Abstract
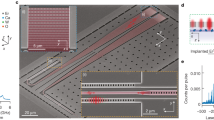
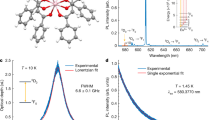
Rare-earth optical materials with large optical gain are of great importance for a wide variety of applications in photonics and quantum information due to their long carrier lifetimes and quantum coherence times, especially in the realization of efficient lasers and amplifiers. Until now, such materials have achieved a gain of less than a few dB cm–1, rendering them unsuitable for applications in nanophotonic integrated circuits. Here, we report the results of the signal enhancement and transmission experiments on a single-crystal erbium chloride silicate nanowire. Our experiments demonstrate that a net material gain over 100 dB cm–1 at wavelengths around 1,530 nm is possible due to the nanowire's single-crystalline material quality and its high erbium concentration. Our results establish that such rare-earth-compound nanowires are a potentially important class of nanomaterials for a variety of applications including, for example, subwavelength-scale optical amplifiers and lasers for integrated nanophotonics, and quantum information.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mørk, J., Nielsen, M. L. & Berg, T. W. The dynamics of semiconductor optical amplifiers: modeling and applications. Opt. Photon. News 14, 42–48 (2003).
Pollnau, M. Rare-earth-ion-doped waveguide lasers on a silicon chip. Proc. SPIE 9359, 935910–935917 (2015).
Bradley, J. D. B. et al. 170 GBit/s transmission in an erbium-doped waveguide amplifier on silicon. Opt. Express 17, 22201–22208 (2009).
Yin, C. et al. Optical addressing of an individual erbium ion in silicon. Nature 497, 91–94 (2013).
Mears, R., Reekie, L., Jauncey, I. & Payne, D. Low-noise erbium-doped fibre amplifier operating at 1.54 μm. Electron. Lett. 23, 1026–1028 (1987).
Giles, C. R. & Desurvire, E. Modeling erbium-doped fiber amplifiers. J. Lightwave Technol. 9, 271–283 (1991).
Wysocki, P. F., Judkins, J. B., Espindola, R. P., Andrejco, M. & Vengsarkar, A. M. Broad-band erbium-doped fiber amplifier flattened beyond 40 nm using long-period grating filter. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 9, 1343–1345 (1997).
Desurvire, E., Giles, C. R. & Simpson, J. R. Gain saturation effects in high-speed, multichannel erbium-doped fiber amplifiers at λ = 1.53 μm. J. Lightwave Technol. 7, 2095–2104 (1989).
Desurvire, E. Analysis of noise figure spectral distribution in erbium doped fiber amplifiers pumped near 980 and 1480 nm. Appl. Opt. 29, 3118–3125 (1990).
Giles, C. R., Simpson, J. R. & Desurvire, E. Transient gain and cross talk in erbium-doped fiber amplifiers. Opt. Lett. 14, 880–882 (1989).
Mears, R. J., Reekie, L., Poole, S. B. & Payne, D. N. Low-threshold tunable CW and Q-switched fibre laser operating at 1.55 μm. Electron. Lett. 22, 159–160 (1986).
Kafka, J. D., Hall, D. W. & Baer, T. Mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser with soliton pulse shaping. Opt. Lett. 14, 1269–1271 (1989).
Yan, Y. C., Faber, A. J., De Waal, H., Kik, P. G. & Polman, A. Erbium-doped phosphate glass waveguide on silicon with 4.1 dB/cm gain at 1.535 μm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 2922–2924 (1997).
Huang, W. et al. Fiber-device-fiber gain from a sol-gel erbium-doped waveguide amplifier. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 14, 959–961 (2002).
Saini, S. et al. Er2O3 for high-gain waveguide amplifiers. J. Electron. Mater. 33, 809–814 (2004).
Zheng, J. et al. Highly efficient photoluminescence of Er2SiO5 films grown by reactive magnetron sputtering method. J. Lumines. 130, 411–414 (2010).
Miniscalco, W. J. Erbium-doped glasses for fiber amplifiers at 1500 nm. J. Lightwave Technol. 9, 234–250 (1991).
Hwang, B. C. et al. Erbium-doped phosphate glass fibre amplifiers with gain per unit length of 2.1 dB/cm. Electron. Lett. 35, 1007–1009 (1999).
Bradley, J. D. B. et al. Gain bandwidth of 80 nm and 2 dB/cm peak gain in Al2O3 Er3+ optical amplifiers on silicon. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27, 187–196 (2010).
Miritello, M. et al. Optical and structural properties of Er2O3 films grown by magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 013502 (2006).
Michael, C. P. et al. Growth, processing, and optical properties of epitaxial Er2O3 on silicon. Opt. Express 16, 19649–19666 (2008).
Choi, H.-J. et al. Self-organized growth of Si/Silica/Er2Si2O7 core-shell nanowire heterostructures and their luminescence. Nano Lett. 5, 2432–2437 (2005).
Wang, B., Guo, R., Wang, L., Wang, X. & Zhou, Z. 1.53 μm electroluminescence of erbium excited by hot carriers in ErRE (RE= Yb, Y) silicates. In 9th Int. Conf. Group IV Photonics (GFP) 72–74 (IEEE, 2012).
Miritello, M. et al. Efficient luminescence and energy transfer in erbium silicate thin films. Adv. Mater. 19, 1582–1588 (2007).
Michael, C. P. Optical Material Characterization Using Microdisk Cavities PhD thesis, California Institute of Technology (2009).
