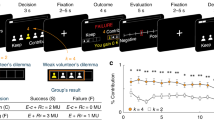
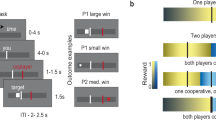
Abstract
Decision making in a social group has two distinguishing features. First, humans and other animals routinely alter their behavior in response to changes in their physical and social environment. As a result, the outcomes of decisions that depend on the behavior of multiple decision makers are difficult to predict and require highly adaptive decision-making strategies. Second, decision makers may have preferences regarding consequences to other individuals and therefore choose their actions to improve or reduce the well-being of others. Many neurobiological studies have exploited game theory to probe the neural basis of decision making and suggested that these features of social decision making might be reflected in the functions of brain areas involved in reward evaluation and reinforcement learning. Molecular genetic studies have also begun to identify genetic mechanisms for personal traits related to reinforcement learning and complex social decision making, further illuminating the biological basis of social behavior.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahneman, D. & Tversky, A. Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica 47, 263–292 (1979).
Sutton, R.S. & Barton, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 1998).
Platt, M.L. & Glimcher, P.W. Neural correlates of decision variables in parietal cortex. Nature 400, 233–238 (1999).
Breiter, H.C., Aharon, I., Kahneman, D., Dale, A. & Shizgal, P. Functional imaging of neural responses to expectancy and experience of monetary gains and losses. Neuron 30, 619–639 (2001).
Fiorillo, C.D., Tobler, P.N. & Schultz, W. Discrete coding of reward probability and uncertainty by dopamine neurons. Science 299, 1898–1902 (2003).
Glimcher, P.W. & Rustichini, A. Neuroeconomics: the consilience of brain and decision. Science 306, 447–452 (2004).
Knutson, B., Taylor, J., Kaufman, M., Peterson, R. & Glover, G. Distributed neural representation of expected value. J. Neurosci. 25, 4806–4812 (2005).
Hsu, M., Bhatt, M., Adolphs, R., Tranel, D. & Camerer, C.F. Neural systems responding to degrees of uncertainty in human decision-making. Science 310, 1680–1683 (2005).
Preuschoff, K., Bossaerts, P. & Quartz, S.R. Neural differentiation of expected reward and risk in human subcortical structures. Neuron 51, 381–390 (2006).
Schultz, W., Dayan, P. & Montague, P.R. A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275, 1593–1599 (1997).
O'Doherty, J.P., Dayan, P., Friston, K., Critchley, H. & Dolan, R.J. Temporal difference models and reward-related learning in the human brain. Neuron 38, 329–337 (2003).
McClure, S.M., Berns, G.S. & Montague, P.R. Temporal prediction errors in a passive learning task activate human striatum. Neuron 38, 339–346 (2003).
O'Doherty, J. et al. Dissociable roles of ventral and dorsal striatum in instrumental conditioning. Science 304, 452–454 (2004).
Tricomi, E.M., Delgado, M.R. & Fiez, J.A. Modulation of caudate activity by action contingency. Neuron 41, 281–292 (2004).
Adolphs, R. Social cognition and the human brain. Trends Cogn. Sci. 3, 469–479 (1999).
Fudenberg, D. & Levine, D.K. The Theory of Learning in Games (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 1998).
Camerer, C.F. Behavioral Game Theory: Experiments in Strategic Interaction (Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton, New Jersey, USA, 2003).
von Neumann, J. & Morgenstern, O. Theory of Games and Economic Behavior (Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton, New Jersey, USA, 1944).
Nash, J.F. Equilibrium points in n-person games. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 36, 48–49 (1950).
Erev, I. & Roth, A.E. Predicting how people play games: reinforcement learning in experimental games with unique, mixed strategy equilibria. Am. Econ. Rev. 88, 848–881 (1998).
Lee, D., Conroy, M.L., McGreevy, B.P. & Barraclough, D.J. Reinforcement learning and decision making in monkeys during a competitive game. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 22, 45–58 (2004).
Sally, D. Conversation and cooperation in social dilemmas. Ration. Soc. 7, 58–92 (1995).
Fehr, E. & Fischbacher, U. The nature of human altruism. Nature 425, 785–791 (2003).
