Abstract
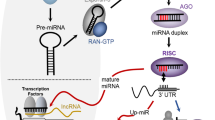
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous, noncoding, single-stranded RNAs of 19–25 nucleotides in length. They regulate gene expression and are important in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes. MiRNAs are attractive as potential biomarkers because their expression pattern is reflective of underlying pathophysiologic processes and they are specific to various disease states. Moreover, miRNAs can be detected in a variety of sources, including tissue, blood and body fluids; they are reasonably stable and appear to be resistant to differences in sample handling, which increases their appeal as practical biomarkers. The clinical utility of miRNAs as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers has been demonstrated in various malignancies and a few nonmalignant diseases. There is accumulating evidence that miRNAs have an important role in systemic rheumatic diseases and that various diseases or different stages of the same disease are associated with distinct miRNA expression profiles. Preliminary data suggest that miRNAs are promising as candidate biomarkers of diagnosis, prognosis, disease activity and severity in autoimmune diseases. MiRNAs identified as potential biomarkers in pilot studies should be validated in larger studies designed specifically for biomarker validation.
Key Points
-
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small regulatory RNAs that have a central role in the regulation of gene expression
-
MiRNAs possess many features of an ideal biomarker: they reflect the physiological or pathological state of cells and tissues, are relatively stable, and can be detected by various methods
-
MiRNAs have been validated as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis in malignant diseases
-
Early studies have linked aberrant miRNA expression to specific rheumatic diseases but, as yet, no miRNA has been validated as a biomarker in these diseases
-
Studies designed specifically to validate miRNAs as biomarkers are needed to assess their potential in rheumatic diseases
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua, J. H., Armugam, A. & Jeyaseelan, K. MicroRNAs: biogenesis, function and applications. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 11, 189–199 (2009).
Lee, R. C., Feinbaum, R. L. & Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75, 843–854 (1993).
Lagos-Quintana, M., Rauhut, R., Lendeckel, W. & Tuschl, T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294, 853–858 (2001).
Lau, N. C., Lim, L. P., Weinstein, E. G. & Bartel, D. P. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294, 858–862 (2001).
Lee, R. C. & Ambros, V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294, 862–864 (2001).
Lee, Y. et al. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 23, 4051–4060 (2004).
Corcoran, D. L. et al. Features of mammalian microRNA promoters emerge from polymerase II chromatin immunoprecipitation data. PLoS ONE 4, e5279 (2009).
Gregory, R. I. et al. The microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature 432, 235–240 (2004).
Yi, R., Qin, Y., Macara, I. G. & Cullen, B. R. Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev. 17, 3011–3016 (2003).
Robb, G. B. & Rana, T. M. RNA helicase A interacts with RISC in human cells and functions in RISC loading. Mol. Cell 26, 523–537 (2007).
Kong, Y. W. et al. The mechanism of micro-RNA-mediated translation repression is determined by the promoter of the target gene. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 8866–8871 (2008).
Baek, D. et al. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 455, 64–71 (2008).
Selbach, M. et al. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 455, 58–63 (2008).
Miranda, K. C. et al. A pattern-based method for the identification of microRNA binding sites and their corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell 126, 1203–1217 (2006).
Tay, Y., Zhang, J., Thomson, A. M., Lim, B. & Rigoutsos, I. MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature 455, 1124–1128 (2008).
Duursma, A. M., Kedde, M., Schrier, M., le Sage, C. & Agami, R. MiR-148 targets human DNMT3b protein coding region. RNA 14, 872–877 (2008).
Card, D. A. et al. Oct4/Sox2-regulated miR-302 targets cyclin D1 in human embryonic stem cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 6426–6438 (2008).
Xu, N., Papagiannakopoulos, T., Pan, G., Thomson, J. A. & Kosik, K. S. MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell 137, 647–658 (2009).
Ren, J., Jin, P., Wang, E., Marincola, F. M. & Stroncek, D. F. MicroRNA and gene expression patterns in the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. J. Transl. Med. 7, 20 (2009).
Yi, R. et al. Morphogenesis in skin is governed by discrete sets of differentially expressed microRNAs. Nat. Genet. 38, 356–362 (2006).
Kloosterman, W. P., Lagendijk, A. K., Ketting, R. F., Moulton, J. D. & Plasterk, R. H. Targeted inhibition of miRNA maturation with morpholinos reveals a role for miR-375 in pancreatic islet development. PLoS Biol. 5, e203 (2007).
