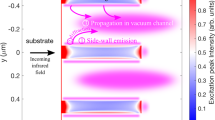
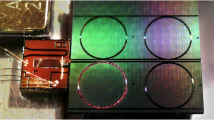
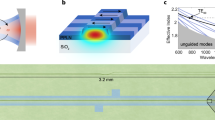
Abstract
Nonlinear harmonic generation is widely used to extend the emission wavelength of laser sources. These devices typically require high peak powers to generate sufficient nonlinear optical response. Here, we demonstrate experimentally and analyse theoretically continuous-wave, visible emission from a silica microresonator on a silicon chip by third-harmonic generation. Emission is observed with pump powers of less than 300 μW, and is verified to scale cubically with pump power. We also observe third-order sum-frequency generation and mixing of the pump with a concomitant Raman laser within the same structure, giving rise to emission of various colours. In addition to providing low-power operation, this result opens the possibility of silicon microphotonic emitters spanning all the way down to the ultraviolet and operating continuously.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desurvire, E. Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers: Principles and Applications (Wiley, New York, 1994).
Becker, P. C., Olsson, N. A. & Simpson, J. R. Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers: Fundamentals and Technology (Academic, San Diego, 1999).
Digonnet, M. J. F. Rare-Earth-Doped Fiber Lasers and Amplifiers 2nd edn (Dekker, New York, 2001).
Boyraz, O. & Jalali, B. Demonstration of a silicon Raman laser. Opt. Express 12, 5269–5273 (2004).
Liu, A. S. et al. A high-speed silicon optical modulator based on a metal–oxide–semiconductor capacitor. Nature 427, 615–618 (2004).
Knight, J. C. Photonic crystal fibres. Nature 424, 847–851 (2003).
Knight, J. C., Birks, T. A., Russell, P. S. & Atkin, D. M. All-silica single-mode optical fiber with photonic crystal cladding. Opt. Lett. 21, 1547–1549 (1996).
Bufetov, I. A., Grekov, M. V., Golant, K. M., Dianov, E. M. & Khrapko, R. R. Ultraviolet-light generation in nitrogen-doped silica fiber. Opt. Lett. 22, 1394–1396 (1997).
Acker, W. P., Leach, D. H. & Chang, R. K. Third-order optical sum-frequency generation in micrometer-sized liquid droplets. Opt. Lett. 14, 402–404 (1989).
Leach, D. H., Acker, W. P. & Chang, R. K. Effect of the phase-velocity and spatial overlap of spherical resonances on sum-frequency generation in droplets. Opt. Lett. 15, 894–896 (1990).
Leach, D. H., Chang, R. K., Acker, W. P. & Hill, S. C. Third-order sum-frequency generation in droplets—experimental results. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 10, 34–45 (1993).
Kasparian, J. et al. Angular dependences of third harmonic generation from microdroplets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 2952–2955 (1997).
Qian, S. X. & Chang, R. K. Multiorder stokes emission from micrometer-size droplets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 926–929 (1986).
Lin, H. B., Eversole, J. D. & Campillo, A. J. Continuous-wave stimulated Raman-scattering in microdroplets. Opt. Lett. 17, 828–830 (1992).
Spillane, S. M., Kippenberg, T. J. & Vahala, K. J. Ultralow-threshold Raman laser using a spherical dielectric microcavity. Nature 415, 621–623 (2002).
Kippenberg, T. J., Spillane, S. M. & Vahala, K. J. Kerr-nonlinearity optical parametric oscillation in an ultrahigh-Q toroid microcavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 083904 (2004).
Ponce, F. A. & Bour, D. P. Nitride-based semiconductors for blue and green light-emitting devices. Nature 386, 351–359 (1997).
Boyd, R. W. Nonlinear Optics 2nd edn (Academic, San Diego, 2003).
Franken, P. A., Weinreich, G., Peters, C. W. & Hill, A. E. Generation of optical harmonics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 7, 118–120 (1961).
Osterberg, U. & Margulis, W. Dye-laser pumped by Nd-YAG laser-pulses frequency doubled in a glass optical fiber. Opt. Lett. 11, 516–518 (1986).