Hauser, M.D., Chen, M.K., Chen, F. & Chuang, E. Give unto others: genetically unrelated cotton-top tamarin monkeys preferentially give food to those who altruistically give food back. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 270, 2363–2370 (2003).
Warneken, F. & Tomasello, M. Altruistic helping in human infants and young chimpanzees. Science 311, 1301–1303 (2006).
de Waal, F.B.M. Putting the altruism back into altruism: the evolution of empathy. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 59, 279–300 (2008).
Nowak, M.A. Five rules for the evolution of cooperation. Science 314, 1560–1563 (2006).
Clutton-Brock, T.H. & Parker, G.A. Punishment in animal societies. Nature 373, 209–216 (1995).
Fehr, E. & Gächter, S. Altruistic punishment in humans. Nature 415, 137–140 (2002).
Boyd, R., Gintis, H., Bowles, S. & Richerson, P.J. The evolution of altruistic punishment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 3531–3535 (2003).
Fehr, E. & Schmidt, K.M. A theory of fairness, competition, and cooperation. Q. J. Econ. 114, 817–868 (1999).
Fehr, E. & Camerer, C.F. Social neuroeconomics: the neural circuitry of social preferences. Trends Cogn. Sci. 11, 419–427 (2007).
Sanfey, A.G. Social decision-making: insights from game theory and neuroscience. Science 318, 598–602 (2007).
Jensen, K., Call, J. & Tomasello, M. Chimpanzees are rational maximizers in an ultimatum game. Science 318, 107–109 (2007).
Sandholm, T.W. & Crites, R.H. Multiagent reinforcement learning in the iterated prisoner's dilemma. Biosystems 37, 147–166 (1996).
Lee, D., McGreevy, B.P. & Barraclough, D.J. Learning and decision making in monkeys during a rock-paper-scissors game. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 25, 416–430 (2005).
Lohrenz, T., McCabe, K., Camerer, C.F. & Montague, P.R. Neural signature of fictive learning signals in a sequential investment task. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 9493–9498 (2007).
Coricelli, G., Dolan, R.J. & Sirigu, A. Brain, emotion and decision making: the paradigmatic example of regret. Trends Cogn. Sci. 11, 258–265 (2007).
Mookherjee, D. & Sopher, B. Learning and decision costs in experimental constant sum games. Games Econ. Behav. 19, 97–132 (1997).
Feltovich, N. Reinforcement learning vs. belief-based learning models in experimental asymmetric-information games. Econometrica 68, 605–641 (2000).
Nowak, M.A. & Sigmund, K. Evolution of indirect reciprocity by image scoring. Nature 393, 573–577 (1998).
Wedekind, C. & Milinski, M. Cooperation through image scoring in humans. Science 288, 850–852 (2000).
Delgado, M.R., Frank, R.H. & Phelps, E.A. Perceptions of moral character modulate the neural systems of reward during the trust game. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1611–1618 (2005).
Kawato, M. & Samejima, K. Efficient reinforcement learning: computational theories, neuroscience and robotics. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 17, 205–212 (2007).
Schultz, W. Behavioral theories and the neurophysiology of reward. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 57, 87–115 (2006).
Roesch, M.R., Calu, D.J. & Schoenbaum, G. Dopamine neurons encode the better option in rats deciding between differently delayed or sized rewards. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 1615–1624 (2007).
Bayer, H.M. & Glimcher, P.W. Midbrain dopamine neurons encode a quantitative reward prediction error signal. Neuron 47, 129–141 (2005).
Paton, J.J., Belova, M.A., Morrison, S.E. & Salzman, C.D. The primate amygdala represents the positive and negative value of visual stimuli during learning. Nature 439, 865–870 (2006).
Kawagoe, R., Takikawa, Y. & Hikosaka, O. Expectation of reward modulates cognitive signals in the basal ganglia. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 411–416 (1998).
Cromwell, H.C. & Schultz, W. Effects of expectations for different reward magnitude on neuronal activity in primate striatum. J. Neurophysiol. 89, 2823–2838 (2003).
Samejima, K., Ueda, Y., Doya, K. & Kimura, M. Representation of action-specific reward values in the striatum. Science 310, 1337–1340 (2005).
