Abstract
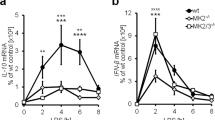
Members of the suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family are potentially key physiological negative regulators of interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling. To examine whether SOCS3 is involved in regulating this signaling, we have used conditional gene targeting to generate mice lacking Socs3 in the liver or in macrophages. We show that Socs3 deficiency results in prolonged activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) and STAT3 after IL-6 stimulation but normal activation of STAT1 after stimulation with interferon-γ (IFN-γ). Conversely, IL-6-induced STAT activation is normal in Socs1-deficient cells, whereas STAT1 activation induced by IFN-γ is prolonged. Microarray analysis shows that the pattern of gene expression induced by IL-6 in Socs3-deficient livers mimics that induced by IFN-γ. Our data indicate that SOCS3 and SOCS1 have reciprocal functions in IL-6 and IFN-γ regulation and imply that SOCS3 has a role in preventing IFN-γ-like responses in cells stimulated by IL-6.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Snick, J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 8, 253–278 (1990).
Bernad, A. et al. Interleukin-6 is required in vivo for the regulation of stem cells and committed progenitors of the hematopoietic system. Immunity 1, 725–731 (1994).
Ramsay, A.J. et al. The role of interleukin-6 in mucosal IgA antibody responses in vivo. Science 264, 561–563 (1994).
Fattori, E. et al. Defective inflammatory response in interleukin 6–deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 180, 1243–1250 (1994).
Hilbert, D.M., Kopf, M., Mock, B.A., Kohler, G. & Rudikoff, S. Interleukin 6 is essential for in vivo development of B lineage neoplasms. J. Exp. Med. 182, 243–248 (1995).
Kopf, M. et al. Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature 368, 339–342 (1994).
Taga, T. et al. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell 58, 573–581 (1989).
O'Shea, J.J., Gadina, M. & Schreiber, R.D. Cytokine signaling in 2002: new surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell 109 (suppl.), S121–S131 (2002).
Hemmann, U. et al. Differential activation of acute phase response factor/Stat3 and Stat1 via the cytoplasmic domain of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130. II. Src homology SH2 domains define the specificity of stat factor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 12999–13007 (1996).
Alonzi, T. et al. Essential role of STAT3 in the control of the acute-phase response as revealed by inducible gene inactivation in the liver. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 1621–1632 (2001).
Alexander, W.S. Suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS) in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 410–416 (2002).
Starr, R. et al. A family of cytokine-inducible inhibitors of signalling. Nature 387, 917–921 (1997).
Alexander, W.S. et al. SOCS1 is a critical inhibitor of interferon-γ signaling and prevents the potentially fatal neonatal actions of this cytokine. Cell 98, 597–608 (1999).
Marine, J.C. et al. SOCS1 deficiency causes a lymphocyte-dependent perinatal lethality. Cell 98, 609–616 (1999).
Metcalf, D. et al. Gigantism in mice lacking suppressor of cytokine signalling-2. Nature 405, 1069–1073 (2000).
Roberts, A.W. et al. Placental defects and embryonic lethality in mice lacking suppressor of cytokine signaling 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 98, 9324–9329 (2001).
Takahashi, Y. et al. SOCS3: an essential regulator of LIF receptor signaling in trophoblast giant cell differentiation. EMBO J. 22, 372–384 (2003).
Marine, J.C. et al. SOCS3 is essential in the regulation of fetal liver erythropoiesis. Cell 98, 617–627 (1999).
Schwenk, F., Baron, U. & Rajewsky, K. A cre-transgenic mouse strain for the ubiquitous deletion of loxP-flanked gene segments including deletion in germ cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 5080–5081 (1995).
Yakar, S. et al. Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96, 7324–7329 (1999).
Clausen, B.E., Burkhardt, C., Reith, W., Renkawitz, R. & Forster, I. Conditional gene targeting in macrophages and granulocytes using LysM-cre mice. Transgenic Res. 8, 265–277 (1999).
Soriano, P. Generalized lacZ expression with the ROSA26 Cre reporter strain. Nat. Genet. 21, 70–71 (1999).
Campbell, J.S. et al. Expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling during liver regeneration. J. Clin. Invest. 107, 1285–1292 (2001).