Callis, T. E., Chen, J. F. & Wang, D. Z. MicroRNAs in skeletal and cardiac muscle development. DNA Cell Biol. 26, 219–225 (2007).
Chen, J. F. et al. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat. Genet. 38, 228–233 (2006).
van Rooij, E. et al. Control of stress-dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science 316, 575–579 (2007).
Cheng, L. C., Pastrana, E., Tavazoie, M. & Doetsch, F. MiR-124 regulates adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone stem cell niche. Nat. Neurosci. 12, 399–408 (2009).
Visone, R. & Croce, C. M. MiRNAs and cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 174, 1131–1138 (2009).
Spizzo, R., Nicoloso, M. S., Croce, C. M. & Calin, G. A. SnapShot: microRNAs in cancer. Cell 137, 586–586.e1 (2009).
Niwa, R., Zhou, F., Li, C. & Slack, F. J. The expression of the Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein-like gene is regulated by developmental timing microRNAs and their targets in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 315, 418–425 (2008).
Zhu, Y., Kalbfleisch, T., Brennan, M. D. & Li, Y. A microRNA gene is hosted in an intron of a schizophrenia-susceptibility gene. Schizophr. Res. 109, 86–89 (2009).
Sarasin-Filipowicz, M., Krol, J., Markiewicz, I., Heim, M. H. & Filipowicz, W. Decreased levels of microRNA miR-122 in individuals with hepatitis C responding poorly to interferon therapy. Nat. Med. 15, 31–33 (2009).
Houzet, L. et al. MicroRNA profile changes in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) seropositive individuals. Retrovirology 5, 118 (2008).
Padgett, K. A. et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis is associated with altered hepatic microRNA expression. J. Autoimmun. 32, 246–253 (2009).
Tang, Y. et al. MicroRNA-146A contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 1065–1075 (2009).
Dai, Y. et al. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in renal biopsies of lupus nephritis patients. Rheumatol. Int. 29, 749–754 (2009).
Dai, Y. et al. Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in peripheral blood cells of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Lupus 16, 939–946 (2007).
Nakamachi, Y. et al. MicroRNA-124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 1294–1304 (2009).
Alsaleh, G. et al. Bruton's tyrosine kinase is involved in miR-346-related regulation of IL-18 release by lipopolysaccharide-activated rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 182, 5088–5097 (2009).
Pauley, K. M. et al. Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 10, R101 (2008).
Nakasa, T. et al. Expression of microRNA-146 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 1284–1292 (2008).
Chen, C. Z., Li, L., Lodish, H. F. & Bartel, D. P. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303, 83–86 (2004).
Baltimore, D., Boldin, M. P., O'Connell, R. M., Rao, D. S. & Taganov, K. D. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat. Immunol. 9, 839–845 (2008).
Lodish, H. F., Zhou, B., Liu, G. & Chen, C. Z. Micromanagement of the immune system by microRNAs. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 120–130 (2008).
Pauley, K. M. & Chan, E. K. MicroRNAs and their emerging roles in immunology. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1143, 226–239 (2008).
Tili, E., Michaille, J. J., Costinean, S. & Croce, C. M. MicroRNAs, the immune system and rheumatic disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 4, 534–541 (2008).
Kitani, A. & Xu, L. Regulatory T cells and the induction of IL-17. Mucosal Immunol. 1 (Suppl. 1), S43–S46 (2008).
Du, C. et al. MicroRNA miR-326 regulates TH-17 differentiation and is associated with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Immunol. 10, 1252–1259 (2009).
Liston, A., Lu, L. F., O'Carroll, D., Tarakhovsky, A. & Rudensky, A. Y. Dicer-dependent microRNA pathway safeguards regulatory T cell function. J. Exp. Med. 205, 1993–2004 (2008).
Lu, L. F. et al. Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive fitness to regulatory T cells by targeting SOCS1 protein. Immunity 30, 80–91 (2009).
Ceppi, M. et al. MicroRNA-155 modulates the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 2735–2740 (2009).
de Yébenes, V. G. et al. MiR-181b negatively regulates activation-induced cytidine deaminase in B cells. J. Exp. Med. 205, 2199–2206 (2008).
Dorsett, Y. et al. MicroRNA-155 suppresses activation-induced cytidine deaminase-mediated Myc-Igh translocation. Immunity 28, 630–638 (2008).
