tRNAs in substantially different manners, and we propose that the tRNA-binding domain III of EF-Tu has acquired a new ribosome-binding function in eIF2γ.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmeing, T.M. et al. The crystal structure of the ribosome bound to EF-Tu and aminoacyl-tRNA. Science 326, 688–694 (2009).
Voorhees, R.M., Schmeing, T.M., Kelley, A.C. & Ramakrishnan, V. The mechanism for activation of GTP hydrolysis on the ribosome. Science 330, 835–838 (2010).
Sonenberg, N. & Hinnebusch, A.G. Regulation of translation initiation in eukaryotes: mechanisms and biological targets. Cell 136, 731–745 (2009).
Fekete, C.A. et al. N- and C-terminal residues of eIF1A have opposing effects on the fidelity of start codon selection. EMBO J. 26, 1602–1614 (2007).
Lomakin, I.B., Kolupaeva, V.G., Marintchev, A., Wagner, G. & Pestova, T.V. Position of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF1 on the 40S ribosomal subunit determined by directed hydroxyl radical probing. Genes Dev. 17, 2786–2797 (2003).
Passmore, L.A. et al. The eukaryotic translation initiation factors eIF1 and eIF1A induce an open conformation of the 40S ribosome. Mol. Cell 26, 41–50 (2007).
Maag, D., Fekete, C.A., Gryczynski, Z. & Lorsch, J.R. A conformational change in the eukaryotic translation preinitiation complex and release of eIF1 signal recognition of the start codon. Mol. Cell 17, 265–275 (2005).
Yu, Y. et al. Position of eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF1A on the 40S ribosomal subunit mapped by directed hydroxyl radical probing. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 5167–5182 (2009).
Carter, A.P. et al. Crystal structure of an initiation factor bound to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Science 291, 498–501 (2001).
Saini, A.K., Nanda, J.S., Lorsch, J.R. & Hinnebusch, A.G. Regulatory elements in eIF1A control the fidelity of start codon selection by modulating tRNAiMet binding to the ribosome. Genes Dev. 24, 97–110 (2010).
Roll-Mecak, A., Alone, P., Cao, C., Dever, T.E. & Burley, S.K. X-ray structure of translation initiation factor eIF2γ: implications for tRNA and eIF2α binding. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 10634–10642 (2004).
Schmitt, E., Blanquet, S. & Mechulam, Y. The large subunit of initiation factor aIF2 is a close structural homologue of elongation factors. EMBO J. 21, 1821–1832 (2002).
Sokabe, M., Yao, M., Sakai, N., Toya, S. & Tanaka, I. Structure of archaeal translational initiation factor 2βγ-GDP reveals significant conformational change of the β-subunit and switch 1 region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 13016–13021 (2006).
Stolboushkina, E. et al. Crystal structure of the intact archaeal translation initiation factor 2 demonstrates very high conformational flexibility in the α- and β-subunits. J. Mol. Biol. 382, 680–691 (2008).
Yatime, L., Mechulam, Y., Blanquet, S. & Schmitt, E. Structural switch of the γ subunit in an archaeal aIF2αγ heterodimer. Structure 14, 119–128 (2006).
Yatime, L., Mechulam, Y., Blanquet, S. & Schmitt, E. Structure of an archaeal heterotrimeric initiation factor 2 reveals a nucleotide state between the GTP and the GDP states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 18445–18450 (2007).
Rabl, J., Leibundgut, M., Ataide, S.F., Haag, A. & Ban, N. Crystal structure of the eukaryotic 40S ribosomal subunit in complex with initiation factor 1. Science 331, 730–736 (2011).
Nissen, P. et al. Crystal structure of the ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu, and a GTP analog. Science 270, 1464–1472 (1995).
Basavappa, R. & Sigler, P.B. The 3 Å crystal structure of yeast initiator tRNA: functional implications in initiator/elongator discrimination. EMBO J. 10, 3105–3111 (1991).
Ben-Shem, A., Jenner, L., Yusupova, G. & Yusupov, M. Crystal structure of the eukaryotic ribosome. Science 330, 1203–1209 (2010).
Selmer, M. et al. Structure of the 70S ribosome complexed with mRNA and tRNA. Science 313, 1935–1942 (2006).
Dorris, D.R., Erickson, F.L. & Hannig, E.M. Mutations in GCD11, the structural gene for eIF-2γ in yeast, alter translational regulation of GCN4 and the selection of the start site for protein synthesis. EMBO J. 14, 2239–2249 (1995).
Hinnebusch, A.G. Translational regulation of GCN4 and the general amino acid control of yeast. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 59, 407–450 (2005).
Harashima, S. & Hinnebusch, A.G. Multiple GCD genes required for repression of GCN4, a transcriptional activator of amino acid biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6, 3990–3998 (1986).
Erickson, F.L. & Hannig, E.M. Ligand interactions with eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2: role of the γ-subunit. EMBO J. 15, 6311–6320 (1996).
Sanderson, L.E. & Uhlenbeck, O.C. Directed mutagenesis identifies amino acid residues involved in elongation factor Tu binding to yeast Phe-tRNAPhe. J. Mol. Biol. 368, 119–130 (2007).
Sanderson, L.E. & Uhlenbeck, O.C. The 51–63 base pair of tRNA confers specificity for binding by EF-Tu. RNA 13, 835–840 (2007).
Dong, J. et al. Genetic identification of yeast 18S rRNA residues required for efficient recruitment of initiator tRNAMet and AUG selection. Genes Dev. 22, 2242–2255 (2008).
