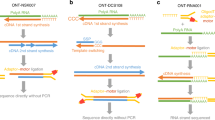
Abstract
We report an alternative approach to transcriptome sequencing for the Illumina Genome Analyzer, in which the reverse transcription reaction takes place on the flowcell. No amplification is performed during the library preparation, so PCR biases and duplicates are avoided, and because the template is poly(A)+ RNA rather than cDNA, the resulting sequences are necessarily strand-specific. The method is compatible with paired- or single-end sequencing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Z., Gerstein, M. & Snyder, M. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 57–63 (2009).
Wu, J.Q. et al. Genome Biol. 9, R3 (2008).
Ozsolak, F. et al. Nature 461, 814–818 (2009).
David, L. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 5320–5325 (2006).
Carninci, P. et al. Science 309, 1559–1563 (2005).
Katayama, S. et al. Science 309, 1564–1566 (2005).
Lister, R. et al. Cell 133, 523–536 (2008).
Cloonan, N. et al. Nat. Methods 5, 613–619 (2008).
Croucher, N.J. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, e148 (2009).
He, Y., Vogelstein, B., Velculescu, V.E., Papadopoulos, N. & Kinzler, K.W. Science 322, 1855–1857 (2008).
Parkhomchuk, D. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, e123 (2009).
Kozarewa, I. et al. Nat. Methods 6, 291–295 (2009).
Lipson, D. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 27, 652–658 (2009).
Chen, D. & Patton, J.T. Biotechniques 30, 574–580, 582 (2001).
Hubbard, T.J. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, D690–D697 (2009).
Marioni, J.C., Mason, C.E., Mane, S.M., Stephens, M. & Gilad, Y. Genome Res. 18, 1509–1517 (2008).
Bentley, D.R. et al. Nature 456, 53–59 (2008).
Smedley, D. et al. BMC Genomics 10, 22 (2009).
Li, H., Ruan, J. & Durbin, R. Genome Res. 18, 1851–1858 (2008).
Yang, Y.H. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, e15 (2002).
Smyth, G.K. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 3, 3 (2004).
Huber, W., von Heydebreck, A., Sultmann, H., Poustka, A. & Vingron, M. Bioinformatics 18 (Suppl. 1), S96–S104 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank N. Bason and M. Quail for preparing the standard RNA-seq library, J. Burton for coordinating the sequencing of standard RNA-seq libraries, and J. Ule and M. Wollerton for advice on RNA ligation. This work was supported by the Wellcome Trust grant (WT079643).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.J.T. and T.W.B.O. devised the project; L.M. and D.J.T. devised the experimental protocols; L.M. and E.M.S. planned and carried out laboratory work; R.M.A. and K.D.J. performed data analysis; P.D.E. performed microarray work; and C.F.L. oversaw analysis and array work. D.J.T., J.E.C. and L.M. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
T.W.B.O. is an Illumina employee, shareholder and share option holder.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8 and Supplementary Tables 1–6 (PDF 2919 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamanova, L., Andrews, R., James, K. et al. FRT-seq: amplification-free, strand-specific transcriptome sequencing. Nat Methods 7, 130–132 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1417
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1417
This article is cited by
-
Nanopore microscope identifies RNA isoforms with structural colours
Nature Chemistry (2022)
-
MERIT reveals the impact of genomic context on sequencing error rate in ultra-deep applications
BMC Bioinformatics (2018)
-
Avian transcriptomics: opportunities and challenges
Journal of Ornithology (2018)
-
Highly parallel direct RNA sequencing on an array of nanopores
Nature Methods (2018)
-
The Antisense Transcriptome and the Human Brain
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2016)