Basso, K. et al. Identification of the human mature B cell miRNome. Immunity 30, 744–752 (2009).
Zhang, J. et al. Patterns of microRNA expression characterize stages of human B-cell differentiation. Blood 113, 4586–4594 (2009).
Glinsky, G. V. An SNP-guided microRNA map of fifteen common human disorders identifies a consensus disease phenocode aiming at principal components of the nuclear import pathway. Cell Cycle 7, 2570–2583 (2008).
Wu, H., Ye, C., Ramirez, D. & Manjunath, N. Alternative processing of primary microRNA transcripts by Drosha generates 5' end variation of mature microRNA. PLoS ONE 4, e7566 (2009).
Mishra, P. J. & Bertino, J. R. MicroRNA polymorphisms: the future of pharmacogenomics, molecular epidemiology and individualized medicine. Pharmacogenomics 10, 399–416 (2009).
Morin, R. D. et al. Application of massively parallel sequencing to microRNA profiling and discovery in human embryonic stem cells. Genome Res. 18, 610–621 (2008).
Jazdzewski, K. & de la Chapelle, A. Genomic sequence matters: a SNP in microRNA-146a can turn anti-apoptotic. Cell Cycle 8, 1642–1643 (2009).
Jazdzewski, K. et al. Common SNP in pre-miR-146a decreases mature miR expression and predisposes to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 7269–7274 (2008).
Xu, T. et al. A functional polymorphism in the miR-146a gene is associated with the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 29, 2126–2131 (2008).
Illei, G. G., Tackey, E., Lapteva, L. & Lipsky, P. E. Biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. I. General overview of biomarkers and their applicability. Arthritis Rheum. 50, 1709–1720 (2004).
Thomas, G. P. & Brown, M. A. Genetics and genomics of ankylosing spondylitis. Immunol. Rev. 233, 162–180 (2010).
de Vries, R. R., Huizinga, T. W. & Toes, R. E. Redefining the HLA and RA association: to be or not to be anti-CCP positive. J. Autoimmun. 25 (Suppl.), 21–25 (2005).
Gregersen, P. K. & Olsson, L. M. Recent advances in the genetics of autoimmune disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 363–391 (2009).
Mackay, I. R. Clustering and commonalities among autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 33, 170–177 (2009).
Scofield, R. H. Genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren's syndrome. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 21, 448–453 (2009).
Nishimura, K. et al. Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 146, 797–808 (2007).
Schulte-Pelkum, J., Fritzler, M. & Mahler, M. Latest update on the Ro/SS-A autoantibody system. Autoimmun. Rev. 8, 632–637 (2009).
Kaltenhäuser, S. et al. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide are associated with the DRB1 shared epitope and predict joint erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46, 100–104 (2007).
Sanmartí, R. et al. Prognostic factors of radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: a two year prospective study after a structured therapeutic strategy using DMARDs and very low doses of glucocorticoids. Clin. Rheumatol. 26, 1111–1118 (2007).
Gunawardena, H., Betteridge, Z. E. & McHugh, N. J. Myositis-specific autoantibodies: their clinical and pathogenic significance in disease expression. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48, 607–612 (2009).
Balow, J. E. Clinical presentation and monitoring of lupus nephritis. Lupus 14, 25–30 (2005).
Cissell, K. A. & Deo, S. K. Trends in microRNA detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 394, 1109–1116 (2009).
Lanford, R. E. et al. Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Science 327, 198–201 (2010).
Lim, L. P. et al. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433, 769–773 (2005).
Doleshal, M. et al. Evaluation and validation of total RNA extraction methods for microRNA expression analyses in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. J. Mol. Diagn. 10, 203–211 (2008).
Chen, X. et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 18, 997–1006 (2008).
Michael, A. et al. Exosomes from human saliva as a source of microRNA biomarkers. Oral Dis. 16, 34–38 (2010).
Hanke, M. et al. A robust methodology to study urine microRNA as tumor marker: microRNA-126 and microRNA-182 are related to urinary bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2009.01.027.
Park, N. J. et al. Salivary microRNA: discovery, characterization, and clinical utility for oral cancer detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 5473–5477 (2009).
Lebanony, D. et al. Diagnostic assay based on hsa-miR-205 expression distinguishes squamous from nonsquamous non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 27, 2030–2037 (2009).
Gilad, S. et al. Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS ONE 3, e3148 (2008).
Mitchell, P. S. et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 10513–10518 (2008).