Myers, R. A., Mukherjee, N. & Brueck, S. R. J. Large second-order nonlinearity in poled fused-silica. Opt. Lett. 16, 1732–1734 (1991).
Dominic, V. & Feinberg, J. Light-induced second-harmonic generation in glass via multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 3446–3449 (1993).
Ilchenko, V. S., Savchenkov, A. A., Matsko, A. B. & Maleki, L. Nonlinear optics and crystalline whispering gallery mode cavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 043903 (2004).
Armani, D. K., Kippenberg, T. J., Spillane, S. M. & Vahala, K. J. Ultra-high-Q toroid microcavity on a chip. Nature 421, 925–928 (2003).
Knight, J. C., Cheung, G., Jacques, F. & Birks, T. A. Phase-matched excitation of whispering-gallery-mode resonances by a fiber taper. Opt. Lett. 22, 1129–1131 (1997).
Cai, M., Painter, O. & Vahala, K. J. Observation of critical coupling in a fiber taper to a silica-microsphere whispering-gallery mode system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 74–77 (2000).
Wang, S., Carmon, T., Ostby, E. P. & Vahala, K. J. Quantum Electronics and Laser Science Conference, May 7, Baltimore, USA (accepted for oral presentation, 2007).
Yang, L., Armani, D. K. & Vahala, K. J. Fiber-coupled erbium microlasers on a chip. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 825–826 (2003).
Ilchenko, V. S., Starodubov, D. S., Gorodetsky, M. L., Maleki, L. & Feinberg, J. Conference on Lasers and ElectroOptics 67 (Optical Society of America, Baltimore, 1999).
Haus, H. A. & Huang, W. P. Coupled-mode theory. Proc. IEEE 79, 1505–1518 (1991).
Stolen, R. H., Bjorkhol, Je. & Ashkin, A. Phase-matched 3-wave mixing in silica fiber optical-waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 24, 308–310 (1974).
Johnson, B. R. Theory of morphology-dependent resonances— shape resonances and width formulas. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 10, 343–352 (1993).
Baak, T. Silicon oxynitride—a material for grin optics. Appl. Opt. 21, 1069–1072 (1982).
Savchenkov, A. A., Ilchenko, V. S., Matsko, A. B. & Maleki, L. Kilohertz optical resonances in dielectric crystal cavities. Phys. Rev. A 70, 051804 (2004).
Robinson, J. T., Manolatou, C., Chen, L. & Lipson, M. Ultrasmall mode volumes in dielectric optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 143901 (2005).
Vahala, K. J. Optical microcavities. Nature 424, 839–846 (2003).
Kippenberg, T. J., Kalkman, J., Polman, A. & Vahala, K. J. Demonstration of an erbium-doped microdisk laser on a silicon chip. Phys. Rev. A 74, 051802 (2006).
Akahane, Y., Asano, T., Song, B. S. & Noda, S. High-Q photonic nanocavity in a two-dimensional photonic crystal. Nature 425, 944–947 (2003).
Savchenkov, A. A. et al. Low threshold optical oscillations in a whispering gallery mode CaF2 resonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 243905 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge helpful discussions with M. Shumate, J. Scheuer and A. Yariv and support from the Caltech Lee Center and DARPA. T.C. acknowledges a fellowship from the Center for the Physics of Information at Caltech.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.C. fabricated the devices, carried out the experiments, analysed the data and derived the analytical and numerical calculations. K.J.V. supervised all aspects of this project. Both authors made contributions to the concepts demonstrated and proposed in the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carmon, T., Vahala, K. Visible continuous emission from a silica microphotonic device by third-harmonic generation. Nature Phys 3, 430–435 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys601
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys601
This article is cited by
-
Wavelength-accurate nonlinear conversion through wavenumber selectivity in photonic crystal resonators
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
Modeling of dual frequency combs and bistable solitons in third-harmonic generation
Communications Physics (2023)
-
Coherent modulation of chiral nonlinear optics with crystal symmetry
Light: Science & Applications (2022)
-
Symmetry-breaking-induced nonlinear optics at a microcavity surface
Nature Photonics (2019)
-
High-Efficiency Plasmonic Third-Harmonic Generation with Graphene on a Silicon Diffractive Grating in Mid-infrared Region
Nanoscale Research Letters (2018)