Isshiki, H., Ushiyama, T. & Kimura, T. Demonstration of ErSiO superlattice crystal waveguide toward optical amplifiers and emitters. Phys. Status Solidi A 205, 52–55 (2008).
Pan, A. et al. Single-crystal erbium chloride silicate nanowires as a Si-compatible light emission material in communication wavelength. Opt. Mater. Express 1, 1202–1209 (2011).
Yin, L. et al. Long lifetime, high density single-crystal erbium compound nanowires as a high optical gain material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 241905 (2012).
Yin, L., Ning, H., Turkdogan, S., Liu, Z. & Ning, C. Z. Significant increase of photoluminescence lifetime at 1.5 μm in erbium chloride silicate nanowires. In Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) CTh3D.4 (OSA, 2012).
Liu, Z., Yin, L. & Ning, C. Z. Extremely large signal enhancement in an erbium chloride silicate single-crystal nanowire. In Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) CF1I.6 (OSA, 2013).
Yin, L., Shelhammer, D., Zhao, G., Liu, Z. & Ning, C. Z. Erbium concentration control and optimization in erbium yttrium chloride silicate single crystal nanowires as a high gain material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 121902 (2013).
Liu, Z., Zhao, G., Yin, L. & Ning, C. Z. Demonstration of net gain in an erbium chloride silicate single nanowire waveguide. In Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) SM4H.4 (OSA, 2014).
Liu, Z., Sun, H., Li, Y., Zhang, J. & Ning, C. Z. Fabrication of 1D photonic crystal on a single erbium chloride silicate nanowire and microcavity laser design. In Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) SW4I.2 (OSA, 2015).
Shukla, P. & Kaur, K. P. Performance analysis of EDFA for different pumping configurations at high data rate. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2, 487–490 (2013).
Suh, K. et al. Cooperative upconversion and optical gain in ion-beam sputter-deposited ErxY2-xSiO5 waveguides. Opt. Express 18, 7724–7731 (2010).
Han, H.-S., Seo, S.-Y., Shin, J. H. & Park, N. Coefficient determination related to optical gain in erbium-doped silicon-rich silicon oxide waveguide amplifier. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 3720–3722 (2002).
Tong, L. M. et al. Assembly of silica nanowires on silica aerogels for microphotonic devices. Nano Lett. 5, 259–262 (2005).
Wang, W. H., Yang, Q., Fan, F. R., Xu, H. X. & Wang, Z. L. Light propagation in curved silver nanowire plasmonic waveguides. Nano Lett. 11, 1603–1608 (2011).
Isshiki, H. & Kimura, T. Toward small size waveguide amplifiers based on erbium silicate for silicon photonics. IEICE Trans. Electron. E91-C, 138–144 (2008).
Sun, H. et al. Record-high optical gain in a single crystal erbium chloride silicate nanowire at 1532 nm. In Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) SM4R.3 (OSA, 2016).
Ning, C. Z. Semiconductor nanolasers. Phys. Status Solidi B 247, 774–788 (2010).
Wang, L., Guo, R., Wang, B., Wang, X. & Zhou, Z. Hybrid Si3N4-Er/Yb/Y silicate waveguide amplifier with 1.25 dB/cm internal gain. In 9th Int. Conf. Group IV Photonics (GFP) 249–251 (IEEE, 2012).
Van den Hoven, G. N. et al. Net optical gain at 1.53 μm in Er-doped Al2O3 waveguides on silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 1886–1888 (1996).
Wang, X. J., Yuan, G., Isshiki, H., Kimura, T. & Zhou, Z. Photoluminescence enhancement and high gain amplification of ErxY2-xSiO5 waveguide. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 013506 (2010).
Wang, W. et al. High gain submicrometer optical amplifier at near-infrared communication band. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 027403 (2015).
Feng, X. et al. Comment on “High gain submicrometer optical amplifier at near-infrared communication band”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 219701 (2016).
Wang, X. et al. Wang et al. reply. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 219702 (2016).
Acknowledgements
This work was primarily supported by the 985 University Project of China and Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program (no. 20141081296). The research at Arizona State University was initially supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (FA9550-10-1-0444, G. Pomrenke) and later partially supported by the National Science Foundation's EAGER Program (award ID 1228512, J. Zavada). We thank G. Zhao of Arizona State University for help in the initial measurement of absorption based on the upconversion method.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.Z.N. guided the research and supervised the overall project. H.S. L.Y., Z.L. and C.Z.N. designed the experiment. L.Y. and S.Z. fabricated the samples. H.S. and Y.Z. built the measurement set-up and carried out the experiments. L.Y., Z.L., F.F., X.F. and Y.L. performed the theoretical calculations and numerical simulations. H.S., L.Y., Z.L. and C.Z.N. performed the data analysis and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the discussions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 1514 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Yin, L., Liu, Z. et al. Giant optical gain in a single-crystal erbium chloride silicate nanowire. Nature Photon 11, 589–593 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2017.115
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2017.115
This article is cited by
-
Silicon photonics-based high-energy passively Q-switched laser
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
Self-optimized single-nanowire photoluminescence thermometry
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Gain-gain and gain-lossless PT-symmetry broken from PT-phase diagram
Journal of Optics (2023)
-
A low-fabrication-temperature, high-gain chip-scale waveguide amplifier
Science China Information Sciences (2022)
-
Enhanced 1.54-μm photo- and electroluminescence based on a perfluorinated Er(III) complex utilizing an iridium(III) complex as a sensitizer
Light: Science & Applications (2020)