Sugrue, L.P., Corrado, G.S. & Newsome, W.T. Matching behavior and the representation of value in the parietal cortex. Science 304, 1782–1787 (2004).
Dorris, M.C. & Glimcher, P.W. Activity in posterior parietal cortex is correlated with the relative subjective desirability of action. Neuron 44, 365–378 (2004).
Watanabe, M. Reward expectancy in primate prefrontal neurons. Nature 382, 629–632 (1996).
Leon, M.I. & Shadlen, M.N. Effect of expected reward magnitude on the response of neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the macaque. Neuron 24, 415–425 (1999).
Barraclough, D.J., Conroy, M.L. & Lee, D. Prefrontal cortex and decision making in a mixed-strategy game. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 404–410 (2004).
Shidara, M. & Richmond, B.J. Anterior cingulate: single neuronal signals related to degree of reward expectancy. Science 296, 1709–1711 (2002).
Seo, H. & Lee, D. Temporal filtering of reward signals in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex during a mixed-strategy game. J. Neurosci. 27, 8366–8377 (2007).
Sohn, J.-W. & Lee, D. Order-dependent modulation of directional signals in the supplementary and presupplementary motor areas. J. Neurosci. 27, 13655–13666 (2007).
Tremblay, L. & Schultz, W. Relative reward preference in primate orbitofrontal cortex. Nature 398, 704–708 (1999).
Roesch, M.R. & Olson, C.R. Neuronal activity related to reward value and motivation in primate frontal cortex. Science 304, 307–310 (2004).
Padoa-Schioppa, C. & Assad, J.A. Neurons in the orbitofrontal cortex encode economic value. Nature 441, 223–226 (2006).
Lee, D., Rushworth, M.F.S., Walton, M.E., Watanabe, M. & Sakagami, M. Functional specialization of the primate frontal cortex during decision making. J. Neurosci. 27, 8170–8173 (2007).
O'Doherty, J.P. Reward representation and reward-related learning in the human brain: insights from neuroimaging. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 14, 769–776 (2004).
Knutson, B. & Cooper, J.C. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of reward prediction. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 18, 411–417 (2005).
Montague, P.R., King-Casas, B.K. & Cohen, J.D. Imaging valuation models in human choice. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 29, 417–448 (2006).
Logothetis, N.K. & Wandell, B.A. Interpreting the BOLD signal. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 66, 735–769 (2004).
Tsujimoto, S. & Sawaguchi, T. Neuronal representation of response-outcome in the primate prefrontal cortex. Cereb. Cortex 14, 47–55 (2004).
Rilling, J.K. et al. A neural basis for social cooperation. Neuron 35, 395–405 (2002).
Rilling, J.K., Sanfey, A.G., Aronson, J.A., Nystrom, L.E. & Cohen, J.D. Opposing BOLD responses to reciprocated and unreciprocated altruism in putative reward pathways. Neuroreport 15, 2539–2543 (2004).
King-Casas, B. et al. Getting to know you: reputation and trust in a two-person economic exchange. Science 308, 78–83 (2005).
Sanfey, A.G., Rilling, J.K., Aronson, J.A., Nystrom, L.E. & Cohen, J.D. The neural basis of economic decision making in the ultimatum game. Science 300, 1755–1758 (2003).
Phillips, M.L. et al. A specific neural substrate for perceiving facial expressions of disgust. Nature 389, 495–498 (1997).
de Quervain, D.J.-F. et al. The neural basis of altruistic punishment. Science 305, 1254–1258 (2004).
Spitzer, M., Fischbacher, U., Herrnberger, B., Grön, G. & Fehr, E. The neural signature of social norm compliance. Neuron 56, 185–196 (2007).
Moll, J. et al. Human fronto-mesolimbic networks guide decisions about charitable donation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 15623–15628 (2006).
Harbaugh, W.T., Mayr, U. & Burghart, D.R. Neural responses to taxation and voluntary giving reveal motives for charitable donations. Science 316, 1622–1625 (2007).
Hoffman, E., McCabe, K., Shachat, K. & Smith, V. Preferences, property rights, and anonymity in bargaining games. Games Econ. Behav. 7, 346–380 (1994).