Zoon, C. K. et al. Current molecular diagnostics of breast cancer and the potential incorporation of microRNA. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 9, 455–467 (2009).
Zhang, X. et al. An array-based analysis of microRNA expression comparing matched frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human tissue samples. J. Mol. Diagn. 10, 513–519 (2008).
Stanczyk, J. et al. Altered expression of microRNA in synovial fibroblasts and synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 1001–1009 (2008).
Yamasaki, K. et al. Expression of microRNA-146a in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 1035–1041 (2009).
Alevizos, I., Bajracharya, S. D., Alexander, S., Turner, R. J. & Illei, G. G. MicroRNA profiling of minor salivary glands identifies disease and inflammation biomarkers in Sjögren's syndrome patients [abstract 1961]. Arthritis Rheum. 60 (Suppl.), S733–S734 (2009).
Iorio, M. V., Casalini, P., Tagliabue, E., Ménard, S. & Croce, C. M. MicroRNA profiling as a tool to understand prognosis, therapy response and resistance in breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 44, 2753–2759 (2008).
Volinia, S. et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 2257–2261 (2006).
Wang, Q. Z., Xu, W., Habib, N. & Xu, R. Potential uses of microRNA in lung cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 9, 572–594 (2009).
Yanaihara, N. et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 9, 189–198 (2006).
Huang, Y. S. et al. Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues without viral hepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 23, 87–94 (2008).
Szafranska, A. E. et al. Accurate molecular characterization of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues by microRNA expression profiling. J. Mol. Diagn. 10, 415–423 (2008).
Bloomston, M. et al. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 297, 1901–1908 (2007).
Dillhoff, M., Liu, J., Frankel, W., Croce, C. & Bloomston, M. MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and a potential predictor of survival. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 12, 2171–2176 (2008).
Schetter, A. J. et al. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA 299, 425–436 (2008).
Calin, G. A. et al. Frequent deletions and downregulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 15524–15529 (2002).
Garzon, R. et al. Distinctive microRNA signature of acute myeloid leukemia bearing cytoplasmic mutated nucleophosmin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 3945–3950 (2008).
Jongen-Lavrencic, M., Sun, S. M., Dijkstra, M. K., Valk, P. J. & Löwenberg, B. MicroRNA expression profiling in relation to the genetic heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 111, 5078–5085 (2008).
Marcucci, G. et al. MicroRNA expression in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 1919–1928 (2008).
Lu, J. et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435, 834–838 (2005).
Calin, G. A. et al. A microRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 1793–1801 (2005).
Prometheus launches ProOncDx cancer diagnostics. Prometheus® Therapeutics & Diagnostics [online], (2009).
Taylor, D. D. & Gercel-Taylor, C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 110, 13–21 (2008).
Lodes, M. J. et al. Detection of cancer with serum miRNAs on an oligonucleotide microarray. PLoS ONE 4, e6229 (2009).
Rabinowits, G., Gercel-Taylor, C., Day, J. M., Taylor, D. D. & Kloecker, G. H. Exosomal microRNA: a diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 10, 42–46 (2009).
Rosell, R., Wei, J. & Taron, M. Circulating microRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes for early diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 10, 8–9 (2009).
Anglicheau, D. et al. MicroRNA expression profiles predictive of human renal allograft status. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 5330–5335 (2009).
Hasemeier, B., Christgen, M., Kreipe, H. & Lehmann, U. Reliable microRNA profiling in routinely processed formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast cancer specimens using fluorescence labeled bead technology. BMC Biotechnol. 8, 90 (2008).
Babak, T., Zhang, W., Morris, Q., Blencowe, B. J. & Hughes, T. R. Probing microRNAs with microarrays: tissue specificity and functional inference. RNA 10, 1813–1819 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alevizos, I., Illei, G. MicroRNAs as biomarkers in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6, 391–398 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.81
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.81
This article is cited by
-
MicroRNAs-mediated regulation pathways in rheumatic diseases
Inflammopharmacology (2023)
-
miRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers and pharmacogenomic indicators in psychiatric disorders
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2022)
-
Host cell response and distinct gene expression profiles at different stages of Chlamydia trachomatis infection reveals stage-specific biomarkers of infection
BMC Microbiology (2021)
-
The non-coding RNA interactome in joint health and disease
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2021)
-
miR-19b-3p and miR-20a-5p are associated with the levels of antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome
Rheumatology International (2021)