Pisarev, A.V. et al. Specific functional interactions of nucleotides at key 3 and +4 positions flanking the initiation codon with components of the mammalian 48S translation initiation complex. Genes Dev. 20, 624–636 (2006).
Battiste, J.L., Pestova, T.V., Hellen, C.U.T. & Wagner, G. The eIF1A solution structure reveals a large RNA-binding surface important for scanning function. Mol. Cell 5, 109–119 (2000).
Agrawal, R.K., Penczek, P., Grassucci, R.A. & Frank, J. Visualization of elongation factor G on the Escherichia coli 70S ribosome: the mechanism of translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6134–6138 (1998).
Connell, S.R. et al. Structural basis for interaction of the ribosome with the switch regions of GTP-bound elongation factors. Mol. Cell 25, 751–764 (2007).
Gao, Y.G. et al. The structure of the ribosome with elongation factor G trapped in the post-translocational state. Science 326, 694–699 (2009).
Shin, B.S. et al. rRNA suppressor of a eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B/initiation factor 2 mutant reveals a binding site for translational GTPases on the small ribosomal subunit. Mol. Cell. Biol. 29, 808–821 (2009).
Simonetti, A. et al. Structure of the 30S translation initiation complex. Nature 455, 416–420 (2008).
Unbehaun, A. et al. Position of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF5B on the 80S ribosome mapped by directed hydroxyl radical probing. EMBO J. 26, 3109–3123 (2007).
Yatime, L., Schmitt, E., Blanquet, S. & Mechulam, Y. Functional molecular mapping of archaeal translation initiation factor 2. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 15984–15993 (2004).
Asano, K. et al. Multiple roles for the carboxyl terminal domain of eIF5 in translation initiation complex assembly and GTPase activation. EMBO J. 20, 2326–2337 (2001).
Laurino, J.P., Thompson, G.M., Pacheco, E. & Castilho, B.A. The β subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 binds mRNA through the lysine repeats and a region comprising the C2-C2 motif. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 173–181 (1999).
Aström, S.U. & Byström, A.S. Rit1, a tRNA backbone-modifying enzyme that mediates initiator and elongator tRNA discrimination. Cell 79, 535–546 (1994).
Aström, S.U., von Pawel-Rammingen, U. & Bystrom, A.S. The yeast initiator tRNAMet can act as an elongator tRNAMetin vivo. J. Mol. Biol. 233, 43–58 (1993).
Dale, T., Sanderson, L.E. & Uhlenbeck, O.C. The affinity of elongation factor Tu for an aminoacyl-tRNA is modulated by the esterified amino acid. Biochemistry 43, 6159–6166 (2004).
LaRiviere, F.J., Wolfson, A.D. & Uhlenbeck, O.C. Uniform binding of aminoacyl-tRNAs to elongation factor Tu by thermodynamic compensation. Science 294, 165–168 (2001).
Kapp, L.D. & Lorsch, J.R. GTP-dependent recognition of the methionine moiety on initiator tRNA by translation factor eIF2. J. Mol. Biol. 335, 923–936 (2004).
Hinnebusch, A.G. A hierarchy of trans-acting factors modulate translation of an activator of amino acid biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 5, 2349–2360 (1985).
Culver, G.M. & Noller, H.F. Directed hydroxyl radical probing of RNA from iron(II) tethered to proteins in ribonucleoprotein complexes. Methods Enzymol. 318, 461–475 (2000).
Lowe, T.M. & Eddy, S.R. A computational screen for methylation guide snoRNAs in yeast. Science 283, 1168–1171 (1999).
McPheeters, D.S., Christensen, A., Young, E.T., Stormo, G. & Gold, L. Translational regulation of expression of the bacteriophage T4 lysozyme gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 14, 5813–5826 (1986).
Acker, M.G., Kolitz, S.E., Mitchell, S.F., Nanda, J.S. & Lorsch, J.R. Reconstitution of yeast translation initiation. Methods Enzymol. 430, 111–145 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Hinnebusch, R. Green and our colleagues in the Dever, Lorsch and Hinnebusch laboratories for advice and helpful discussions. We thank J. Fringer (US National Institutes of Health), D. Eyler, S. He, H. Zaher (all Johns Hopkins University) and O. Uhlenbeck (Northwestern University) for protocols and reagents. This work was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, US National Institutes of Health (T.E.D.) and by grant GM62128 from the NIH (J.R.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.-S.S. and J.-R.K. carried out the mutagenesis and protein purification; B.-S.S. conducted the hydroxyl radical mapping experiments, biochemical analyses and model building; S.E.W. did the toe-printing assay and J.D. provided reagents. The manuscript was prepared by B.-S.S., S.E.W., J.R.L. and T.E.D.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5, Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 4685 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, BS., Kim, JR., Walker, S. et al. Initiation factor eIF2γ promotes eIF2–GTP–Met-tRNAiMet ternary complex binding to the 40S ribosome. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18, 1227–1234 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2133
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2133
This article is cited by
-
Rapid and selective simultaneous quantitative analysis of modified nucleosides using multi-column liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
Journal of Analytical Science and Technology (2017)
-
Cryo-EM study of start codon selection during archaeal translation initiation
Nature Communications (2016)
-
X-exome sequencing of 405 unresolved families identifies seven novel intellectual disability genes
Molecular Psychiatry (2016)
-
The crystal structure of the eukaryotic 40S ribosomal subunit in complex with eIF1 and eIF1A
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2013)
-
A mechanistic overview of translation initiation in eukaryotes
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2012)