Hong, F. et al. Opposing roles of STAT1 and STAT3 in T cell–mediated hepatitis: regulation by SOCS. J. Clin. Invest. 110, 1503–1513 (2002).
Stoiber, D. et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces in macrophages the synthesis of the suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 and suppresses signal transduction in response to the activating factor IFN-γ. J. Immunol. 163, 2640–2647 (1999).
Nicholson, S.E. et al. Mutational analyses of the SOCS proteins suggest a dual domain requirement but distinct mechanisms for inhibition of LIF and IL-6 signal transduction. EMBO J. 18, 375–385 (1999).
Song, M.M. & Shuai, K. The suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 1 and SOCS3 but not SOCS2 proteins inhibit interferon-mediated antiviral and antiproliferative activities. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 35056–35062 (1998).
Brysha, M. et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 attenuates the duration of interferon-γ signal transduction in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 22086–22089 (2001).
Takeda, K. et al. Enhanced Th1 activity and development of chronic enterocolitis in mice devoid of Stat3 in macrophages and neutrophils. Immunity 10, 39–49 (1999).
Xaus, J. et al. Interferon-γ induces the expression of p21waf-1 and arrests macrophage cell cycle, preventing induction of apoptosis. Immunity 11, 103–113 (1999).
Cascio, S. & Zaret, K.S. Hepatocyte differentiation initiates during endodermal-mesenchymal interactions prior to liver formation. Development 113, 217–225 (1991).
Cressman, D.E. et al. Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6–deficient mice. Science 274, 1379–1383 (1996).
Costa-Pereira, A.P. et al. Mutational switch of an IL-6 response to an interferon-γ–like response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 8043–8047 (2002).
Lee, C. et al. STAT3 is a negative regulator of granulopoiesis but is not required for G-CSF–dependent differentiation. Immunity 17, 63–72 (2002).
Lang, R. et al. SOCS3 regulates the plasticity of gp130 signaling. Nat. Immunol. advance online publication, 18 May 2003 (doi:10.1038/ni932).
Finbloom, D.S. & Winestock, K.D. IL-10 induces the tyrosine phosphorylation of tyk2 and Jak1 and the differential assembly of STAT1α and STAT3 complexes in human T cells and monocytes. J. Immunol. 155, 1079–1090 (1995).
Cassatella, M.A. et al. Interleukin-10 (IL-10) selectively enhances CIS3/SOCS3 mRNA expression in human neutrophils: evidence for an IL-10-induced pathway that is independent of STAT protein activation. Blood 94, 2880–2889 (1999).
Bertolino, P., Trescol-Biemont, M.C. & Rabourdin-Combe, C. Hepatocytes induce functional activation of naive CD8+ T lymphocytes but fail to promote survival. Eur. J. Immunol. 28, 221–236 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. LeRoith for providing the Alb-cre transgenic mice; G. Panoschi for animal husbandry; S. Cane and J. Mighall for genotyping; and A. Steptoe, L. Hartley and T. Speed for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (Program Grant 257500); US National Institutes of Health Grant CA22556; the Cancer Council of Victoria Carden Fellowship (to D.M.) and the Sir Edward Dunlop Clinical Fellowship (to A.W.R.); and AMRAD Operations Pty Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
N.N. and D.J.H. work as consultants for AMRAD Operations Pty Ltd. This company provided support for the work described in this paper.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Croker, B., Krebs, D., Zhang, JG. et al. SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-6 signaling in vivo. Nat Immunol 4, 540–545 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni931
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni931
This article is cited by
-
The constitutive activation of STAT3 gene and its mutations are at the crossroad between LGL leukemia and autoimmune disorders
Blood Cancer Journal (2024)
-
Alpha-7 Nicotinic Receptor Agonist Protects Mice Against Pulmonary Emphysema Induced by Elastase
Inflammation (2024)
-
Does non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-related preemptive analgesia modulate SOCS3/IL-6 pathway in oral surgery?
Inflammopharmacology (2024)
-
Double-edged sword of JAK/STAT signaling pathway in viral infections: novel insights into virotherapy
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
IL-6 prevents Th2 cell polarization by promoting SOCS3-dependent suppression of IL-2 signaling
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2023)