Schotter, A., Weiss, A. & Zapater, I. Fairness and survival in ultimatum and dictatorship games. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 31, 37–56 (1996).
Fliessbach, K. et al. Social comparison affects reward-related brain activity in the human ventral striatum. Science 318, 1305–1308 (2007).
Decety, J., Jackson, P.L., Sommerville, J.A., Chaminade, T. & Meltzoff, A.N. The neural bases of cooperation and competition: an fMRI investigation. Neuroimage 23, 744–751 (2004).
Gallagher, H.L. & Frith, C.D. Functional imaging of 'theory of mind'. Trends Cogn. Sci. 7, 77–83 (2003).
Saxe, R. Uniquely human social cognition. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 16, 235–239 (2006).
McCabe, K., Houser, D., Ryan, L., Smith, V. & Trouard, T. A functional imaging study of cooperation in two-person reciprocal exchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 11832–11835 (2001).
Gallagher, H.L., Jack, A.I., Roepstorff, A. & Frith, C.D. Imaging the intentional stance in a competitive game. Neuroimage 16, 814–821 (2002).
Rilling, J.K., Sanfey, A.G., Aronson, J.A., Nystrom, L.E. & Cohen, J.D. The neural correlates of theory of mind with interpersonal interactions. Neuroimage 22, 1694–1703 (2004).
Bhatt, M. & Camerer, C.F. Self-referential thinking and equilibrium as states of mind in games: fMRI evidence. Games Econ. Behav. 52, 424–459 (2005).
Fukui, H. et al. The neural basis of social tactics: an fMRI study. Neuroimage 32, 913–920 (2006).
Tomlin, D. et al. Agent-specific responses in the cingulate cortex during economic exchange. Science 312, 1047–1050 (2006).
Tankersley, D., Stowe, C.J. & Huettel, S.A. Altruism is associated with an increased neural response to agency. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 150–151 (2007).
Penke, L., Denissen, J.J.A. & Miller, G.F. The evolutionary genetics of personality. Eur. J. Pers. 21, 549–587 (2007).
Wallace, B., Cesarini, D., Lichtenstein, P. & Johannesson, M. Heritability of ultimatum game responder behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 15631–15634 (2007).
Klein, T.A. et al. Genetically determined differences in learning from errors. Science 318, 1642–1645 (2007).
Frank, M.J., Moustafa, A.A., Haughey, H.M., Curran, T. & Hutchison, K.E. Genetic triple dissociation reveals multiple roles for dopamine in reinforcement learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 16311–16316 (2007).
Hariri, A.R., Drabant, E.M. & Weinberger, D.R. Imaging genetics: perspectives from studies of genetically driven variation in serotonin function and corticolimbic affective processing. Biol. Psychiatry 59, 888–897 (2006).
Canli, T. & Lesch, K.-P. Long story short: the serotonin transporter in emotion regulation and social cognition. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 1103–1109 (2007).
Izquierdo, A., Newman, T.K., Higley, J.D. & Murray, E.A. Genetic modulation of cognitive flexibility and socioemotional behavior in rhesus monkeys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 14128–14133 (2007).
Yacubian, J. et al. Gene-gene interaction associated with neural reward sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 8125–8130 (2007).
Burnham, T.C. High-testosterone men reject low ultimatum game offers. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 274, 2327–2330 (2007).
Kosfeld, M., Heinrichs, M., Zak, P.J., Fischbacher, U. & Fehr, E. Oxytocin increases trust in humans. Nature 435, 673–676 (2005).
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to Michael Frank for discussions. This research was supported by the US National Institutes of Health (MH073246 and DA024855).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D. Game theory and neural basis of social decision making. Nat Neurosci 11, 404–409 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2065
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2065
This article is cited by
-
Humans utilize sensory evidence of others’ intended action to make online decisions
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Dynamic influences on the neural encoding of social valence
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2022)
-
Explicit and implicit markers of fairness preeminence in criminal judges
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The fair decision-making of children and adolescents with high-functioning autism spectrum disorder from the perspective of dual-process theories
BMC Psychiatry (2020)
-
Experimental Demonstration on Quantum Sensitivity to Available Information in Decision Making
Scientific Reports (2019)